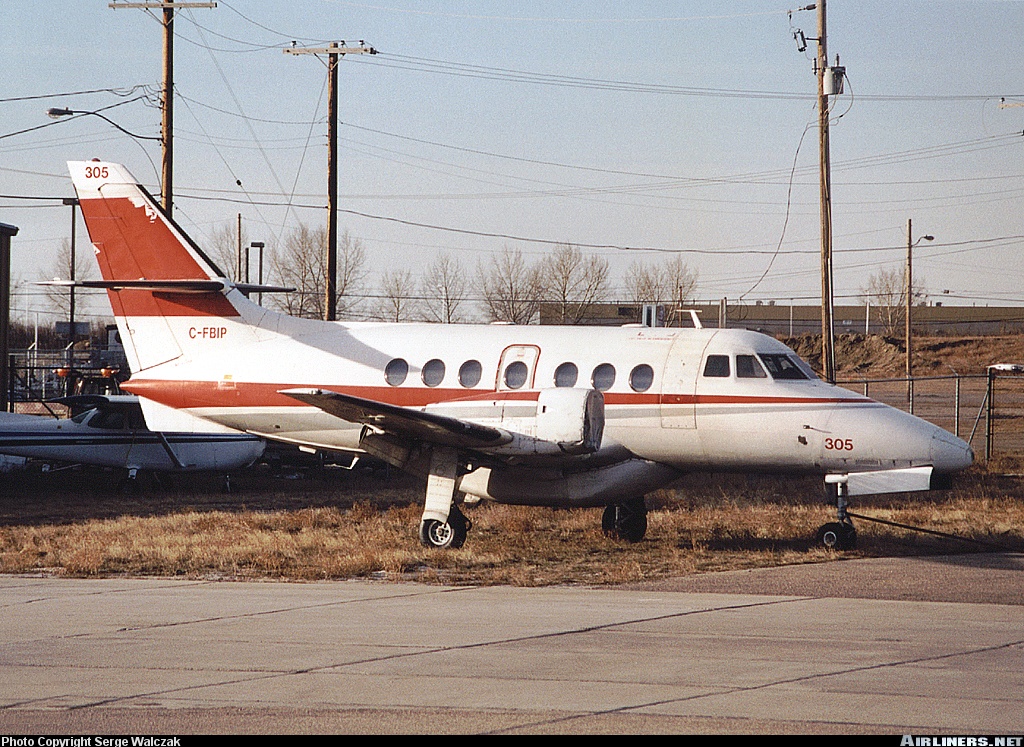
Crash of a BAe 3112 Jetstream 31 in Fort Saint John
Date & Time:
Jan 9, 2007 at 1133 LT
Registration:
C-FBIP
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Grande Prairie – Fort Saint John
MSN:
820
YOM:
1988
Flight number:
PEA905
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
10
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Captain / Total hours on type:
300.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
20
Circumstances:
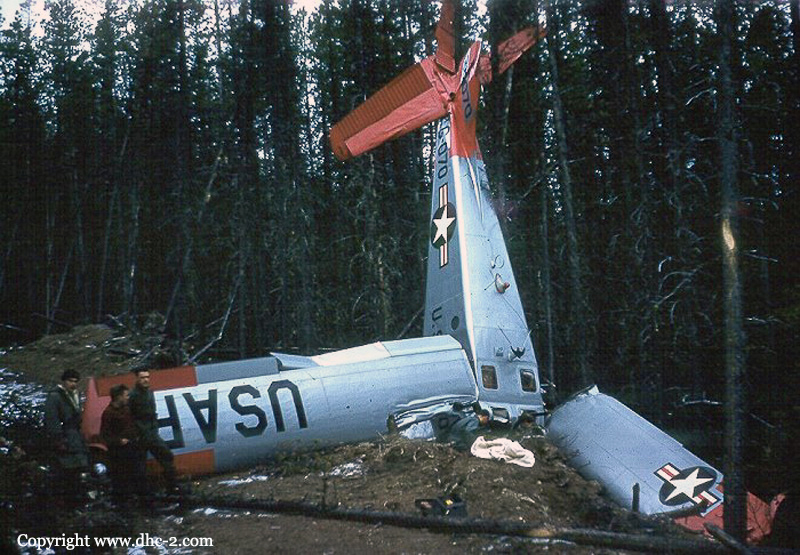
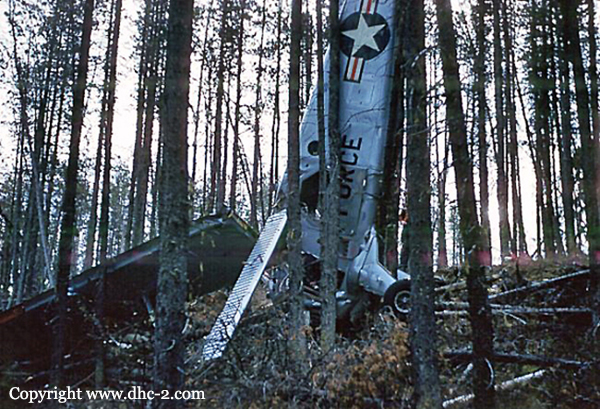
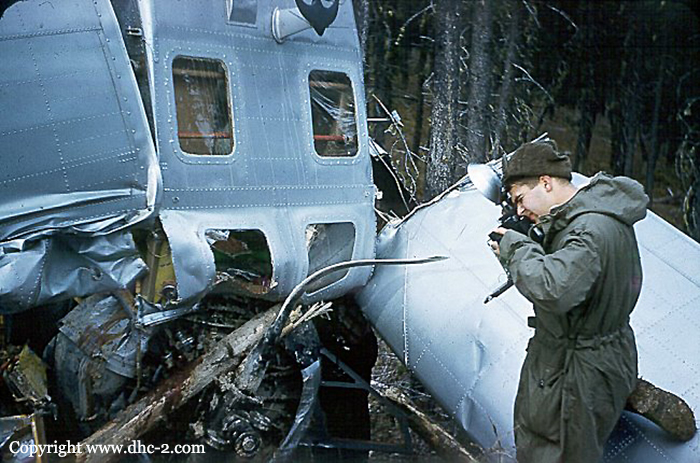
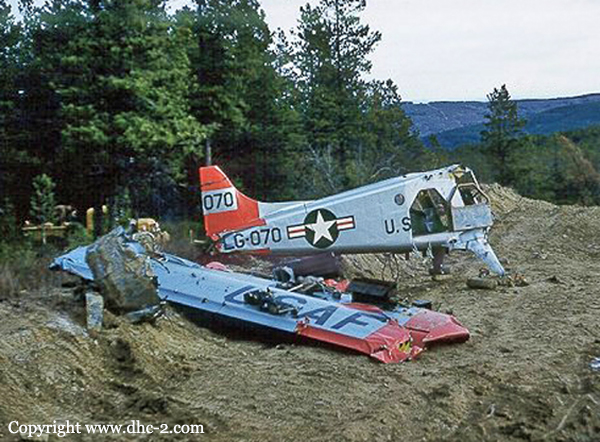
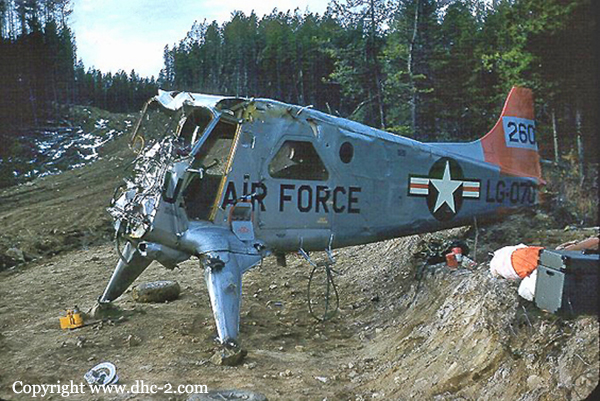
The aircraft was conducting an instrument approach to Runway 29 at Fort St. John, British Columbia, on a scheduled instrument flight rules flight from Grande Prairie, Alberta. At 1133 mountain standard time, the aircraft touched down 320 feet short of the runway, striking approach and runway threshold lights. The right main and nose landing gear collapsed and the aircraft came to rest on the right side of the runway, 380 feet from the threshold. There were no injuries to the 2 pilots and 10 passengers. At the time of the occurrence, runway visual range was fluctuating between 1800 and 2800 feet in snow and blowing snow, with winds gusting to 40 knots.
Probable cause:
Findings as to Causes and Contributing Factors:
1. A late full flap selection at 300 feet above ground level (agl) likely destabilized the aircraft’s pitch attitude, descent rate and speed in the critical final stage of the precision approach, resulting in an increased descent rate before reaching the runway threshold.
2. After the approach lights were sighted at low altitude, both pilots discontinued monitoring of instruments including the glide slope indicator. A significant deviation below the optimum glide slope in low visibility went unnoticed by the crew until the aircraft descended into the approach lights.
Finding as to Risk:
1. The crew rounded the decision height (DH) figure for the instrument landing system (ILS) approach downward, and did not apply a cold temperature correction factor. The combined error could have resulted in a descent of 74 feet below the DH on an ILS approach to minimums, with a risk of undershoot.
Other Finding:
1. The cockpit voice recorder (CVR) was returned to service following an intelligibility test that indicated that the first officer’s hot boom microphone intercom channel did not record. Although the first officer voice was recorded by other means, a potential existed for loss of information, which was key to the investigation.
1. A late full flap selection at 300 feet above ground level (agl) likely destabilized the aircraft’s pitch attitude, descent rate and speed in the critical final stage of the precision approach, resulting in an increased descent rate before reaching the runway threshold.
2. After the approach lights were sighted at low altitude, both pilots discontinued monitoring of instruments including the glide slope indicator. A significant deviation below the optimum glide slope in low visibility went unnoticed by the crew until the aircraft descended into the approach lights.
Finding as to Risk:
1. The crew rounded the decision height (DH) figure for the instrument landing system (ILS) approach downward, and did not apply a cold temperature correction factor. The combined error could have resulted in a descent of 74 feet below the DH on an ILS approach to minimums, with a risk of undershoot.
Other Finding:
1. The cockpit voice recorder (CVR) was returned to service following an intelligibility test that indicated that the first officer’s hot boom microphone intercom channel did not record. Although the first officer voice was recorded by other means, a potential existed for loss of information, which was key to the investigation.
Final Report: