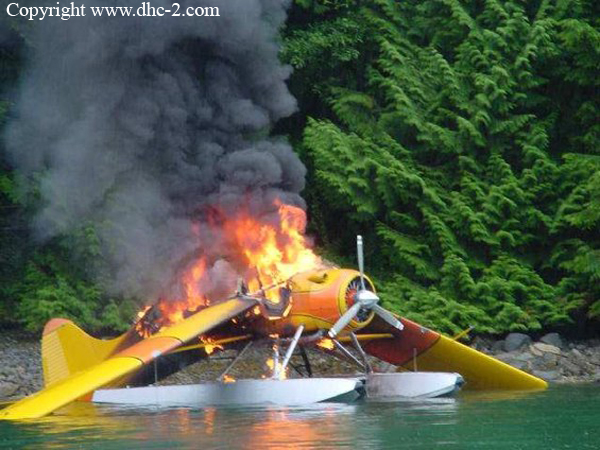
Region
Ground fire of a De Havilland DHC-2 Beaver off Minstrel Island
Date & Time:
Aug 1, 2001
Registration:
C-GNWS
Survivors:
Yes
MSN:
1382
YOM:
1959
Crew on board:
1
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
3
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Circumstances:
he float-equipped aircraft had landed at Minstrel Island and was taxiing to the dock when the pilot of a company aircraft that was following C-GNWS to the dock radioed that he saw smoke coming from the lower right area of C-GNWS's engine cowling. The pilot of C-GNWS docked the aircraft, unloaded the three passengers and emptied a fire extinguisher onto the burning aircraft. The fire was not extinguished and the aircraft was pushed away from the dock where it burnt to the water.

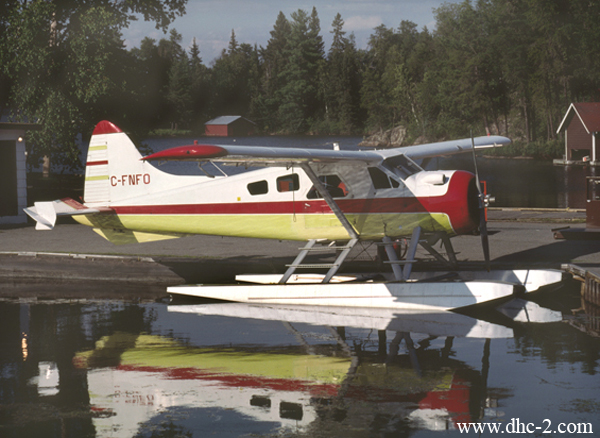
Crash of a De Havilland DHC-2 Beaver near Nestor Falls: 1 killed
Date & Time:
Jul 7, 2001 at 1530 LT
Registration:
C-FNFO
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Kakabikitchiwan Lake - Aremis Lake
MSN:
819
YOM:
1955
Crew on board:
1
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
1
Captain / Total hours on type:
1300.00
Aircraft flight hours:
11843
Circumstances:
A de Havilland DHC-2 Beaver seaplane, registration C-FNFO, serial number 819, departed from Kakabikitchiwan Lake, Ontario, on a visual flight rules flight for Aremis Lake with only the pilot on board. Shortly after take-off, the aircraft was observed flying northbound at a very low altitude above Sabaskong Bay with the engine operating at a high power setting. The aircraft started to climb and bank to the left. The right wing struck the lower of two electrical wires strung across a channel between two islands. The aircraft was destroyed; the pilot sustained fatal injuries.
Probable cause:
Findings as to Causes and Contributing Factors:
1. The power line running overhead the channel was invisible, except at very short range, and was not marked to indicate its presence.
2. The pilot was flying at a very low altitude and likely did not see the power line.
Findings as to Risk:
1. The Standards Obstruction Markings Manual allows for discretion in deciding whether to assess obstructions, making it possible for some obstructions to not be assessed and, consequently, to not be marked.
1. The power line running overhead the channel was invisible, except at very short range, and was not marked to indicate its presence.
2. The pilot was flying at a very low altitude and likely did not see the power line.
Findings as to Risk:
1. The Standards Obstruction Markings Manual allows for discretion in deciding whether to assess obstructions, making it possible for some obstructions to not be assessed and, consequently, to not be marked.
Final Report:

Crash of a Piper PA-31-310 Navajo in Charlottetown: 3 killed
Date & Time:
Jun 5, 2001 at 1621 LT
Registration:
C-GMTT
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Gander – Charlottetown – Natuashish
MSN:
31-7712004
YOM:
1977
Crew on board:
1
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
3
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
3
Captain / Total hours on type:
185.00
Circumstances:
The flight took off on Runway 22 at Gander, Newfoundland and Labrador, at 1428 Newfoundland daylight time with the pilot and four passengers on board. Their destination was Sango Bay, Newfoundland and Labrador, with an intermediate stop in Charlottetown, Newfoundland and Labrador, to drop off one of the passengers. Radar data show that, on departure from Gander, the aircraft climbed at about 500 feet per minute at 125 knots ground speed to 2500 feet, then descended and proceeded en route to Charlottetown at 1900 feet and 150 knots. The aircraft landed at Charlottetown at 1615. After a brief stop, the flight continued to Sango Bay. The pilot broadcast his intention to take off on Runway 10, taxied the aircraft to the threshold of the runway, and commenced the take-off roll. Part-way down the runway, the pilot aborted the take-off. He then broadcast his intention to take off on Runway 28. Both radio broadcasts were acknowledged by a local pilot who was approaching the airport to land. Upon reaching the threshold of Runway 28, the aircraft turned and accelerated, without stopping, on the take-off roll. The aircraft lifted off shortly before the runway end and remained near treetop height until disappearing from view. After lift-off, the stall warning horn sounded intermittently until impact. The aircraft was unable to climb above the hilly terrain and struck the road 1.5 nautical miles from the departure end of the runway. A passing motorist spotted the downed aircraft and notified firefighters and medical personnel who were then dispatched to the scene. The accident occurred at about 1621 during daylight hours, at 58°45' N, 55°66' W, at 440 feet above sea level.
Probable cause:
Findings as to Causes and Contributing Factors:
1. The aircraft was over the maximum allowable take-off weight throughout its journey, reducing aircraft performance: the pilot apparently did not complete weight and balance calculations for
either of the flights.
2. The pilot did not use the proper short field take-off technique, and the aircraft was forced into the air before reaching sufficient flying speed.
3 The best angle of climb speed was not attained.
4. The unsecured cargo, some of which was found on top of the back of the rear passenger seat, most probably contributed to the severity of the injuries to the passenger in this seat.
1. The aircraft was over the maximum allowable take-off weight throughout its journey, reducing aircraft performance: the pilot apparently did not complete weight and balance calculations for
either of the flights.
2. The pilot did not use the proper short field take-off technique, and the aircraft was forced into the air before reaching sufficient flying speed.
3 The best angle of climb speed was not attained.
4. The unsecured cargo, some of which was found on top of the back of the rear passenger seat, most probably contributed to the severity of the injuries to the passenger in this seat.
Final Report:
Crash of a Boeing 737-210C in Yellowknife
Date & Time:
May 22, 2001 at 1325 LT
Registration:
C-GNWI
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Edmonton – Yellowknife
MSN:
21066
YOM:
1975
Flight number:
7F953
Crew on board:
6
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
98
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Captain / Total hours on type:
7000.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
840
Circumstances:
First Air Flight 953, a Boeing 737-210C, serial number 21066, was on a scheduled flight from Edmonton, Alberta, to Yellowknife, Northwest Territories. On board were 2 flight crew, 4 cabin crew, and 98 passengers. The flight departed Edmonton at 1130 mountain daylight time, with an estimated time en route of 1 hour 35 minutes. As the aircraft approached Yellowknife, the spoilers were armed, and the aircraft was configured for a visual approach and landing on Runway 33. The computed Vref was 128 knots, and target speed was 133 knots. While in the landing flare, the aircraft entered a higher-than-normal sink rate, and the pilot flying (the first officer) corrected with engine power and nose-up pitch. The aircraft touched down on the main landing gear and bounced twice. While the aircraft was in the air, the captain took control and lowered the nose to minimize the bounce. The aircraft landed on its nose landing-gear, then on the main gear. The aircraft initially touched down about 1300 feet from the approach end of Runway 33. Numerous aircraft rubber scrub marks were present in this area and did not allow for an accurate measurement. During the third touchdown on the nose landing-gear, the left nose-tire burst, leaving a shimmy-like mark on the runway. The aircraft was taxied to the ramp and shut down. The aircraft was substantially damaged. There were no reported injuries to the crew or the passengers. The accident occurred at 1325, during the hours of daylight.
Probable cause:
Findings as to Causes and Contributing Factors:
1. Incorrect bounced landing recovery procedures were carried out when the captain pushed forward on the control column to prevent a further bounce, and the aircraft landed nosewheel first.
2. The high sink rate on the initial flare was not recognized and corrected in time to prevent a bounced landing and a subsequent bounced landing.
Other Findings:
1. The power increase during the flair resulted in the speedbrake/spoilers retracting.
2. The captain had not received a line check of at least three sectors before returning to flight duties, although this check was required to regain competency after pilot proficiency check expiry.
1. Incorrect bounced landing recovery procedures were carried out when the captain pushed forward on the control column to prevent a further bounce, and the aircraft landed nosewheel first.
2. The high sink rate on the initial flare was not recognized and corrected in time to prevent a bounced landing and a subsequent bounced landing.
Other Findings:
1. The power increase during the flair resulted in the speedbrake/spoilers retracting.
2. The captain had not received a line check of at least three sectors before returning to flight duties, although this check was required to regain competency after pilot proficiency check expiry.
Final Report: