Zone
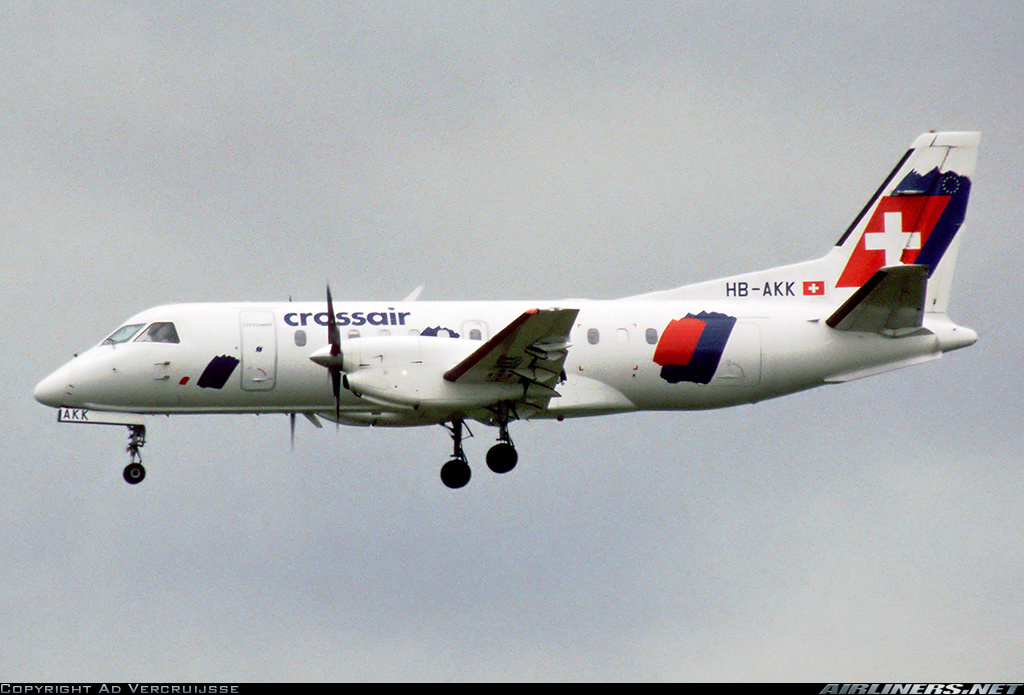
Crash of a Saab 340B in Nassenwil: 10 killed
Date & Time:
Jan 10, 2000 at 1756 LT
Registration:
HB-AKK
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Zurich - Dresden
MSN:
213
YOM:
1990
Flight number:
LX498
Crew on board:
3
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
7
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
10
Captain / Total hours on type:
1870.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
1162
Aircraft flight hours:
21676
Aircraft flight cycles:
20589
Circumstances:
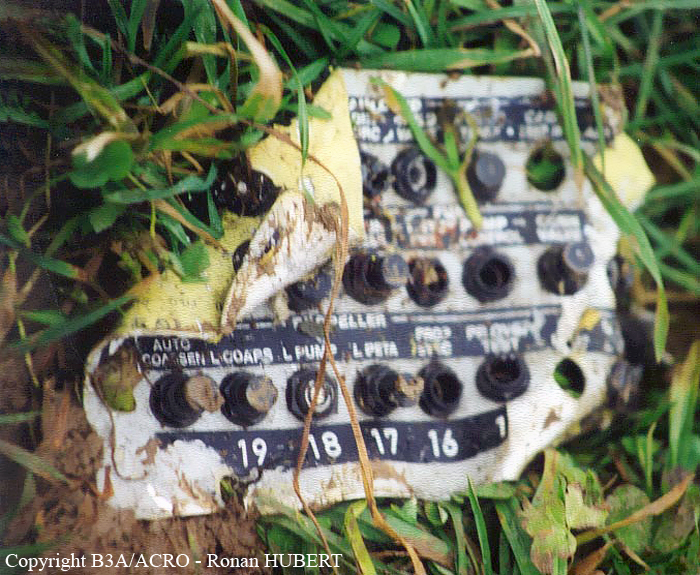
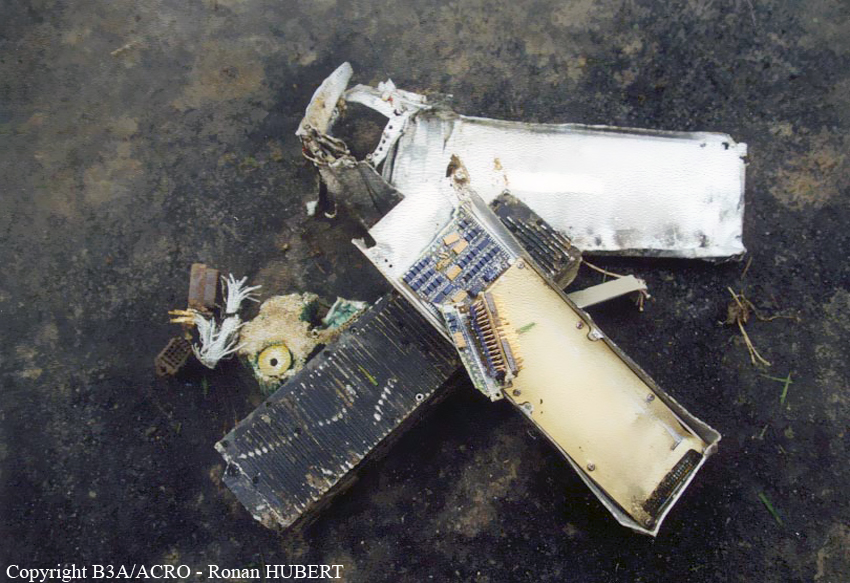
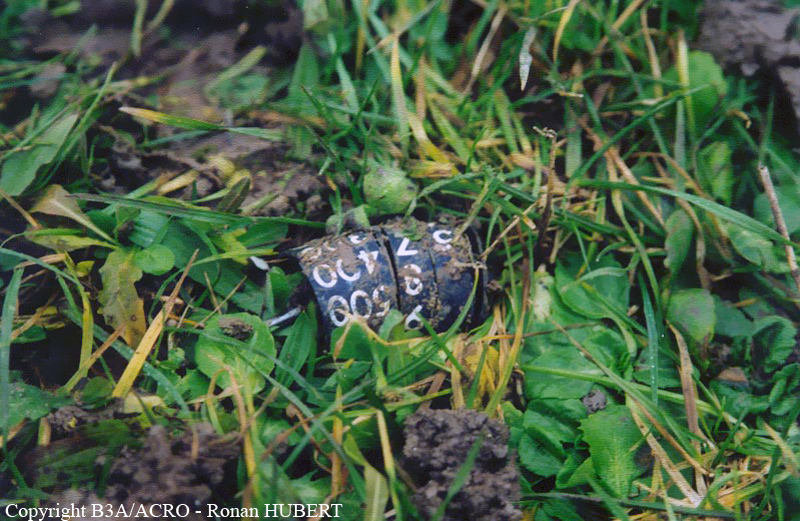
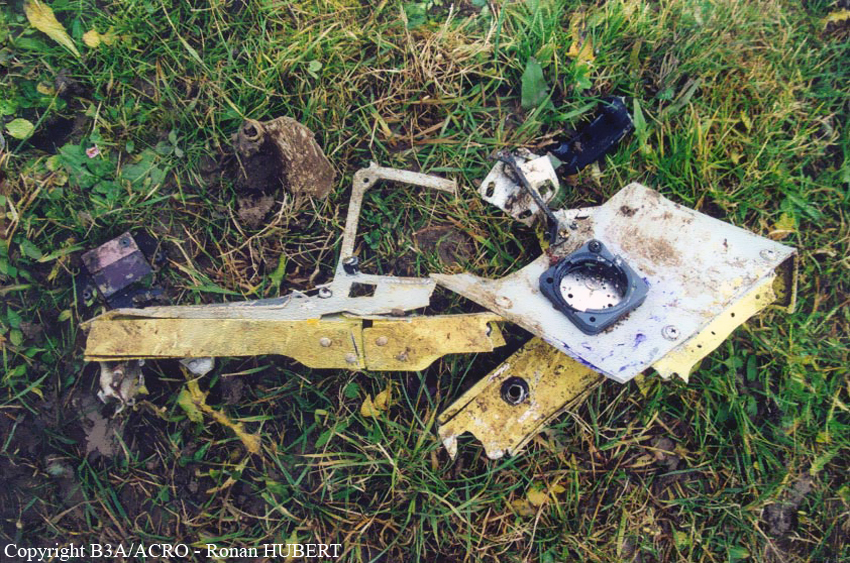
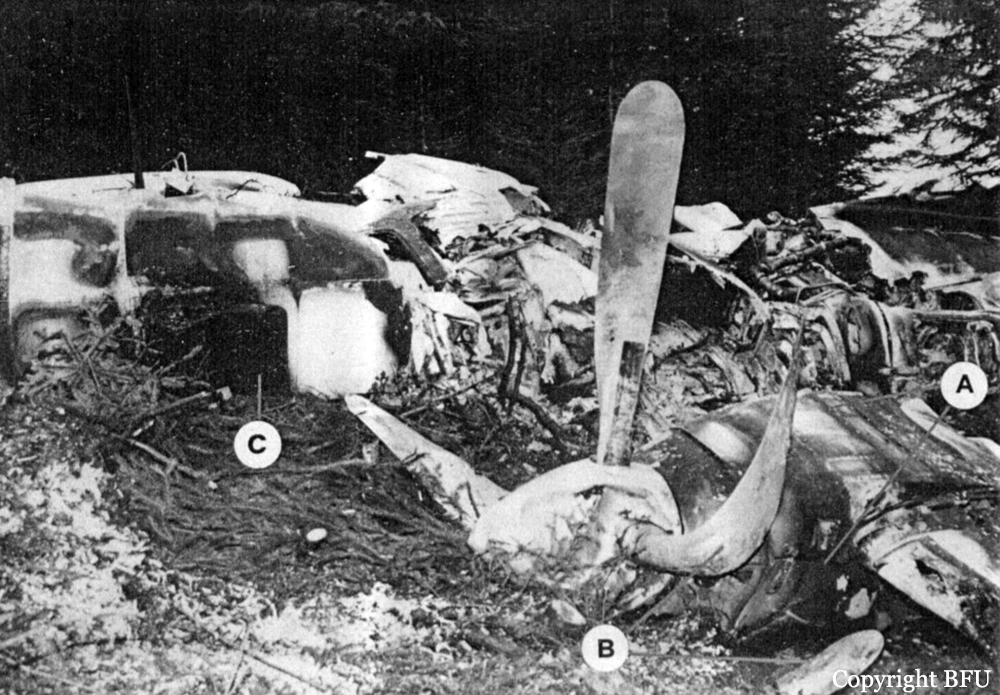
Aircraft HB-AKK had landed in Zurich on 10 January 2000 as Crossair flight CRX 842 from Guernsey and reached stand F74 at 16:00 UTC, which is located near to the threshold of runway 28. The aircraft was then prepared for the next flight at this stand. According to statements from the Swissport ground personnel the preparation of the aircraft took place without any special occurrence. During its time on the ground, the aircraft was supplied with electric power by a ground power unit (GPU). An air-conditioning truck was not used and the aircraft was not de-iced. The crew prepared for the flight using the computer-aided briefing system. The following description of the history of the flight was reconstructed with the help of recordings from the cockpit voice recorder (CVR), digital flight data recorder (DFDR), voice radio communications and ATC radar (cf. Annex 1). According to the available recordings, the commander, as planned by the crew, was pilot flying (PF) and the first officer was pilot non flying (PNF) throughout the flight. At 16:39:14 UTC, flight CRX 498 to Dresden received from clearance delivery (DEL) the following ATC-clearance: "runway two eight, Dresden, Zurich East One Yankee Departure, squawk three zero zero four". The crew was then instructed to change to the apron (APR) frequency. Permission to start engines was given at 16:45:00 UTC by APR. At 16:49:22 UTC the first officer signaled readiness to taxi to APR. While the crew waited for taxi clearance, a few points of the taxi checklist were performed. At 16:50:30 UTC APR cleared flight CRX 498 to follow a Swissair Airbus A320 (SWR 014) to the holding position of runway 28. In accordance with this clearance, CRX 498 started to move. The flight crew performed the outstanding items on the taxi checklist and contacted the tower (TWR), which gave line-up clearance at 16:52:36 UTC. Take-off clearance was given at 16:54:00 UTC: "Crossair four nine eight, wind three zero zero degrees, three knots, cleared take-off runway two eight". According to the automatic terminal information service (ATIS) at 16:50 UTC the following meteorological conditions existed: wind 290° at 2 knots, visibility 6 km in drizzle, broken, cloud base at 500 feet above ground level, temperature 2 °C, dew point 1 °C, QNH 1032 hPa. The aircraft began its take-off roll at 16:54:10 UTC in darkness. The landing lights were on and the flaps were fully retracted. After take-off at 16:54:31 UTC the landing gear was retracted. Then, on the commander's order, the flight director (FD) was switched on and the NAV mode was armed. Both pilots confirmed that the long range navigation system number 1 (LRN 1) was following the track (LRN 1 captured). The commander controlled the aircraft in a stable climb with a pitch of 15° attitude nose up (ANU) and a speed of 136 knots indicated airspeed (KIAS). For the remaining flight, the autopilot was never engaged. Since the cloud base was indicated as 500 ft above ground level (AGL), it can be assumed that the aircraft, once above an altitude of approx. 1900 ft above mean sea level (AMSL) entered instrument meteorological conditions (IMC). The initial flight path, at a heading of 276°, followed the centre line of the runway. After the request from TWR, CRX 498 switched to the departure control frequency (DEP) at 16:55:07 UTC. The radar recording then showed a deviation in the flight path by 5° to the south. However, this slight deviation was reduced before waypoint DME 2.1 KLO was reached by initiating a right turn. At 16:55:15 UTC flight CRX 498 was cleared to climb to flight level 110. At 16:55:39 UTC, Zurich departure issued the instruction to turn to VOR ZUE: "four nine eight, turn left to Zurich East". The first officer confirmed by radio: "turning left to Zurich East, Crossair four niner eight". At the same time the aircraft reached waypoint DME 2.1 KLO. At this point the departure procedure ZUE1Y specifies a left turn, in order to capture and follow radial 255 of VOR KLO. At 16:55:45 the bank angle to the left reached a maximum of 16.9° on a compass heading of 270°. At 16:55:47 UTC the first officer informed the commander that the LRN system was programmed from the present position to ZUE: "from present, LRN is to Zurich East, yeah". The commander confirmed with: "checked". The left turn instruction from DEP was not mentioned. After the aircraft had remained briefly at a 16° bank angle to the left, it began to roll to the right. From 16:55:47 UTC the bank angle rate amounted to 3°/s to the right. In this phase the first officer was very busy carrying out the orders routinely issued by the commander ("CTOT/APR off, yaw damper on, bleed air on"). All relevant flight parameters in this phase indicated a stable climb with a pitch of 13-14° ANU. The communication being conducted internally did not give any indication of difficulties of any kind. At 16:55:55 UTC, at a bank angle of 8.4° to the right, the bank angle rate increased and the nose of the aircraft began to drop from 14.2° to 10.8° ANU. At 16:56:00 UTC the right bank angle attained a value of 31.0°, when the commander gave the order to set climb power: "set climb power". The first officer confirmed with a whispered "coming" and began to set the climb power – a procedure which takes quite some time. Between 16:56:03 UTC and 16:56:10 UTC the commander stabilized the bank angle to the right between 39° and 42° by corresponding flight control inputs. The pitch reduced further and stabilized at a value of 1° ANU at 16:56:06 UTC as a result of corresponding elevator inputs for four seconds. As a consequence, the trajectory reached its maximum altitude of 4720 ft AMSL. According to information from the crew of the preceding flight SWR 014 the cloud top at that time was approx. 5000 ft AMSL. The speed of the aircraft involved in the accident increased to 158 KIAS. 16:56:10 UTC marked the beginning of a nine-second period which was characterized by destabilization of the attitude. It featured uncoordinated deflections of the ailerons to the left and right. Meanwhile, the elevator remained practically in the neutral position. Since the rightward deflections of the aileron were dominant, the bank angle increased from 42° to 80° to the right. Given the neutral position of the elevator, because of the high bank angle the pitch increased to 25° attitude nose down (AND). The aircraft therefore quickly lost altitude and its speed increased to 207 KIAS. At 16:56:12 UTC the first officer made the commander aware that they should turn left to ZUE: "turning left to Zurich East, we should left". At 16:56:15 UTC, at a bank angle of 65.8° to the right, the commander muttered unclearly: "ohna-na". Three seconds later at 16:56:18 UTC, DEP requested confirmation that the aircraft was turning to the left: "Crossair four nine eight, confirm you are turning left". The first officer responded immediately: "moment please, standby". DEP then instructed the crew to continue the right turn: "ok, continue right to Zurich East." In the final phase of flight, beginning at 16:56:20 UTC, the aircraft went into a spiral dive. As a result of massive aileron deflections, the aircraft attained a maximum bank angle of 137° to the right. The engines still provided high power, since setting of climb power had not yet been terminated. At a speed of 250 KIAS the over speed warning horn sounded. At 16:56:24 UTC the first officer vigorously warned the commander to turn left: "turning left, left, left, left... left!" At the end of the data recording at 16:56:25 UTC the aircraft still exhibited a bank angle of 76° to the right. The nose of the aircraft had dropped to 63° AND at an air speed of 285 KIAS. Several witnesses observed the aircraft breaking out of the clouds in a steep descent and performing a right turn. At 16:56:27.2 UTC the aircraft crashed in an open field near Au, Nassenwil, ZH. None of the three crew members and seven passengers survived the impact.
Probable cause:
The accident is attributable to a collision with the ground, after the flight crew had lost control of the aircraft for the following reasons:
• The flight crew reacted inappropriately to the change in departure clearance SID ZUE 1Y by ATC.
• The co-pilot made an entry in the FMS, without being instructed to do so by the commander, which related to the change to the SID ZUE 1 standard instrument departure. In doing so, he omitted to select a turn direction.
• The commander dispensed with use of the autopilot under instrument flight conditions and during the work-intensive climb phase of the flight.
• The commander took the aircraft into a spiral dive to the right because, with a probability bordering on certainty, he had lost spatial orientation.
• The first officer took only inadequate measures to prevent or recover from the spiral dive.
The following factors may have contributed to the accident:
• The commander remained unilaterally firm in perceptions which suggested a left turn direction to him.
• When interpreting the attitude display instruments under stress, the commander resorted to a reaction pattern (heuristics) which he had learned earlier.
• The commander’s capacity for analysis and critical assessment of the situation were possibly limited as a result of the effects of medication.
• After the change to standard instrument departure SID ZUE 1Y the crew set inappropriate priorities for their tasks and their concentration remained one-sided.
• The commander was not systematically acquainted by Crossair with the specific features of western systems and cockpit procedures.
• The flight crew reacted inappropriately to the change in departure clearance SID ZUE 1Y by ATC.
• The co-pilot made an entry in the FMS, without being instructed to do so by the commander, which related to the change to the SID ZUE 1 standard instrument departure. In doing so, he omitted to select a turn direction.
• The commander dispensed with use of the autopilot under instrument flight conditions and during the work-intensive climb phase of the flight.
• The commander took the aircraft into a spiral dive to the right because, with a probability bordering on certainty, he had lost spatial orientation.
• The first officer took only inadequate measures to prevent or recover from the spiral dive.
The following factors may have contributed to the accident:
• The commander remained unilaterally firm in perceptions which suggested a left turn direction to him.
• When interpreting the attitude display instruments under stress, the commander resorted to a reaction pattern (heuristics) which he had learned earlier.
• The commander’s capacity for analysis and critical assessment of the situation were possibly limited as a result of the effects of medication.
• After the change to standard instrument departure SID ZUE 1Y the crew set inappropriate priorities for their tasks and their concentration remained one-sided.
• The commander was not systematically acquainted by Crossair with the specific features of western systems and cockpit procedures.
Final Report:
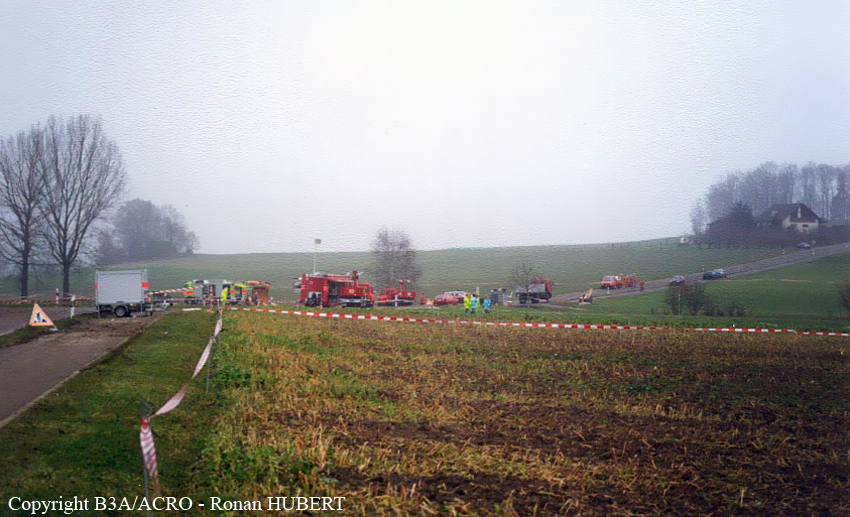
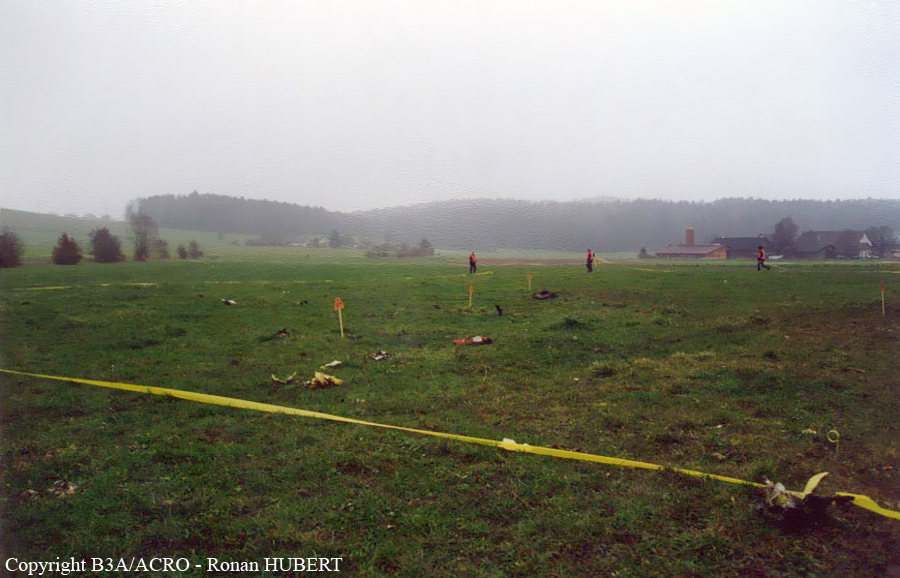
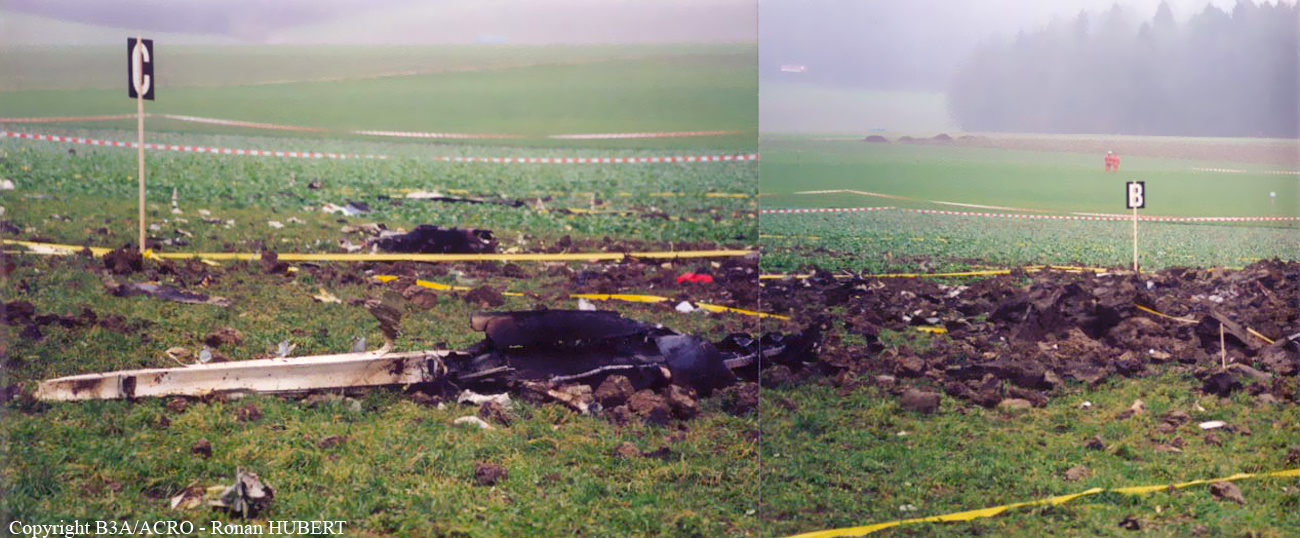
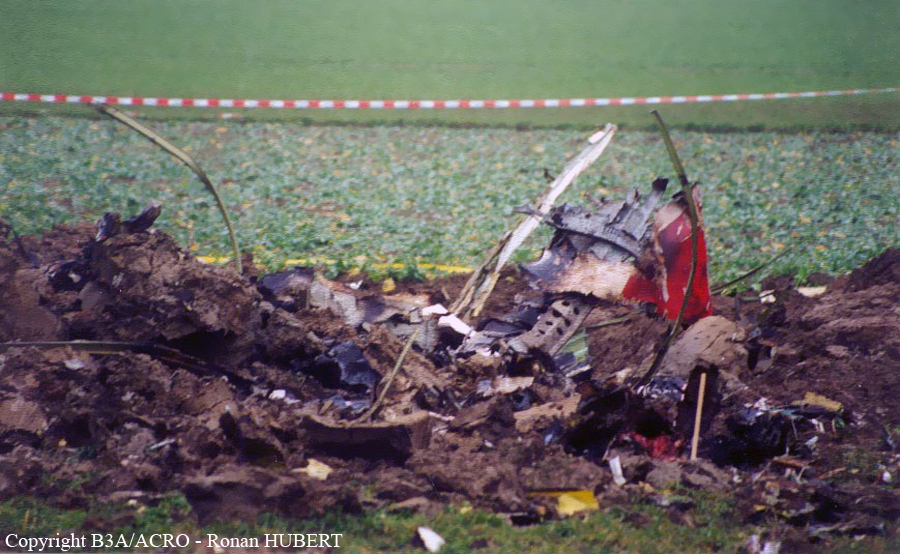
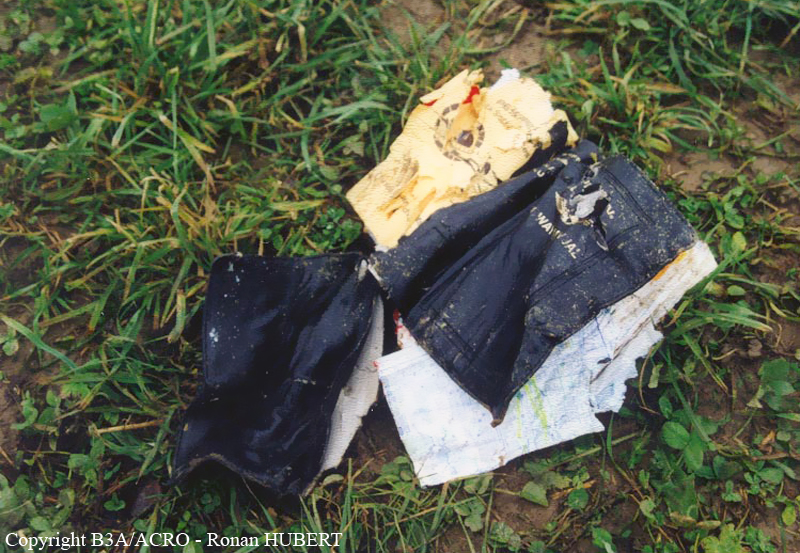
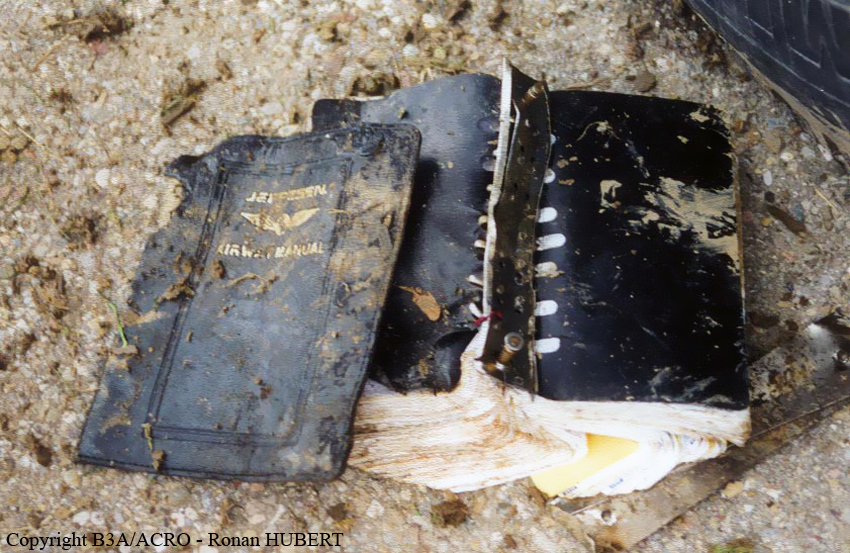
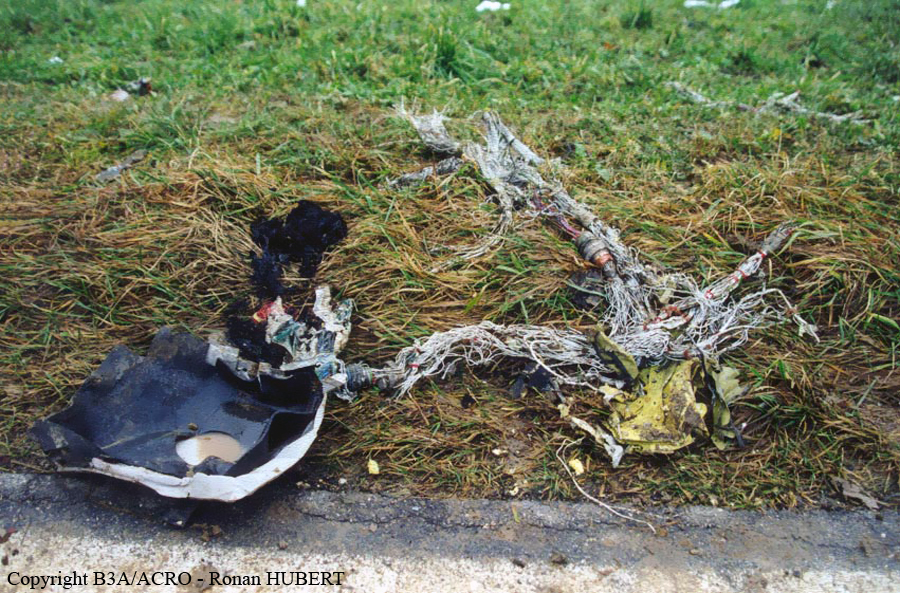
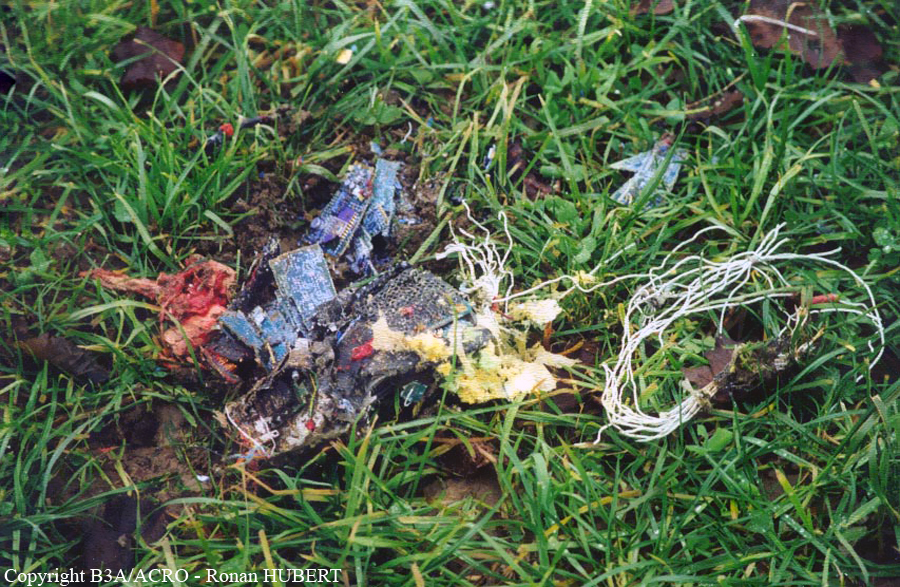
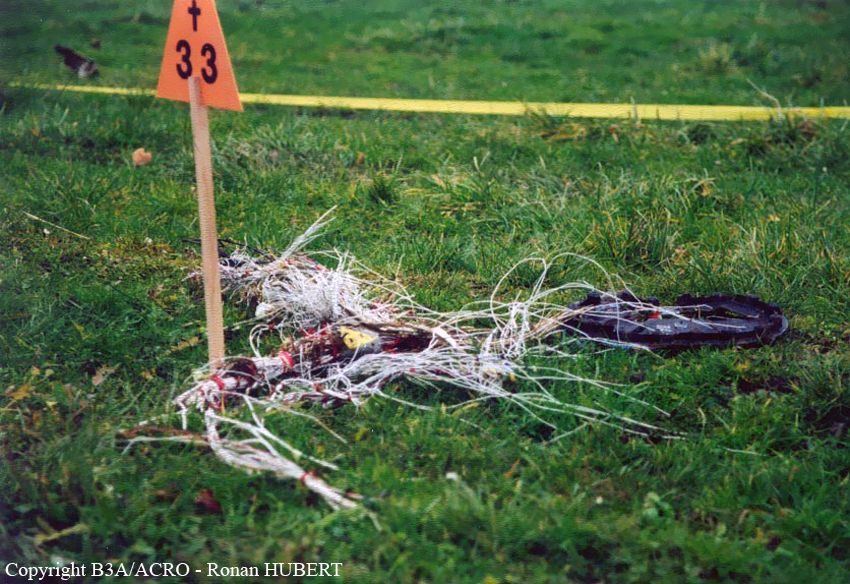
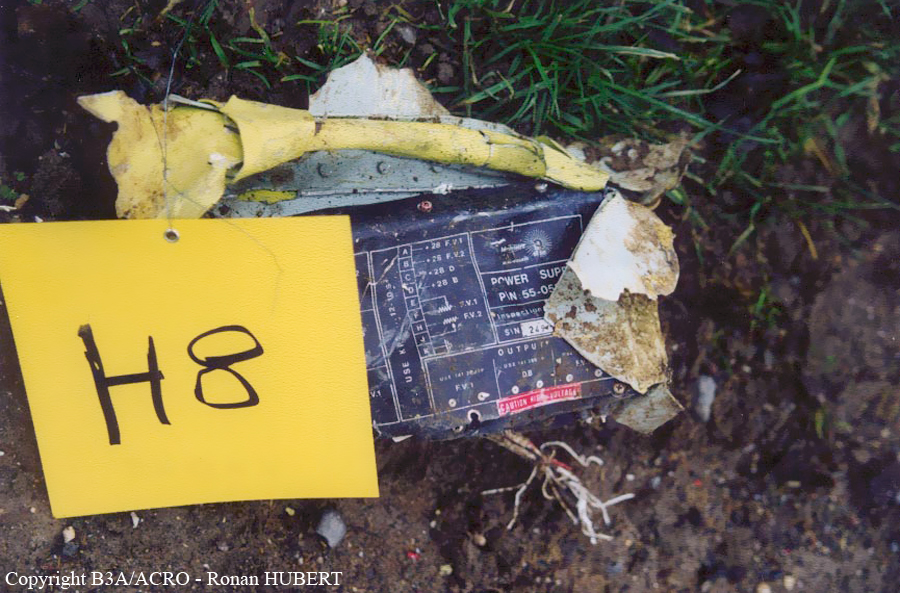
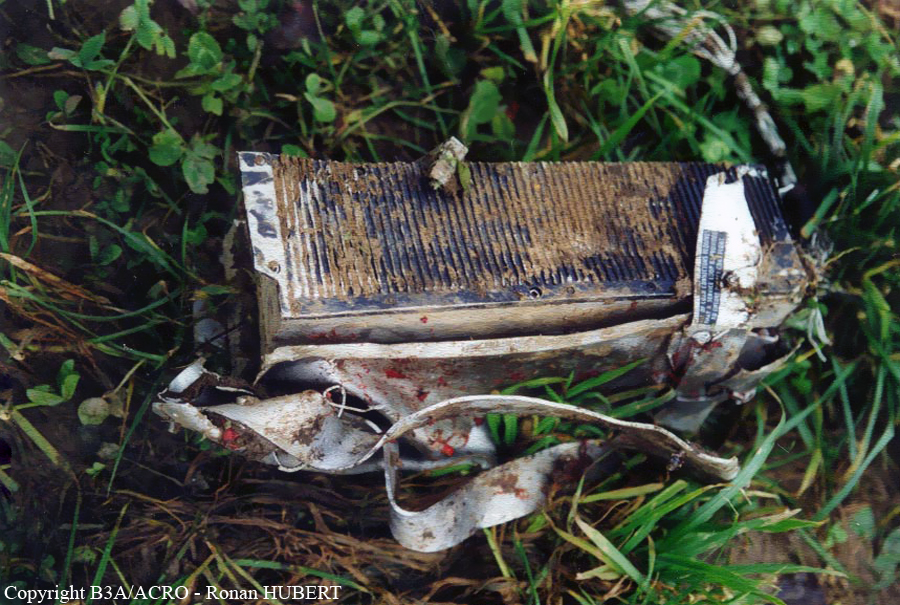
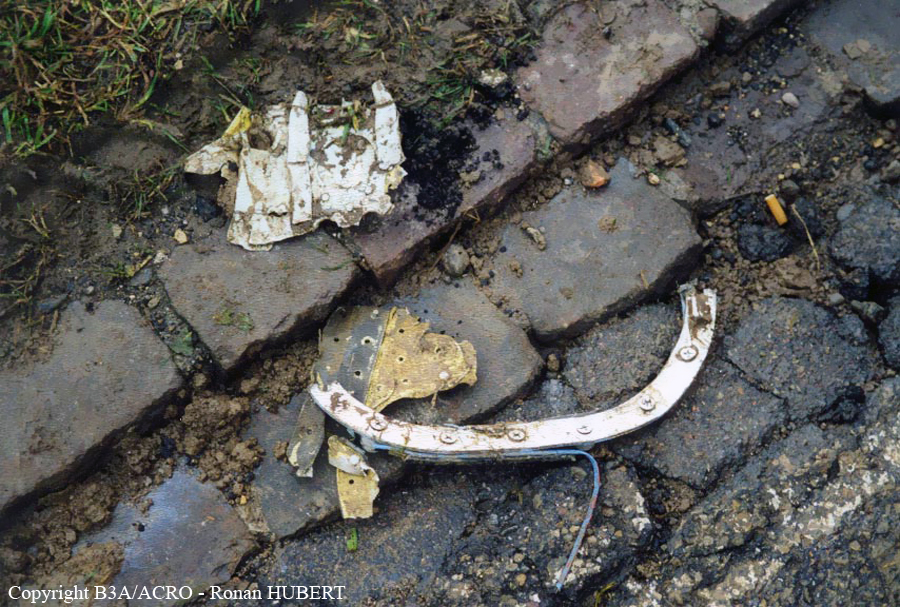
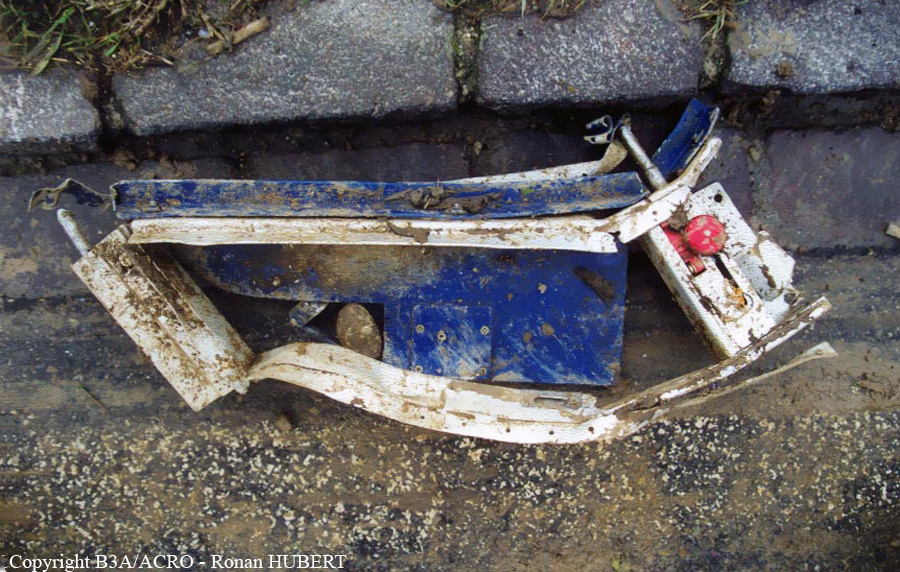
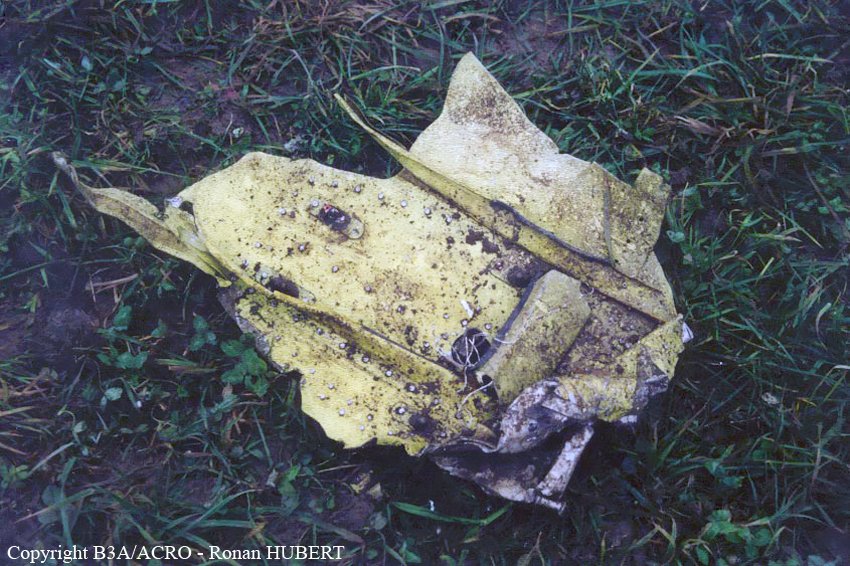
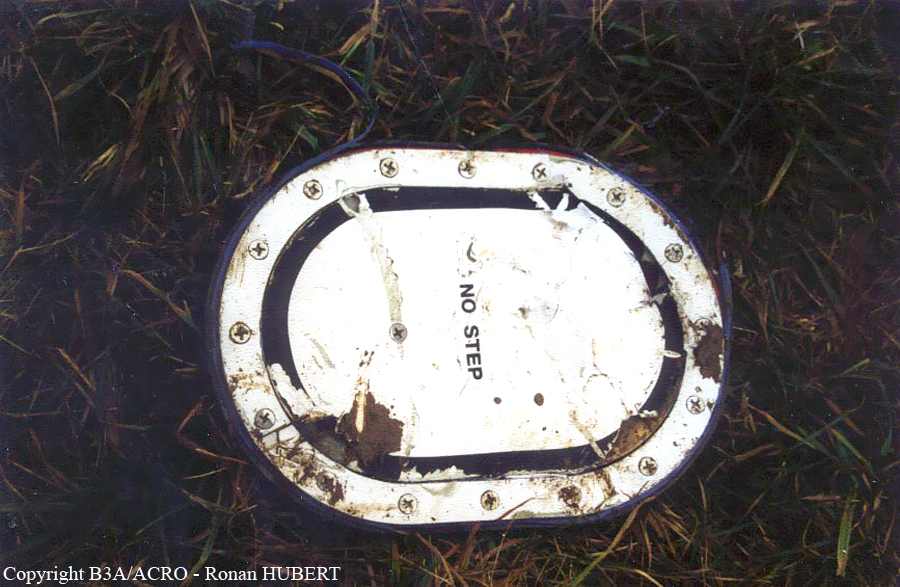
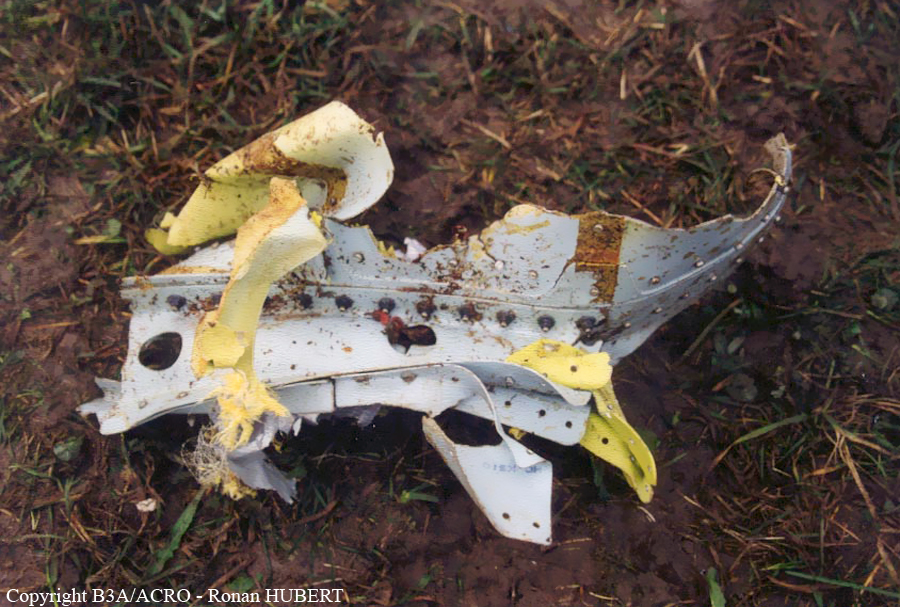
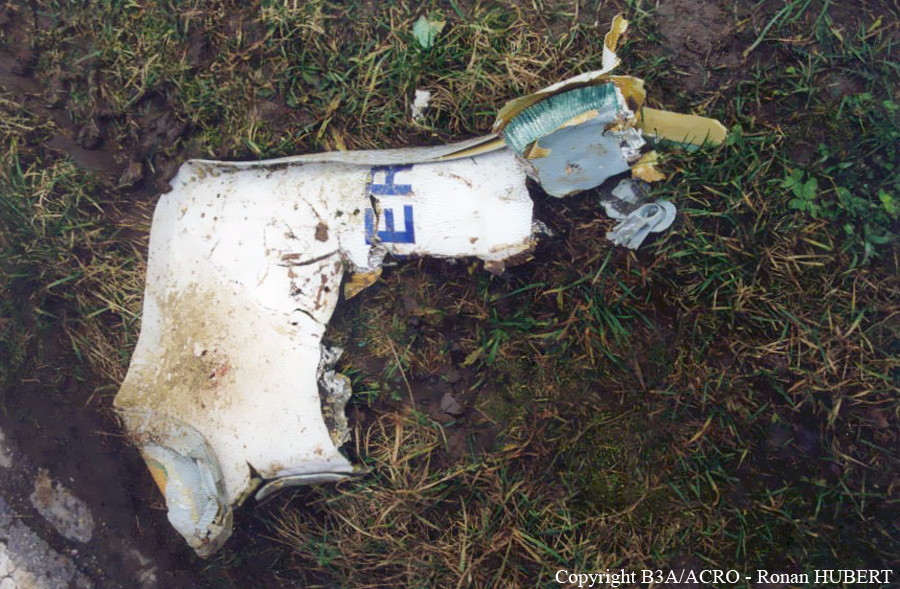
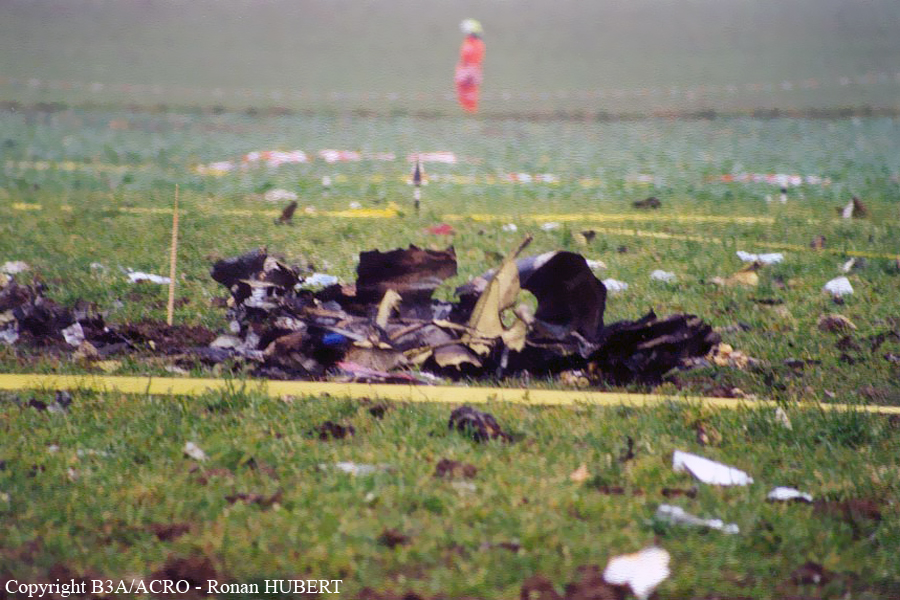
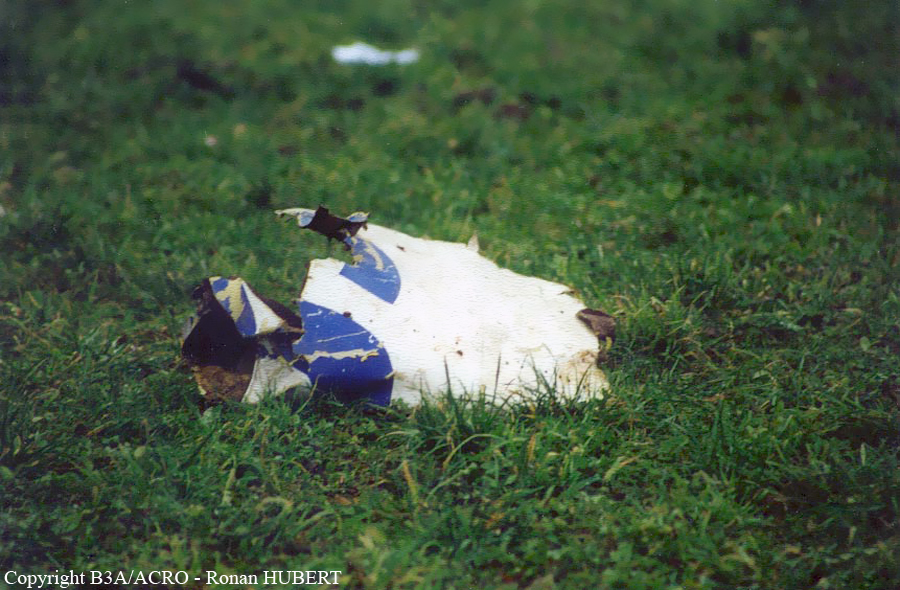
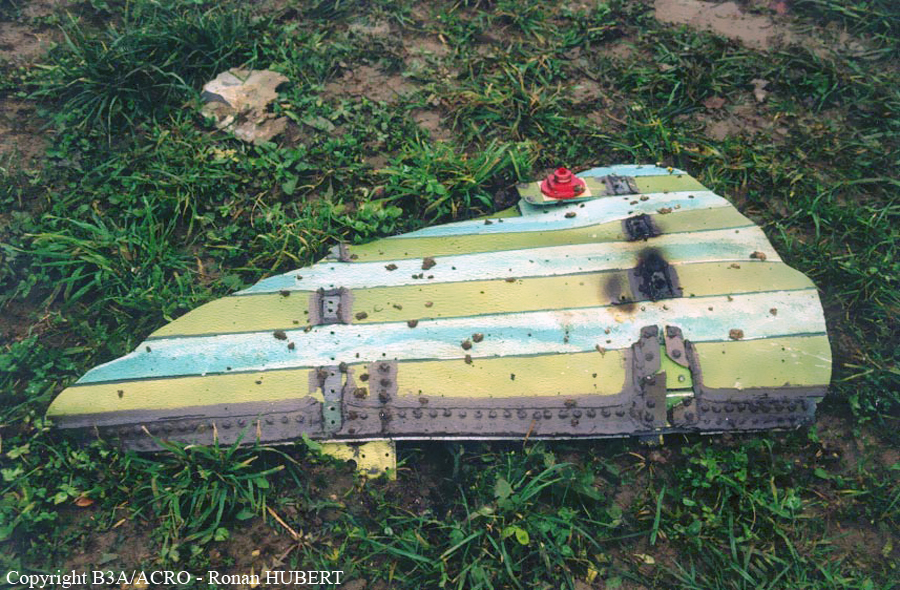
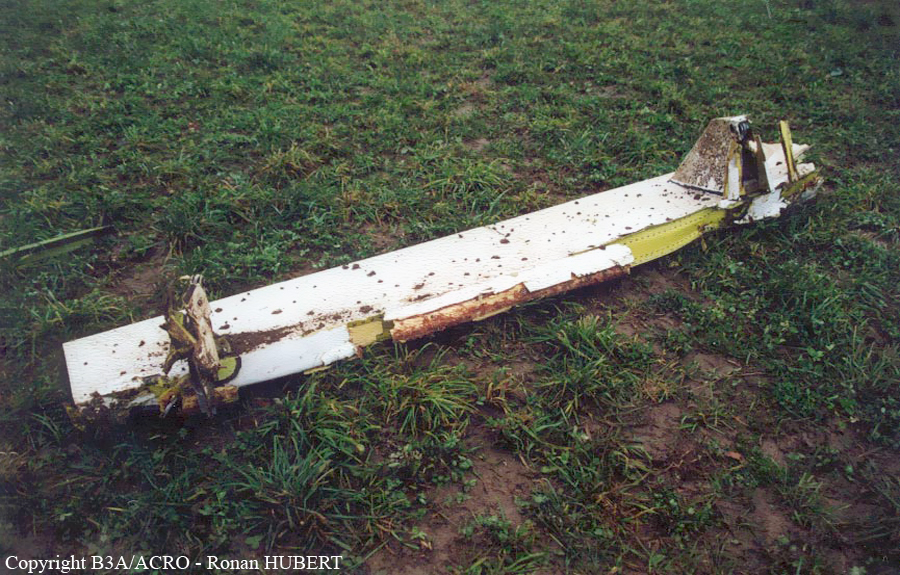
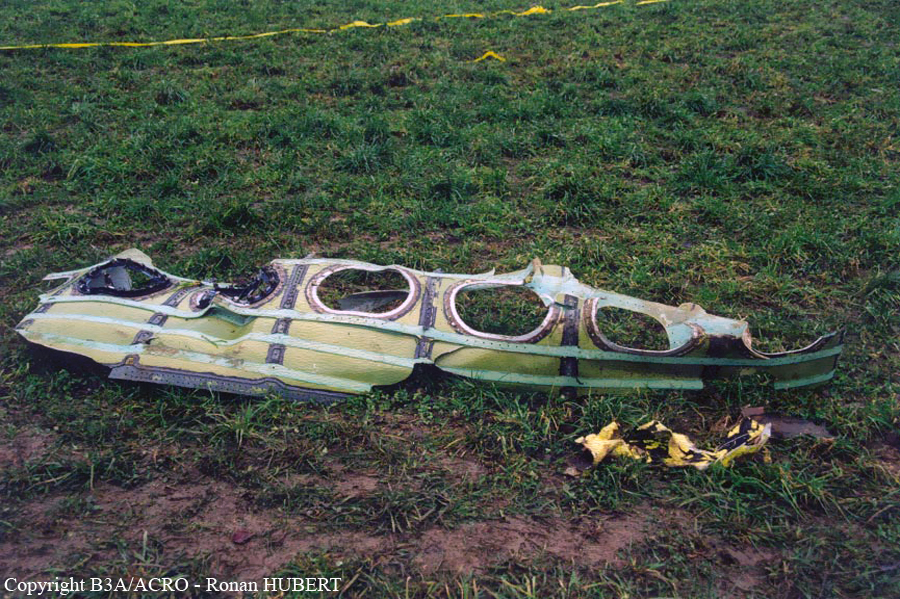
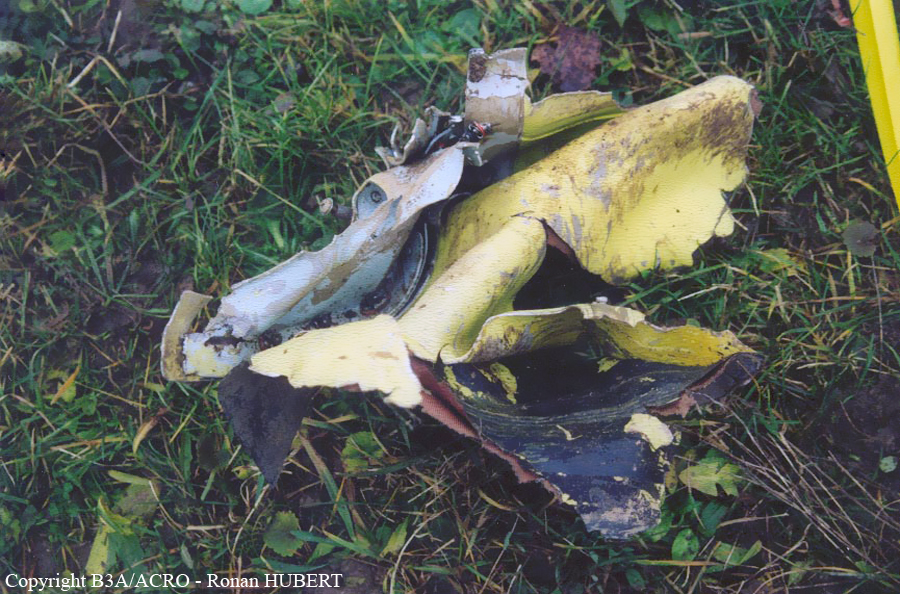





























Crash of a Cessna 414A Chancellor in Zurich: 1 killed
Date & Time:
Apr 10, 1997 at 2101 LT
Registration:
HB-LPN
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Colmar – Basel – Zurich
MSN:
414A-0842
YOM:
1982
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
1
Captain / Total hours on type:
350.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
2
Aircraft flight hours:
2318
Circumstances:
The crew was completing a flight from Colmar to Zurich with an intermediate stop in Basel. While on a night approach to runway 28 at Zurich-Kloten Airport, both engines lost power simultaneously. The aircraft lost height, struck a three-floor building and crashed on a second one located few dozen metres further. The captain was seriously injured while the copilot was killed.
Probable cause:
The accident was the consequence of the following factors:
- Insufficient flight preparation;
- Insufficient fuel supply;
- An emergency landing at night in a densely populated area following a double engine failure as a result of an inappropriate operation of the fuel selector switch.
- Insufficient flight preparation;
- Insufficient fuel supply;
- An emergency landing at night in a densely populated area following a double engine failure as a result of an inappropriate operation of the fuel selector switch.
Final Report:


Crash of a Piper PA-46-310P Malibu in Zurich: 1 killed
Date & Time:
Oct 10, 1995 at 1649 LT
Registration:
HB-PLN
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Bern - Zurich
MSN:
46-08124
YOM:
1988
Crew on board:
1
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
1
Captain / Total hours on type:
540.00
Circumstances:
Following an uneventful flight from Bern, the pilot started the descent to Zurich-Kloten Airport in relative good weather conditions (scattered 7,000 feet, visibility 5 km, wind from 340° at 4 knots and OAT 20° C). On short final to runway 14, the single engine aircraft entered an uncontrolled descent, struck the ground, lost its left wing and came to rest about 500 metres short of runway threshold. The pilot, sole on board, was killed.
Probable cause:
It was determined that the loss of control on short final occurred after the pilot suffered a heart attack.
Final Report:
Crash of a Mitsubishi MU-2B-60 Marquise in Urnäsch: 1 killed
Date & Time:
Sep 3, 1994 at 1531 LT
Registration:
HB-LLP
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Zurich - Zurich
MSN:
767
YOM:
1979
Crew on board:
1
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
1
Captain / Total hours on type:
666.00
Aircraft flight hours:
5845
Circumstances:
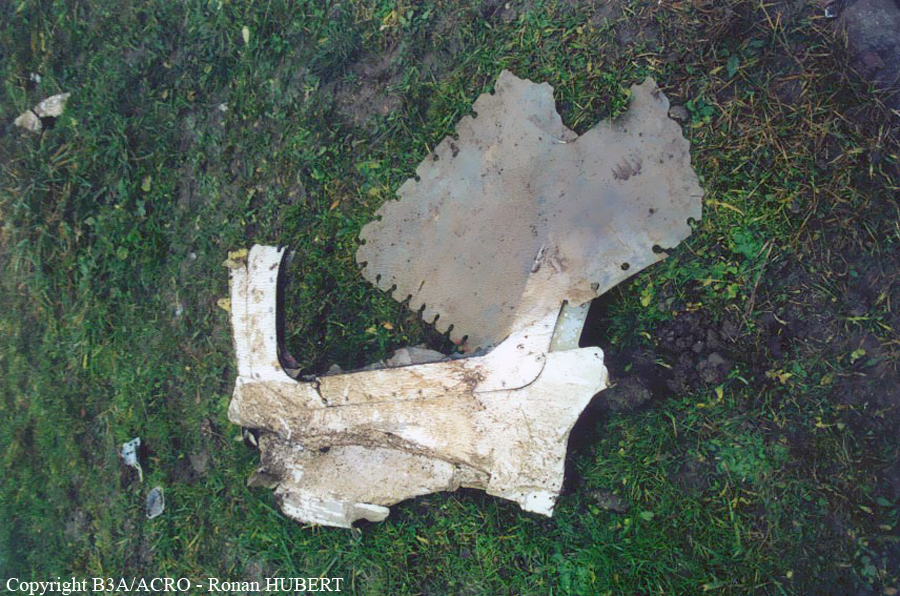
The day prior to the accident, both propellers have been changed at Basel Airport and the pilot returned to his base in Zurich. Due to poor weather conditions en route, he was unable to conduct a test of both propellers, reason why a test flight was scheduled on September 3. After his departure from Zurich-Kloten Airport runway 28, the pilot flew to the east and was cleared to climb to FL130, the assigned altitude where the test should be performed. Ten minutes after takeoff, he informed ATC that he would shut the right engine down. The aircraft lost speed and height then deviated from the prescribed flight path. The pilot was able to restart the right engine and to regain control when, three minutes later, he informed ATC he would shut the right engine down for the second time. The aircraft entered a right turn then a rapid descent and crashed in a wooded area, bursting into flames. The aircraft was destroyed and the pilot, sole on board, was killed.
Probable cause:
Detailed examination of the right engine and its peripherals as well as a simulator reconstitution were able to identify the probable causes of the accident:
- Malfunction of the Negative Torque System (NTS) on the right engine,
- Blocking of the condition lever in the 'fuel off' position prior to the 'emergency stop' position,
- Continuation of a technical control flight despite the malfunction of the Negative Torque System (NTS),
- Loss of control during an extreme asymmetrical thrust caused by the fact that the right propeller was in windmilling position with a high number of rounds.
- Malfunction of the Negative Torque System (NTS) on the right engine,
- Blocking of the condition lever in the 'fuel off' position prior to the 'emergency stop' position,
- Continuation of a technical control flight despite the malfunction of the Negative Torque System (NTS),
- Loss of control during an extreme asymmetrical thrust caused by the fact that the right propeller was in windmilling position with a high number of rounds.
Final Report:



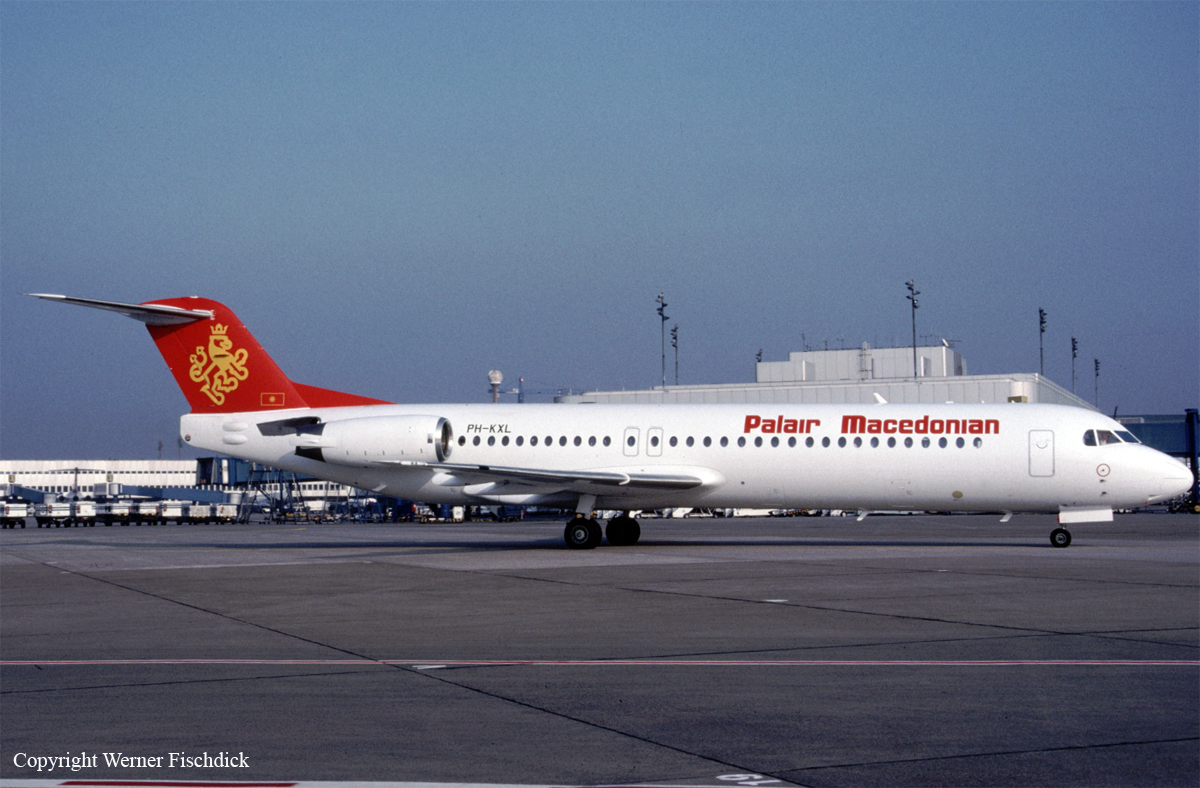
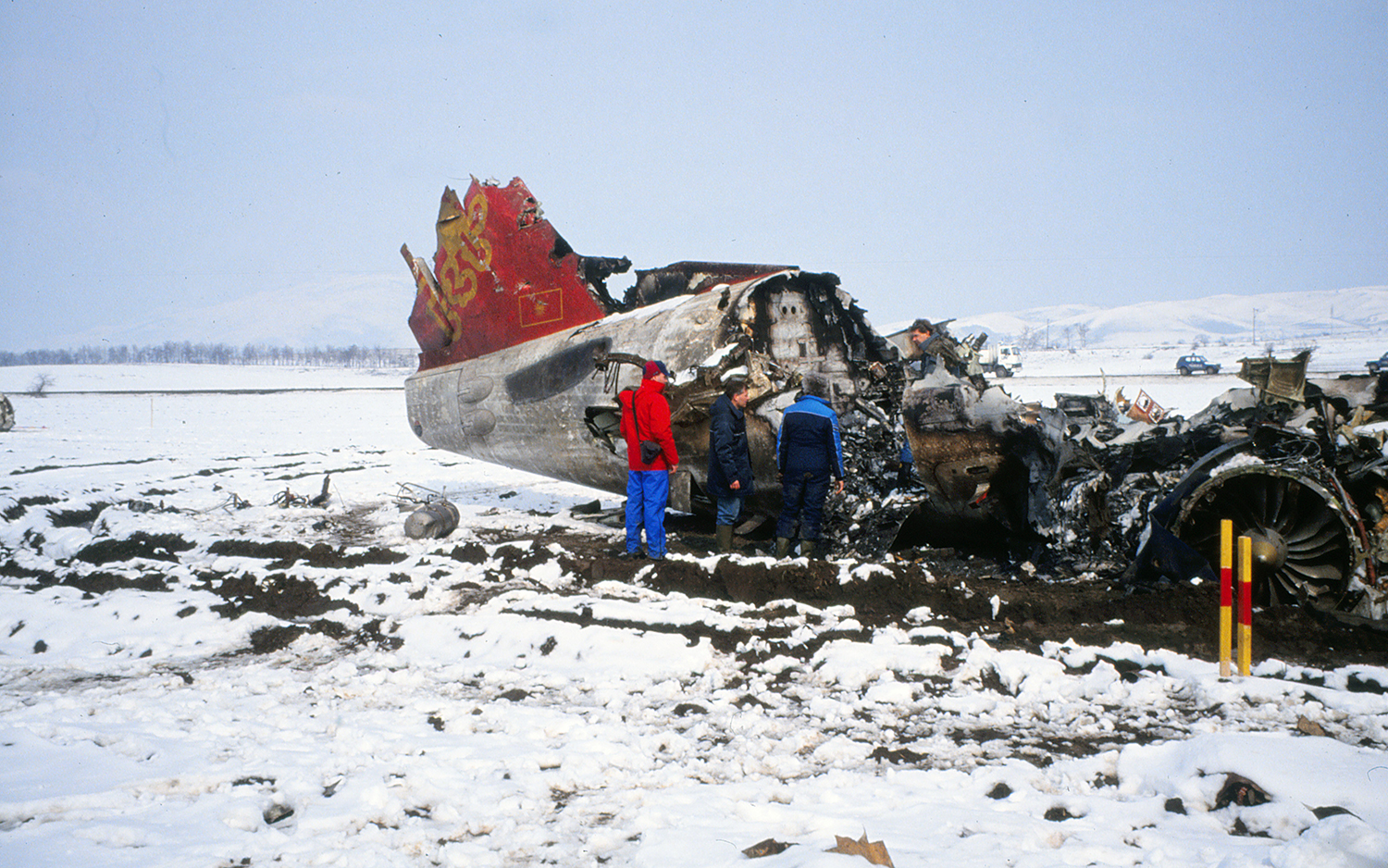
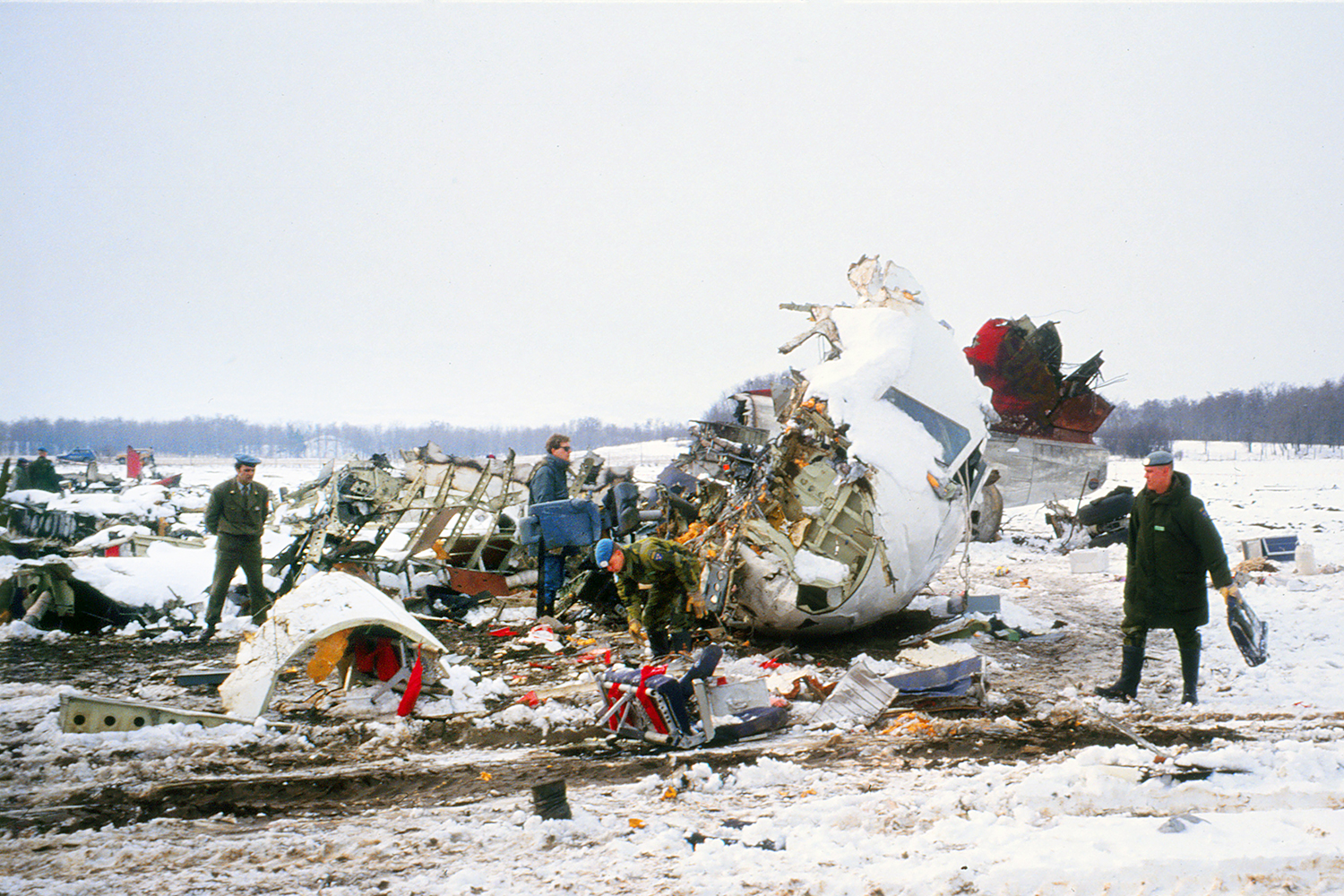
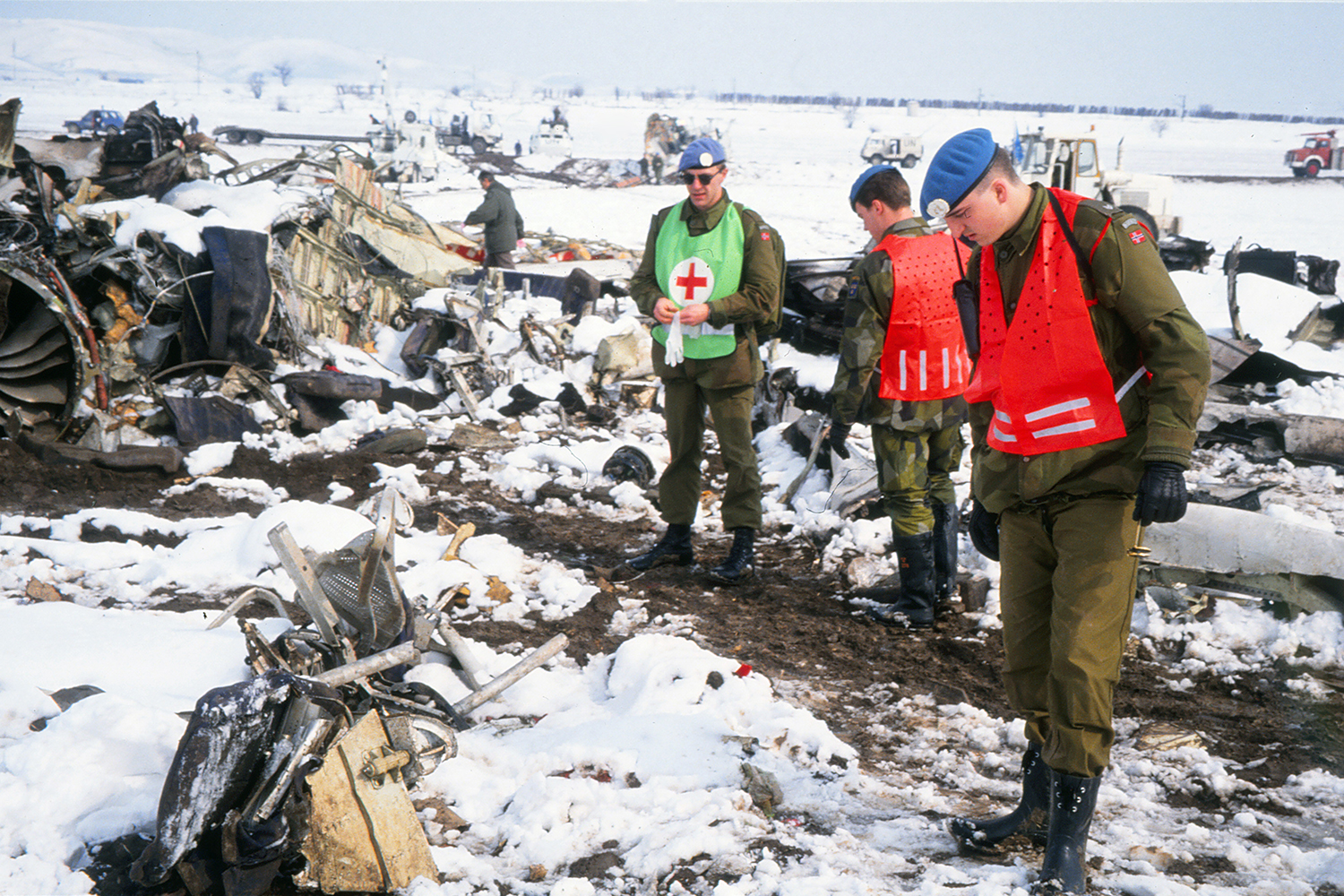
Crash of a Fokker 100 in Skopje: 83 killed
Date & Time:
Mar 5, 1993 at 1112 LT
Registration:
PH-KXL
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Skopje - Zurich
MSN:
11393
YOM:
1992
Flight number:
PMK301
Crew on board:
5
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
92
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
83
Captain / Total hours on type:
1180.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
65
Aircraft flight hours:
188
Aircraft flight cycles:
136
Circumstances:
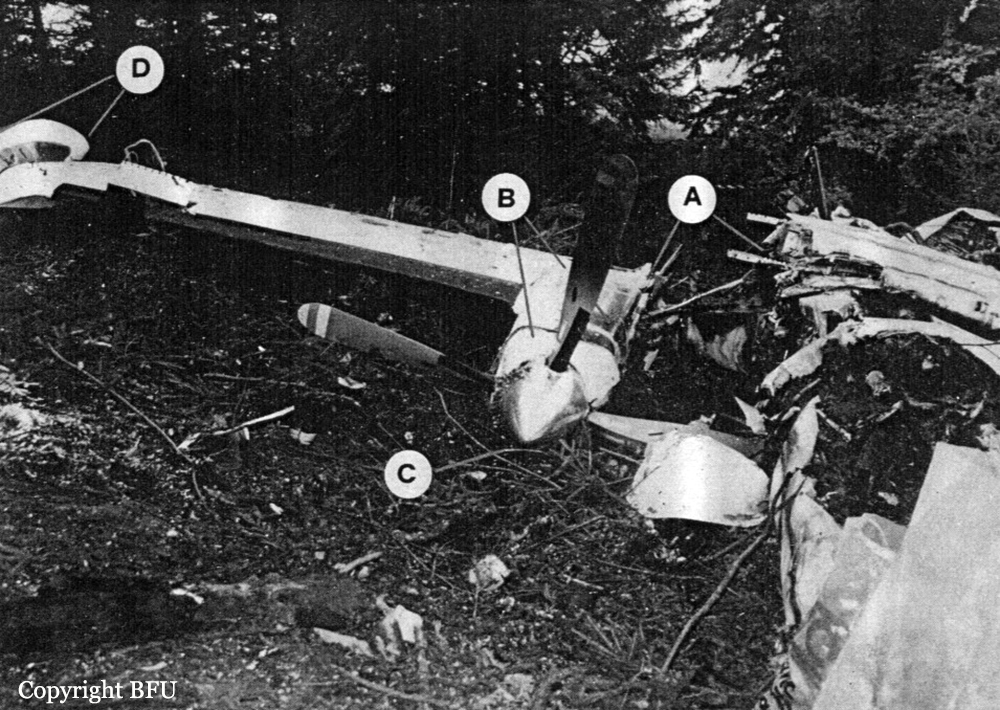
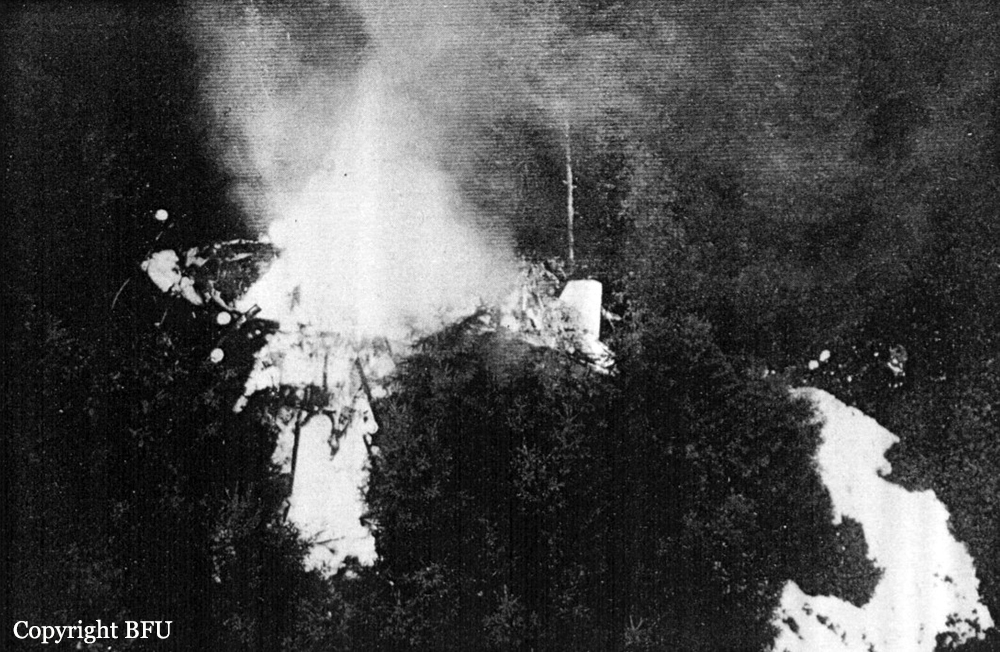
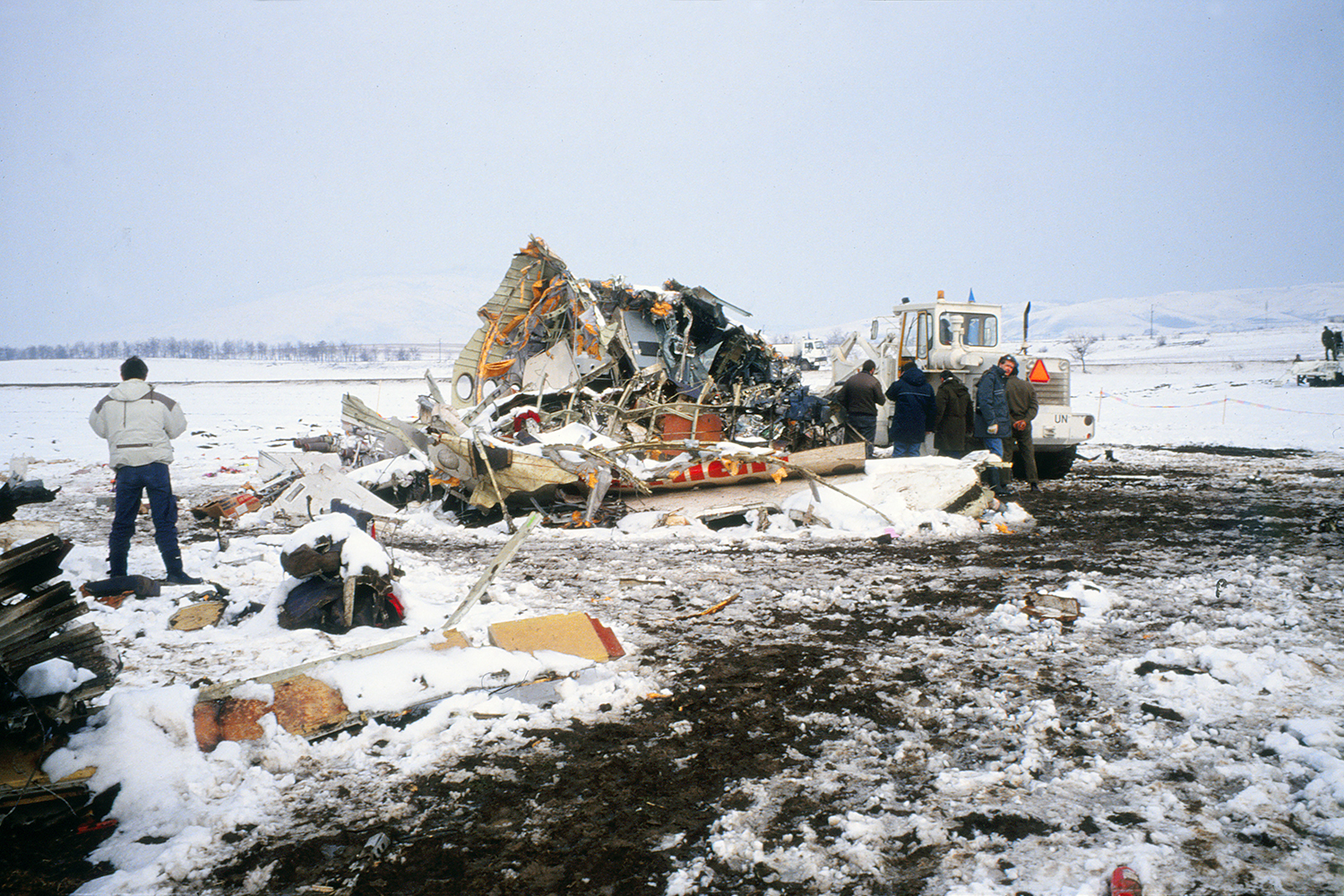
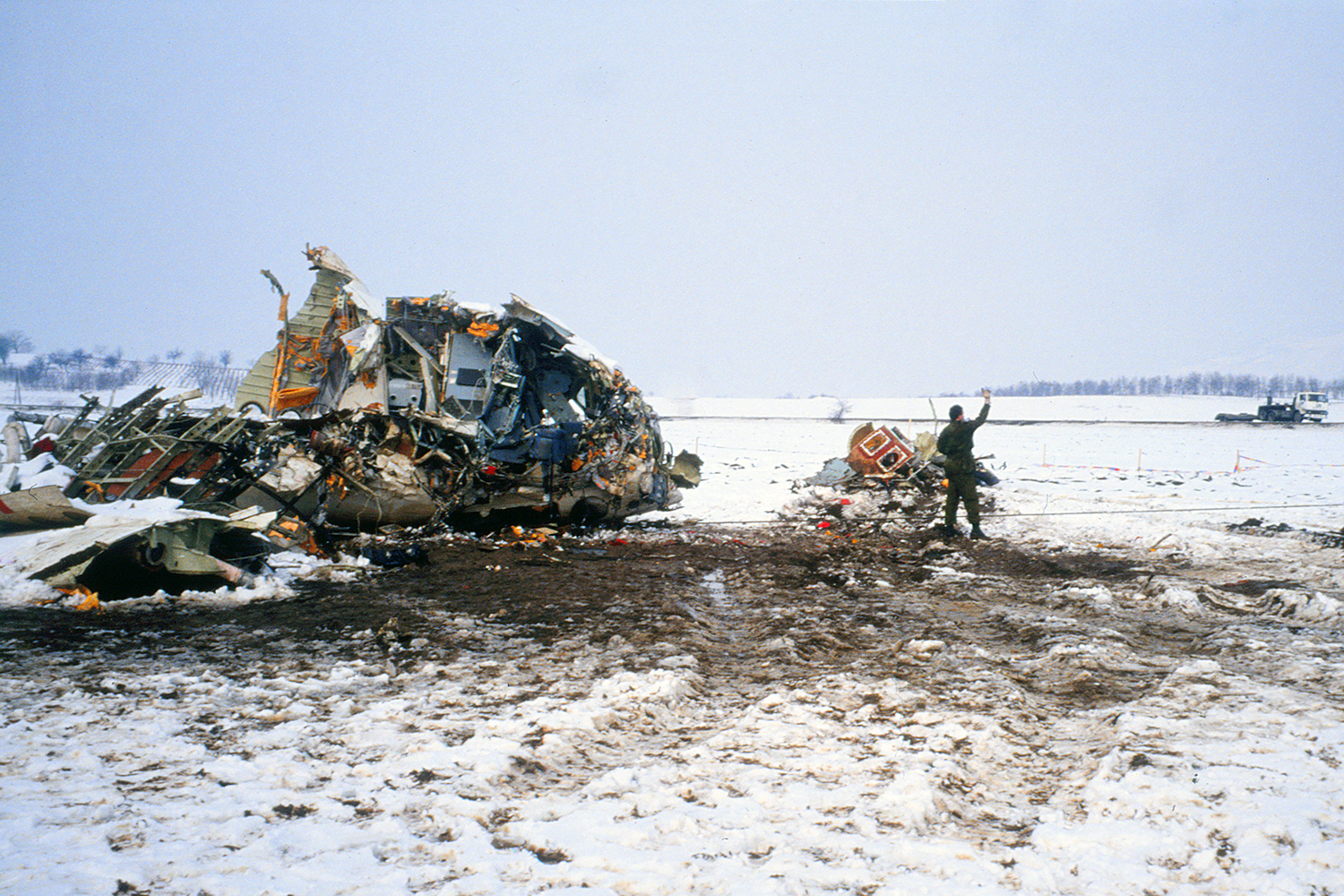
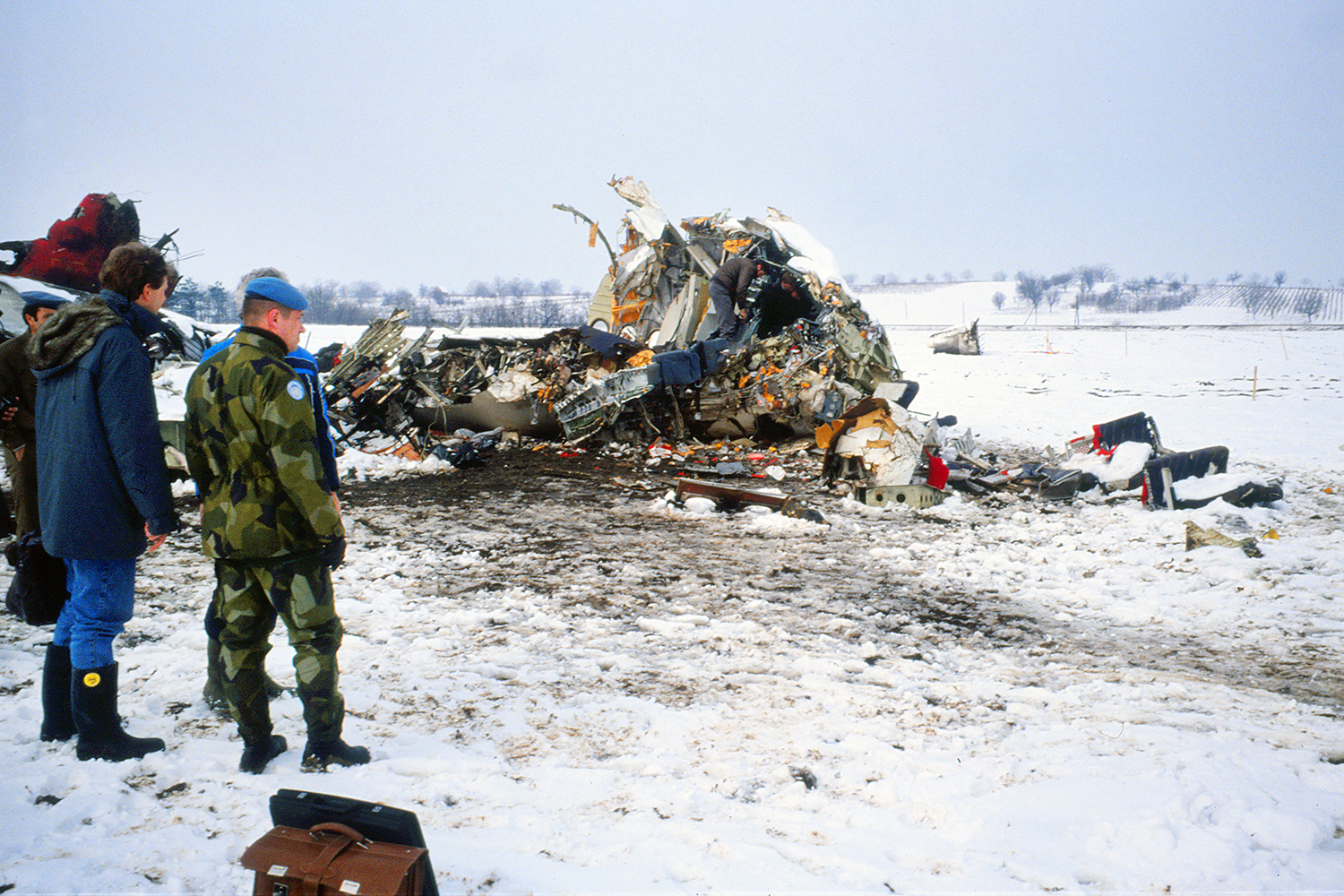
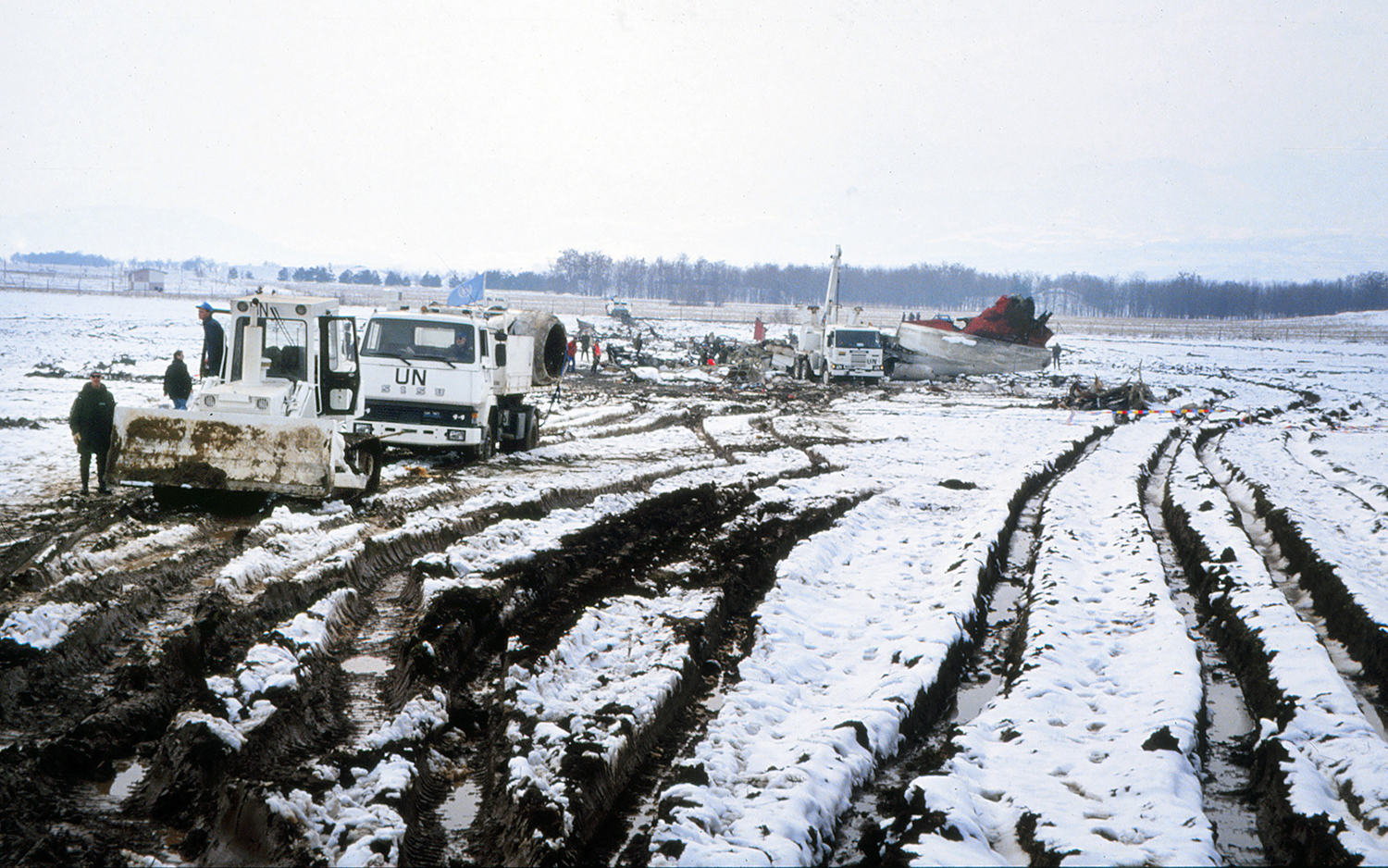
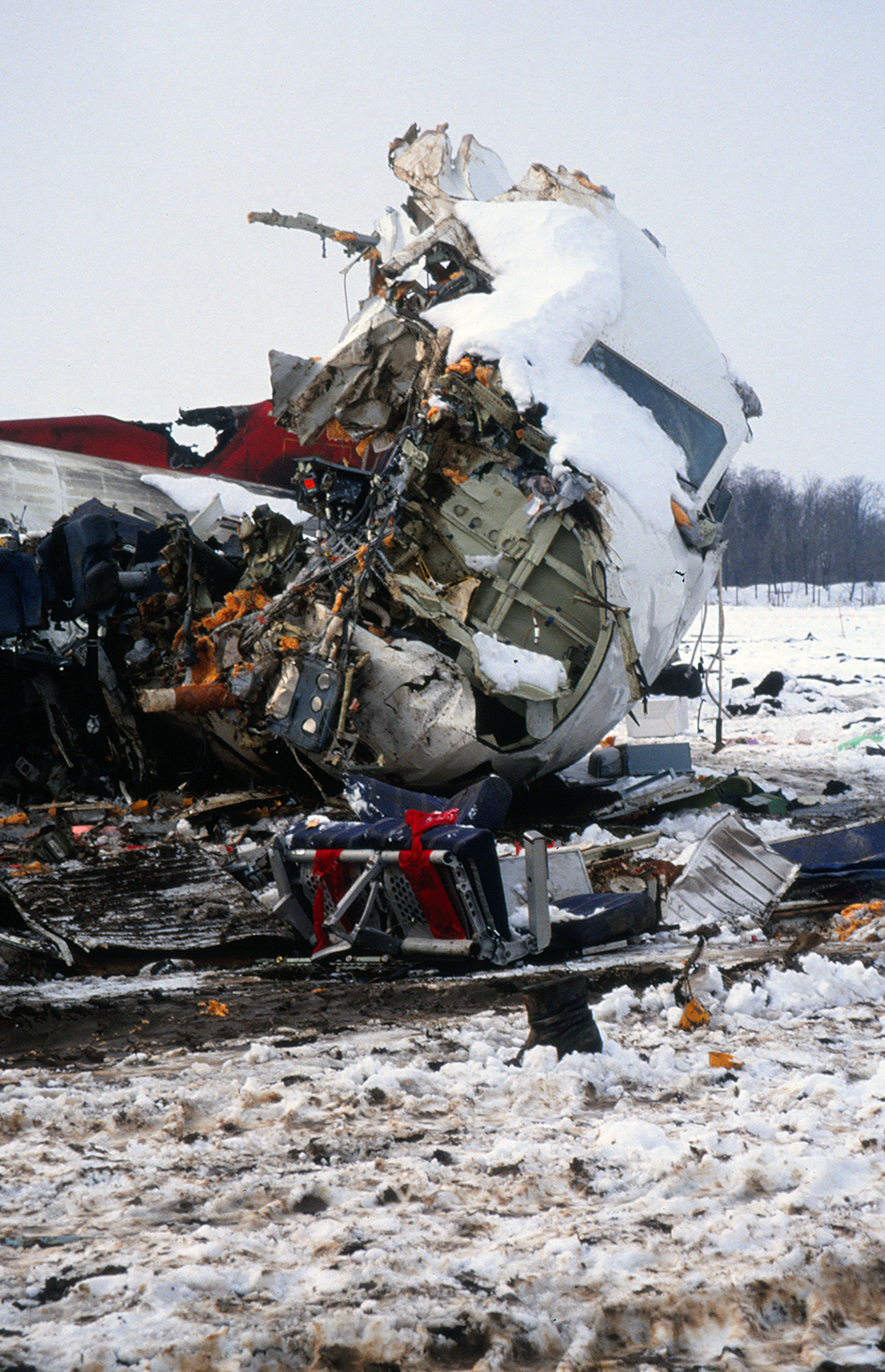
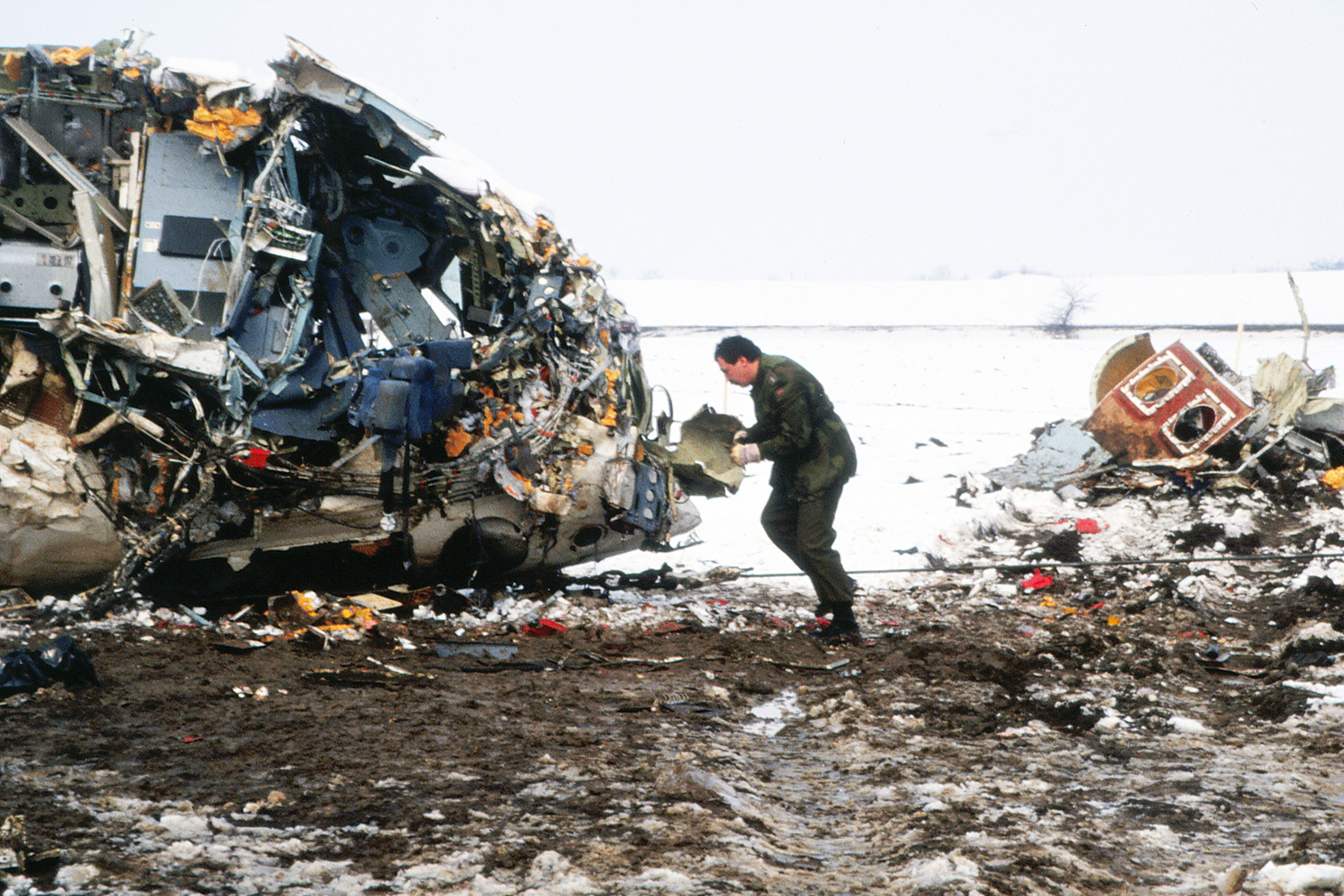
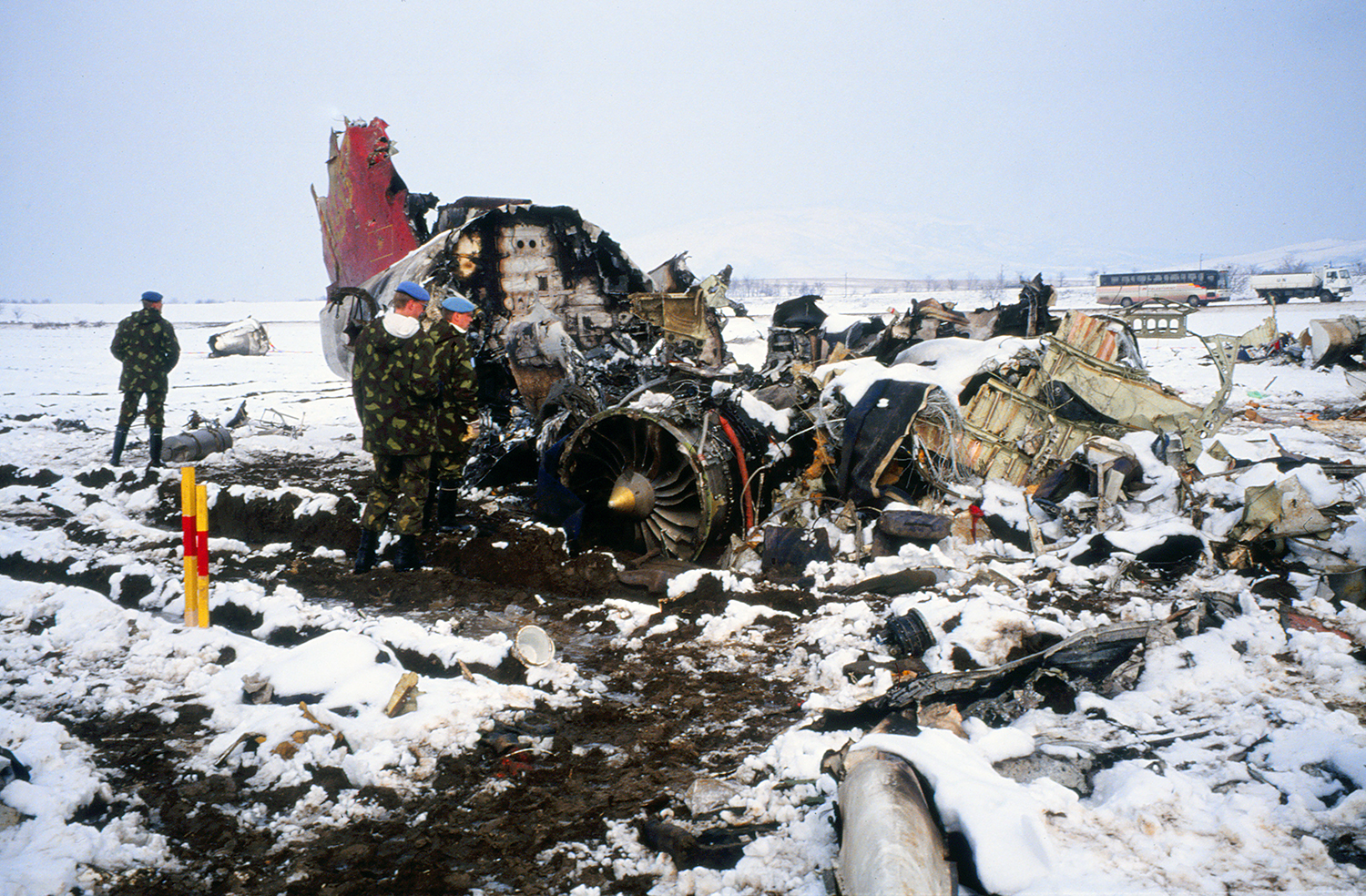
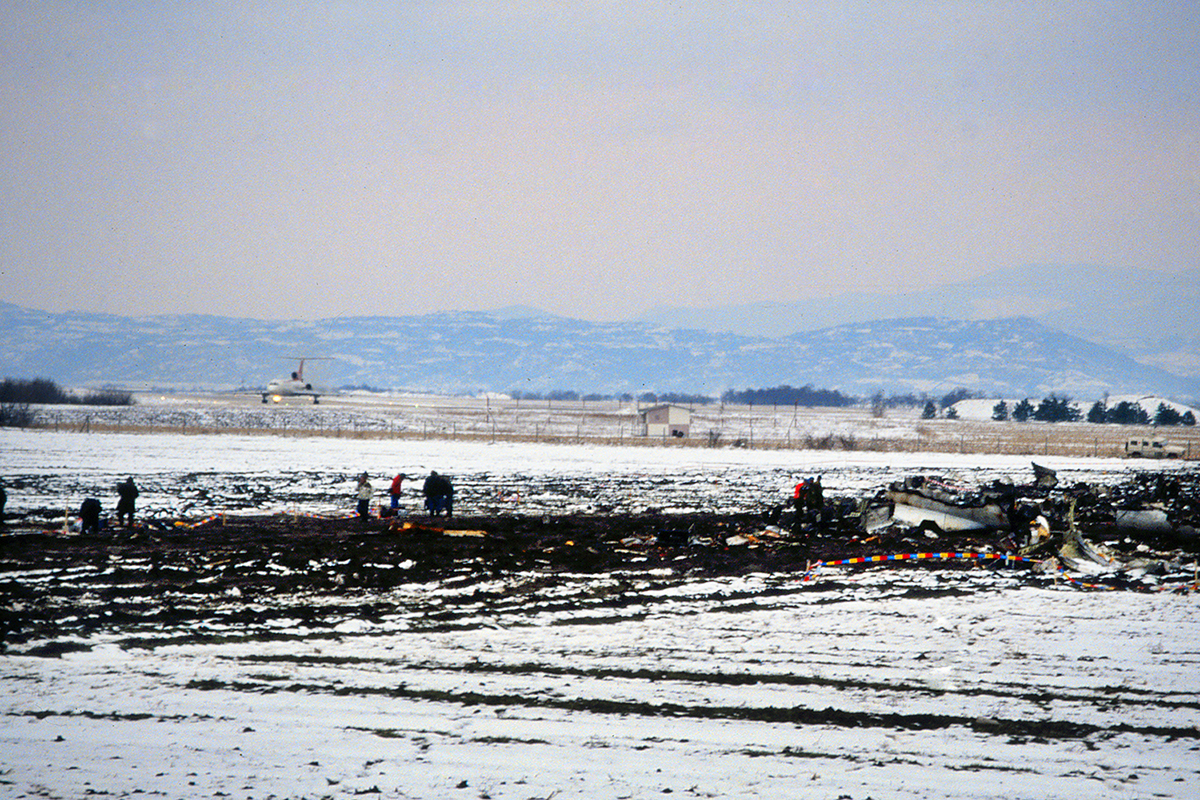
Palair Macedonian Airlines flight PMK301 was destroyed when it crashed immediately after takeoff from Skopje Airport, North Macedonia. Fourteen of the 97 occupants survived the accident. The aircraft, a Fokker 100 jet, was leased to Palair by Aircraft Financing and Trading (AFT) of the Netherlands since January 1993. AFT provided route training captains, while Palair provided the first officer or candidate Palair captain and the cabin crew. The aircraft arrived on a scheduled flight from Frankfurt to Skopje at 09:40 hours local time with a 35 minute delay. The new crew arrived at Skopje Airport at approximately 10:30 and they went straight to the aircraft. It was snowing lightly. The temperature was 0° Celsius, dewpoint -1° Celsius. The AFT Director Flight Operations was the pilot-in-command and was sitting in the right seat. He performed the first officer duties and was the pilot not flying (PNF). He was also giving route-instruction. A captain-under-training was sitting in the left seat. He was acting captain and was pilot flying (PF), receiving route-training. The dispatch officer checked both wing leading edges and saw they were not contaminated with ice or snow, but were only wet of melted snow. The Flying Station Engineer subsequently performed the walk around and was accompanied by three Palair ground handling crew members. The ground handling crew members stated that they had a brief discussion with the FSE about the weather and asked if the aircraft needed deicing since there was some snow on the right wing inner flap. The FSE replied that de-icing was not necessary and that any deposit would blow off the wing during take off. The total time the aircraft remained on the ground at Skopje Airport was about 1 hour 35 minutes. At 11:05 hours start-up was approved and clearance was given to taxi to holding point runway 34. During taxying, a Yak-42D from Vardar Air, which was standing on the apron, was de-iced. This was the first aircraft that day being deiced. In the meantime the snowfall had increased to moderate. According to the Cockpit Voice Recorder, no discussion about the weather conditions took place by the pilots. At 11:11 Palair 301 was cleared for take off, the wind was given as 010° with 3 knots. The tower controller stated that the visibility was 900 meters and it was snowing. The aircraft rotated normally and the PNF then called "positive", followed by the call "gear up" from the PF, which was confirmed by the PNF. Two seconds after lift off the aircraft experienced heavy vibrations followed by a sudden right bank to approximately 10°, immediately followed by approximately 50° left bank and 55° right bank in sequence within 2 seconds. The roll movements were counteracted by aileron and rudder input. Approximately 10 seconds before impact the PNF called "deselect" followed by sounds which were determined to be the autopilot cavalry charge (twice) followed by the GPWS aural alert, "sink rate" (twice). The aircraft right wingtip hit the ground 382 meters beyond the end of the runway with approximately 90° bank, the fuselage was more or less in a horizontal position. The right wing disintegrated towards the wing-fuselage attachment, followed by major impact of the fuselage, which broke up into three major parts, and the impact of the right engine and stabilizer. The right engine separated and subsequently impacted and penetrated the aft fuselage. The stabilizer and the upper part of the vertical tail plane also separated. Witnesses stated that explosions followed shortly after impact and several residual fires broke out on the debris.
Probable cause:
The Board determined that the impact with the ground in a steep right bank shortly after lift off was caused by a loss of roll controllability due to contamination of the wings with ice. This situation resulted from an omission to carry out spraying of the aircraft with deicing or anti-icing fluid in meteorological conditions conducive to icing, due to a lack of ice-awareness of the flight crew and the Flying Station Engineer. Contributing factors were a lack of common background and procedures in a difficult multi-sources operational environment.
Final Report:













Crash of a Cessna 421C Golden Eagle III in Munich: 5 killed
Date & Time:
Jan 25, 1992
Registration:
D-IBHH
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Zurich - Augsburg
MSN:
421C-0162
YOM:
1976
Crew on board:
1
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
4
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
5
Circumstances:
On approach to Augsburg-Mühlhausen Airport, the pilot encountered foggy conditions with a visibility down to 500 meters. Unable to establish a visual contact with the runway, he initiated a go-around procedure and diverted to Munich-Riem Airport. On approach to Munich, weather conditions were poor. On short final, he realize the aircraft was not properly aligned and decided to attempt a go-around maneuver when the aircraft struck the ground and crashed to the left of the runway. The aircraft was destroyed upon impact and all five occupants were killed. At the time of the accident, visibility and RVR were below minimums.




