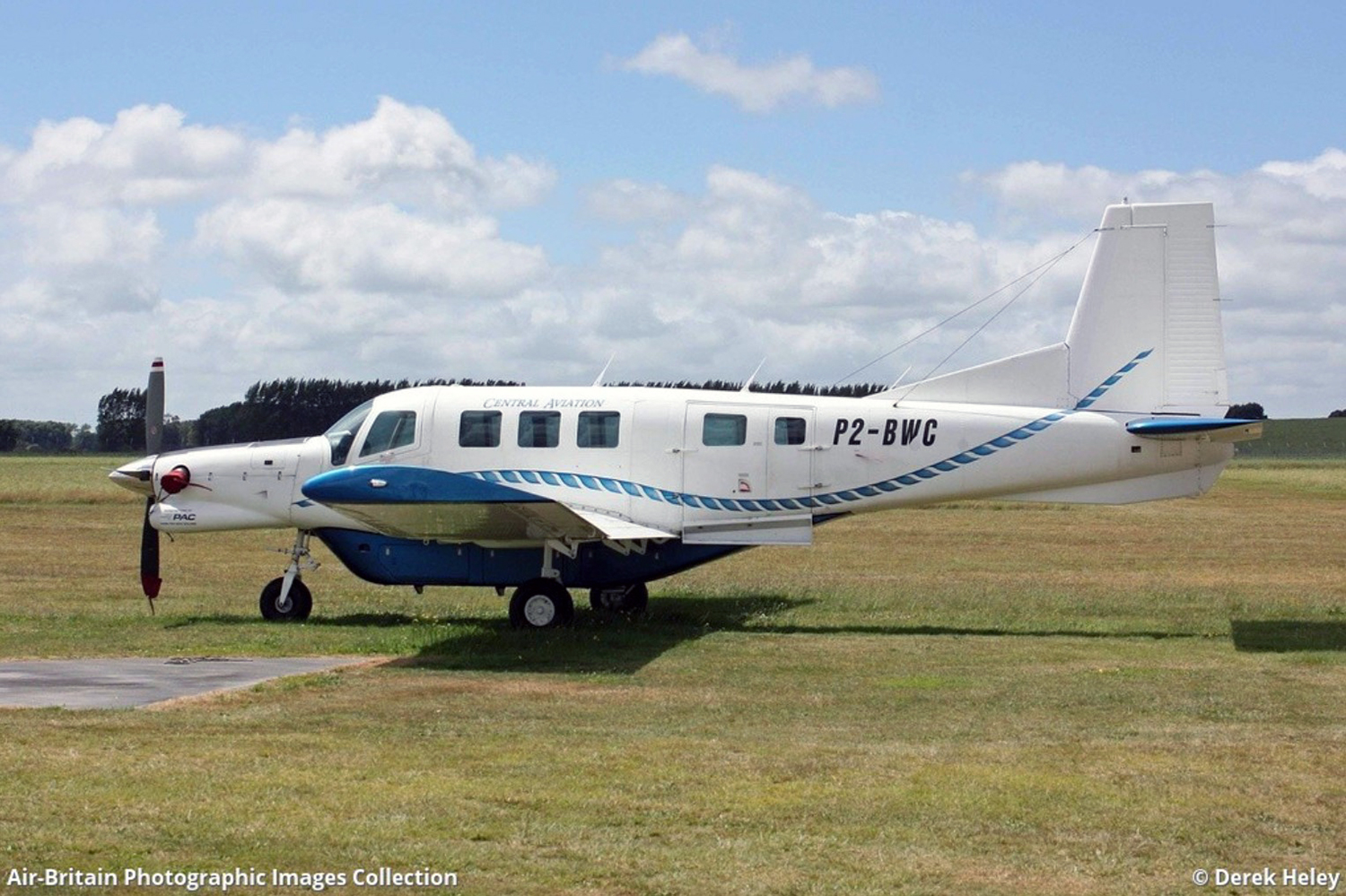
Crash of a De Havilland DHC-3T Otter into the Mutiny Bay: 10 killed
Date & Time:
Sep 4, 2022 at 1509 LT
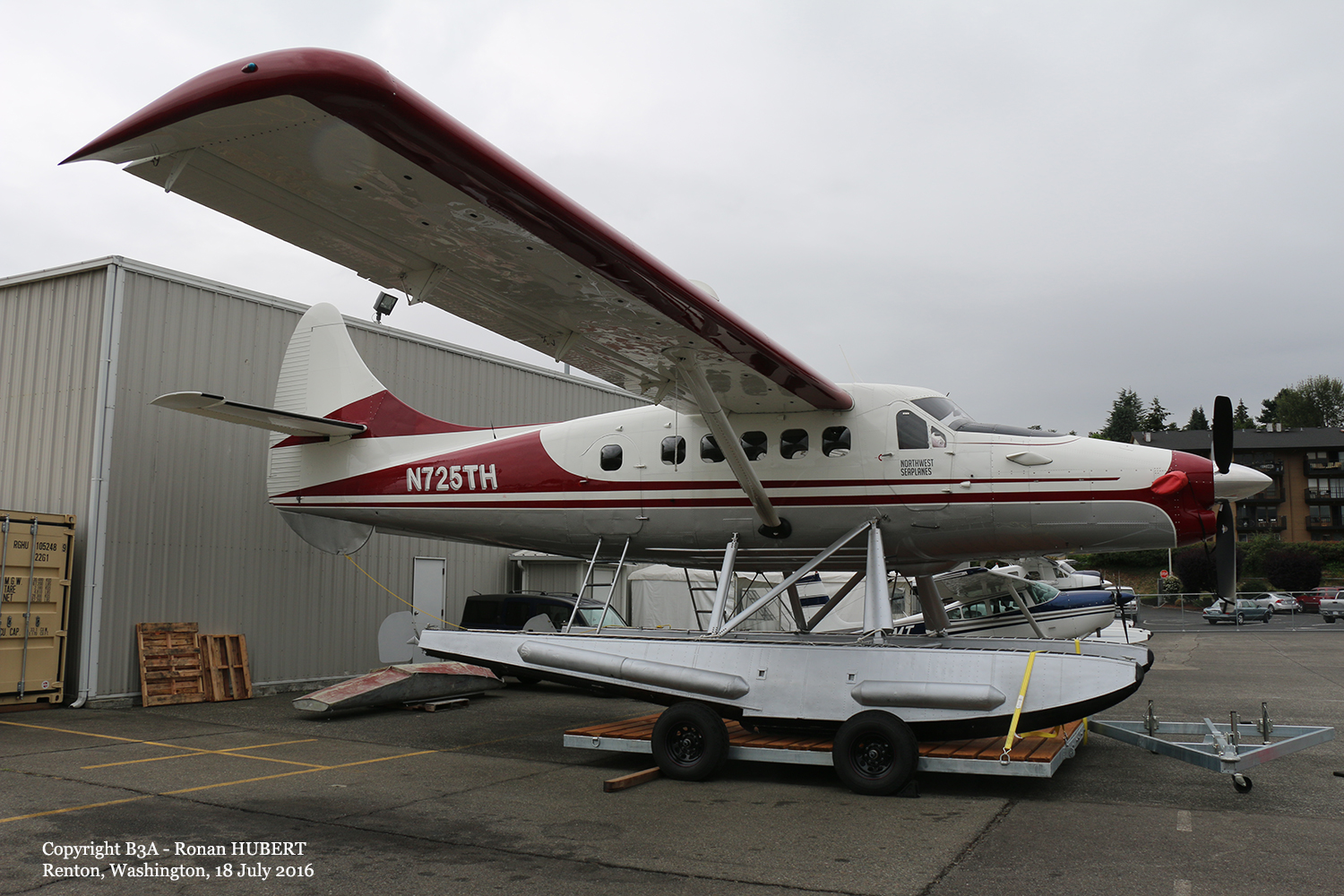
Registration:
N725TH
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Friday Harbor – Renton
MSN:
466
YOM:
1967
Crew on board:
1
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
9
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
10
Captain / Total hours on type:
1300.00
Aircraft flight hours:
24430
Circumstances:
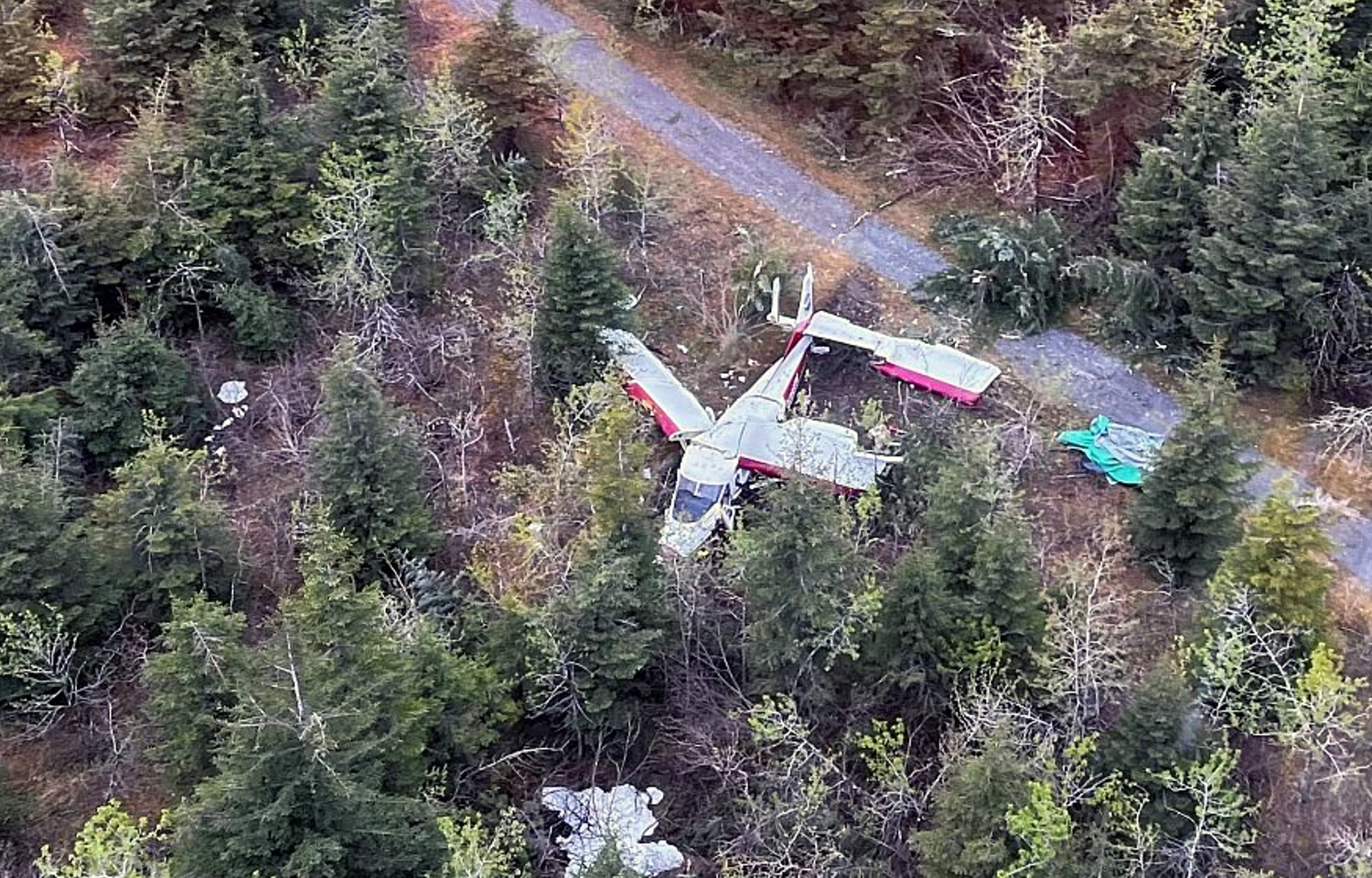
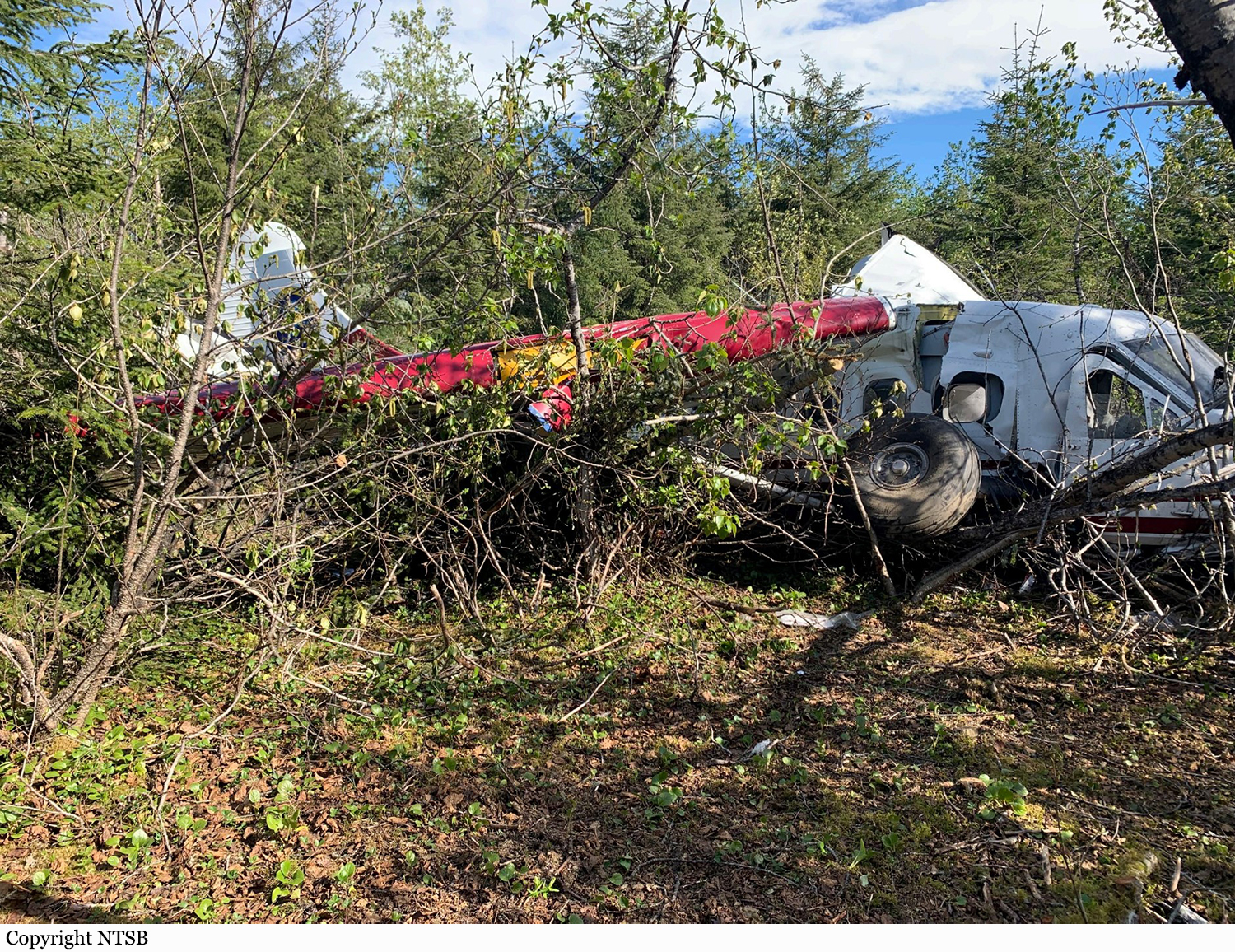
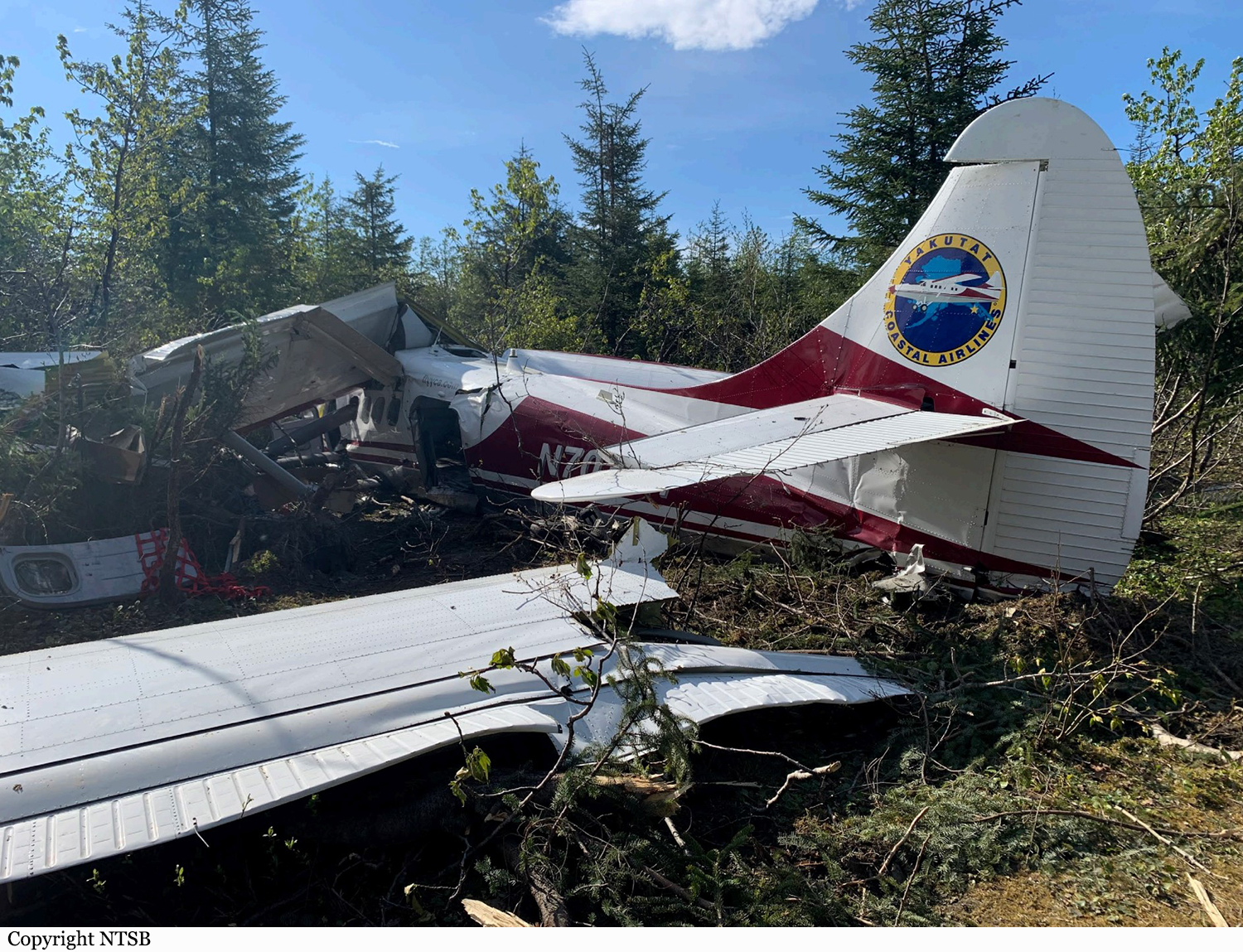
On September 4, 2022, about 1509 Pacific daylight time, a float-equipped de Havilland DHC-3 (Otter), N725TH, was destroyed when it impacted the water in Mutiny Bay, near Freeland, Washington, and sank. The pilot and nine passengers were fatally injured. The airplane was owned by Northwest Seaplanes, Inc., and operated as a Title 14 Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Part 135 scheduled passenger flight by West Isle Air dba Friday Harbor Seaplanes. The flight originated at Friday Harbor Seaplane Base (W33), Friday Harbor, Washington, with an intended destination of Will Rogers Wiley Post Memorial Seaplane Base (W36), Renton, Washington. Visual meteorological conditions prevailed at the time of the accident. The accident pilot was scheduled to fly the accident airplane on three multiple leg roundtrips on the day of the accident. The first roundtrip flight was uneventful; it departed from W36 about 0930, made four stops, and returned about 1215. The accident occurred during the pilot’s second trip of the day. A review of recorded automatic dependent surveillance–broadcast (ADS-B) data revealed that the second roundtrip departed 36 about 1253 and arrived at Lopez Seaplane Base, (W81), Lopez Island, Washington, about 1328.2 The data showed that the flight then departed W81 and landed at Roche Harbor Seaplane Base (W39) about 1356. The airplane departed W39 about 1432, arrived at W33 about 1438, and departed about 1450. According to ADS-B data, after the airplane departed W33, it flew a southerly heading before turning south-southeast. The en route altitude was between 600 and 1,000 ft above mean sea level (msl), and the groundspeed was between 115 and 135 knots. At 1508:40, the altitude was 1,000 ft msl, and the groundspeed had decreased to 111 knots. Based on performance calculations, at 1508:43, the airplane pitched up about 8° and then abruptly pitched down about 58°. The data ended at 1508:51, when the airplane’s altitude was 600 ft msl and the estimated descent rate was more than 9,500 ft per minute (the flightpath of the airplane is depicted in figure. Witnesses near the accident site reported, and security camera video confirmed, the airplane was in level flight before it entered a slight climb and then pitched down. One witness described the descent as “near vertical” and estimated the airplane was in an 85° nose-down attitude before impact with the water. Several witnesses described the airplane as “spinning,” “rotating,” or “spiraling” during portions of the steep descent. One witness reported hearing the engine/propeller and noted that he did not hear any “pitch change” in the sounds. The airplane continued in a nose-low, near-vertical descent until it impacted water in Mutiny Bay.
Probable cause:
It was determined that the probable cause of this accident was the in-flight unthreading of the clamp nut from the horizontal stabilizer trim actuator barrel due to a missing lock ring, which resulted in the horizontal stabilizer moving to an extreme trailing-edge-down position rendering the airplane’s pitch uncontrollable.
Final Report: