Country
Crash of an Embraer EMB-120RT Brasília in Fortaleza: 4 killed
Date & Time:
Oct 21, 1998 at 0851 LT
Registration:
PT-WKH
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Teresina - Fortaleza
MSN:
120-076
YOM:
1988
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
1
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
4
Captain / Total hours on type:
1500.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
1300
Circumstances:
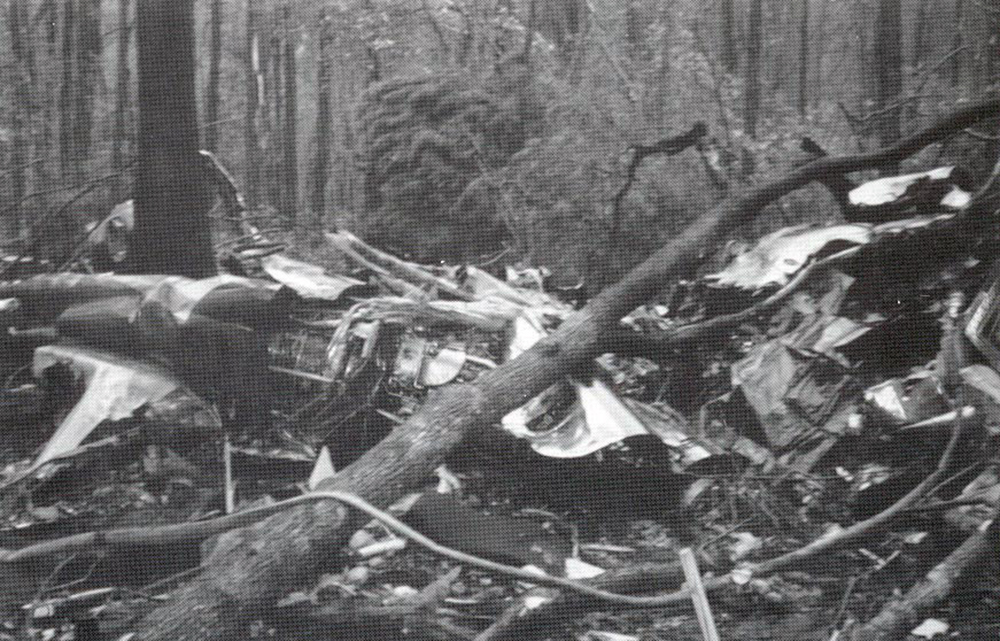
The twin engine aircraft was completing a cargo flight from Teresina to Fortaleza, carrying one passenger, two pilots and a load of 2,5 tons of medicines. On final approach to Fortaleza-Pinto Martins Airport, the aircraft was approaching at an excessive speed when flaps and landing gear were selected down. The aircraft became unstable and the captain who was the pilot-in-command continued the approach and the copilot did not intervene to correct the situation. On final, the thrust levers were positioned below the flight idle position, causing the aircraft to lose speed and to enter a right bank. It struck power cables and eventually crashed onto a house. The aircraft and the house were destroyed. The copilot was seriously injured while both other occupants and one people on the ground were killed. Seven other people on the ground were injured. Few hours later, the copilot died from his injuries.
Probable cause:
The following factors were identified:
- In the individual aspect, there were signs of concern of the crew member with prolonged waiting caused by the local traffic in Fortaleza and by another traffic that was approaching the aerodrome and, because of this, accelerated the procedure of the final approach, descending at high speed and triggering the other operational failures that led to the accident; in the same way, there were signs of excessive self-confidence by the pilot.
- The operator's delay in submitting the requested documentation for the aircraft reduced the credibility of the submitted material. The possibility that the secondary stop was deactivated, despite statements to the contrary by a mechanic, would have been caused by inadequate participation of maintenance personnel in the services performed and by non-compliance with the planned AD.
- There are reports from several pilots about this commander's habits of performing unforeseen procedures, including some that avoided flying with him. It was not researched if the other crew members took this fact to the company's management. The company's response was not researched if it was aware of these operational deviations.
- The pilot misused the resources available in the operation of the aircraft, due to ineffective management of the tasks related to the PF and PNF and the noncompliance with operational rules.
- The PNF did not advise the PF during the approach. The PNF accepted the non-stabilized approach and did not react to reverse the situation.
- The crew made the approach above the glide slope and at high speed; thought inappropriately that it could proceed in those conditions and that there would be ways to reduce the speed and make the landing.
- The crew disobeyed the aircraft's operating rules by performing a destabilized approach outside the envelope recommended by the manufacturer and by placing the power levers below the flight idle position.
- In the individual aspect, there were signs of concern of the crew member with prolonged waiting caused by the local traffic in Fortaleza and by another traffic that was approaching the aerodrome and, because of this, accelerated the procedure of the final approach, descending at high speed and triggering the other operational failures that led to the accident; in the same way, there were signs of excessive self-confidence by the pilot.
- The operator's delay in submitting the requested documentation for the aircraft reduced the credibility of the submitted material. The possibility that the secondary stop was deactivated, despite statements to the contrary by a mechanic, would have been caused by inadequate participation of maintenance personnel in the services performed and by non-compliance with the planned AD.
- There are reports from several pilots about this commander's habits of performing unforeseen procedures, including some that avoided flying with him. It was not researched if the other crew members took this fact to the company's management. The company's response was not researched if it was aware of these operational deviations.
- The pilot misused the resources available in the operation of the aircraft, due to ineffective management of the tasks related to the PF and PNF and the noncompliance with operational rules.
- The PNF did not advise the PF during the approach. The PNF accepted the non-stabilized approach and did not react to reverse the situation.
- The crew made the approach above the glide slope and at high speed; thought inappropriately that it could proceed in those conditions and that there would be ways to reduce the speed and make the landing.
- The crew disobeyed the aircraft's operating rules by performing a destabilized approach outside the envelope recommended by the manufacturer and by placing the power levers below the flight idle position.
Final Report:
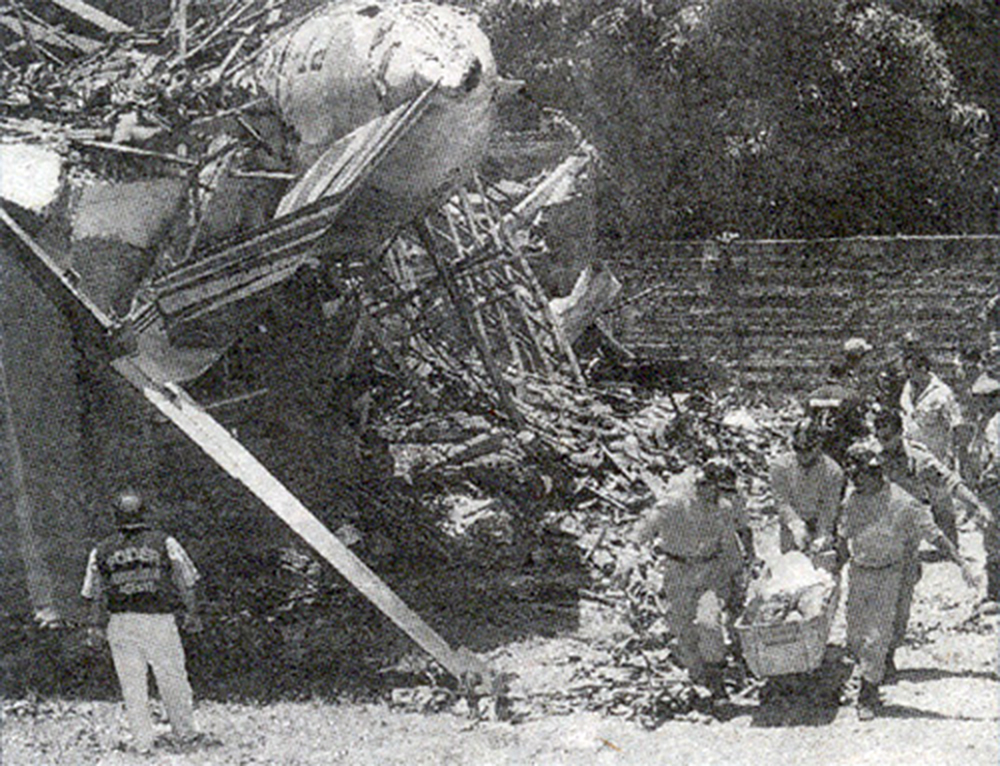
Crash of an Embraer EMB-120RT Brasília in Vilhena
Date & Time:
Mar 3, 1997 at 0044 LT
Registration:
PT-MFC
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Campo Grande - Vilhena
MSN:
120-206
YOM:
1990
Flight number:
PTN126
Crew on board:
3
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
13
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Captain / Total hours on type:
2501.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
1988
Circumstances:
En route from Campo Grande to Vilhena, while in cruising altitude, the crew received the last weather bulletin about Vilhena with conditions below minimums. The copilot (under line check on this flight) suggested to divert to the alternate airport but the captain/instructor preferred to attempt an approach via Echo 1 and the NDB for runway 03. If visual contact would not be established at decision height, the crew would divert to the alternate airport. Then the copilot set the decision height at 2,500 feet which was wrong as the correct decision height was fixed at 2,560 feet. Nor the copilot nor the captain realized this mistake prior to start the descent to Vilhena Airport. On approach, the copilot was told by captain to monitor the horizon. He focused his attention on the horizon and failed to monitor the altimer. On his side, the captain elected to establish a visual contact with the ground and the runway light but is was later confirmed that the city of Vilhena suffered a general blackout. On final, the aircraft descended below MDA then struck trees and crashed less than one km from the runway threshold, bursting into flames. All 16 occupants evacuated safely while the aircraft was destroyed by fire.
Probable cause:
The following findings were identified:
- Poor crew coordination,
- Wrong approach configuration,
- The crew's attention was focused on their respective tasks without monitoring the approach configuration, causing the aircraft to descent below the glide,
- The captain/instructor failed to supervise properly the copilot's manoeuvres,
- No approach briefing,
- Lack of visibility due to a general blackout.
- Poor crew coordination,
- Wrong approach configuration,
- The crew's attention was focused on their respective tasks without monitoring the approach configuration, causing the aircraft to descent below the glide,
- The captain/instructor failed to supervise properly the copilot's manoeuvres,
- No approach briefing,
- Lack of visibility due to a general blackout.
Final Report:

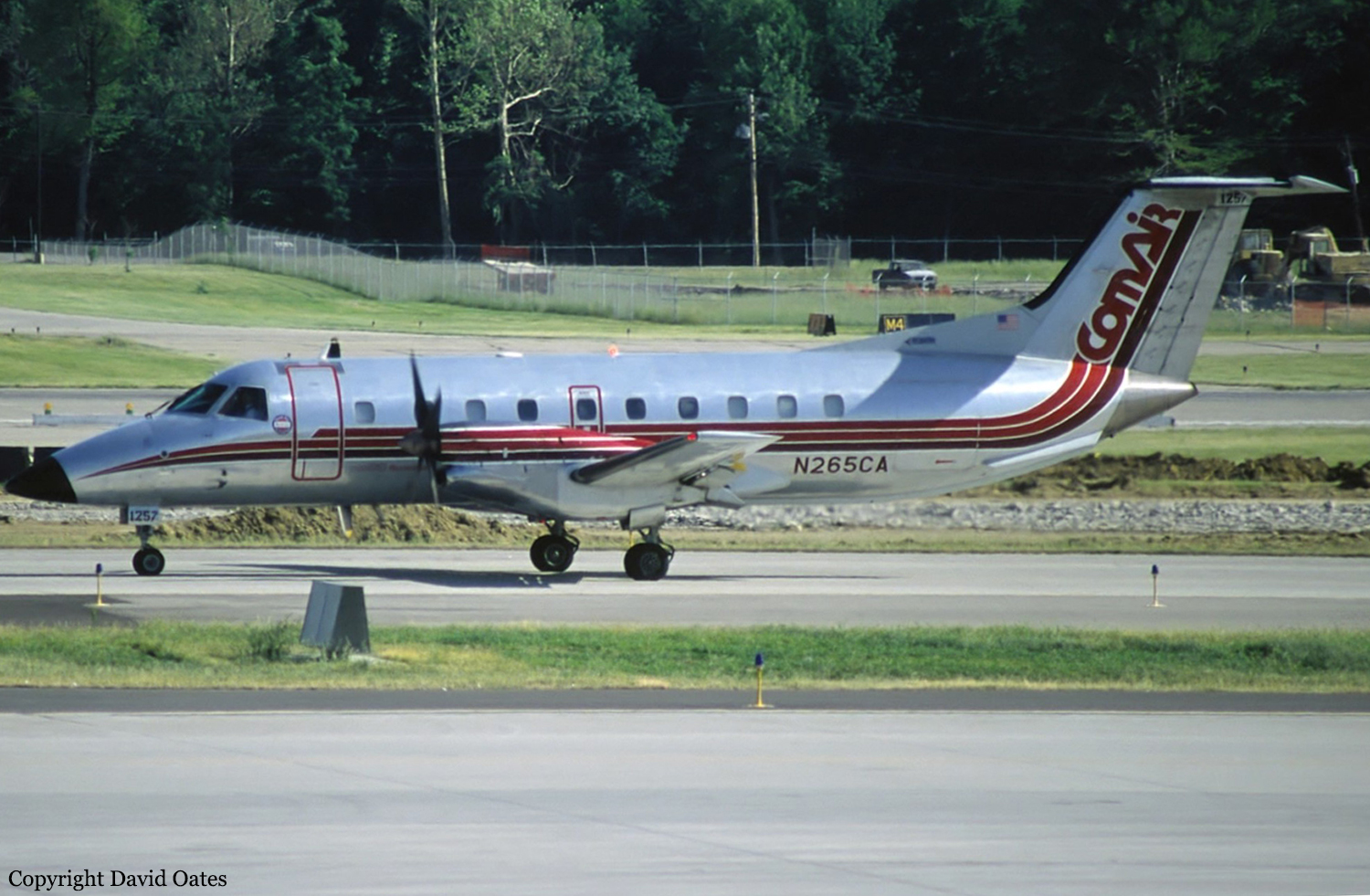
Crash of an Embraer EMB-120 Brasília in Detroit: 29 killed
Date & Time:
Jan 9, 1997 at 1554 LT
Registration:
N265CA
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Cincinnati - Detroit
MSN:
120-257
YOM:
1991
Flight number:
OH3272
Crew on board:
3
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
26
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
29
Captain / Total hours on type:
2302.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
1494
Aircraft flight hours:
12752
Aircraft flight cycles:
12734
Circumstances:
The flight was being vectored for the approach to runway 3R at Detroit Metropolitan Wayne County Airport (DTW) when the aircraft descended and impacted the ground. The aircraft struck the ground in a steep nose-down attitude in a level field in a rural area about 19 nm southwest of DTW. The flight carried 26 passengers and 3 crew members. There were no survivors and the airplane was destroyed by impact forces and a post crash fire. Instrument meteorological conditions prevailed at the time of the accident. The investigation revealed that it was likely that the airplane gradually accumulated a thin, rough glaze/mixed ice coverage on the leading edge deicing boot surfaces, possibly with ice ridge formation on the leading edge upper surface, as the airplane descended from 7,000 feet mean sea level (msl) to 4,000 feet msl in icing conditions, which may have been imperceptible to the pilots. The pilots had been instructed by air traffic control to slow to 150 knots and according to flight data recorder information, the airplane began to show signs of departure from controlled flight as it decelerated from 155 to 156 knots while in a flaps-up configuration. The investigation disclosed that the FAA failed to adopt a systematic and proactive approach to the certification, and operational issues of turbopropeller-driven transport airplane icing. The icing certification process has been inadequate because it has not required manufacturers to demonstrate the airplane's flight handling and stall characteristics under a sufficiently realistic range of adverse ice accretion/flight handling conditions. The aircraft manufacturer had issued a revision in April, 1996 to the approved flight manual which included activation of the leading edge deicing boots at the first sign of ice formation. The airplane operator did not incorporate the procedure, because it was contrary to the company's trained procedures and practices and of the belief that enacting the changes would result in potentially unsafe operation. Investigators' discussion with management personnel at each of the seven U.S.-based operators of the aircraft indicated that at the time of the accident only two of these operators had changed their procedures to reflect the information in the revision. The FAA, at the time of the accident, did not require manufacturers of all turbine-engine driven airplanes to publish minimum airspeed information for various flap configurations and phases and conditions of flight. During Safety Board investigators postaccident interviews with company pilots, there were inconsistent answers on the complex and varied minimum airspeed requirements established by the company for both icing and nonicing conditions. It was also noted that the pilots uncertainty of the appropriate airspeeds might have been associated with the language used, the different airspeeds and criteria contained in the guidance, the company's methods of distribution, and the company's failure t o incorporate the guidance as a formal, permanent revision to the flight standards manual.
Probable cause:
The Federal Aviation Administration's (FAA) failure to establish adequate aircraft certification standards for flight in icing conditions, the FAA's failure to ensure that at Centro Tecnico Aeroespacial/FAA-approved procedure for the accident airplane's deice system operation was implemented by U.S.-based air carriers, and the FAA's failure to require the establishment of
adequate minimum airspeeds for icing conditions, which led to the loss of control when the airplane accumulated a thin, rough, accretion of ice on its lifting surfaces. Contributing to the
accident were the flightcrew's decision to operate in icing conditions near the lower margin of the operating airspeed envelope (with flaps retracted) and Comair's failure to establish and adequately disseminate unambiguous minimum airspeed values for flap configurations and for flight in icing conditions.
adequate minimum airspeeds for icing conditions, which led to the loss of control when the airplane accumulated a thin, rough, accretion of ice on its lifting surfaces. Contributing to the
accident were the flightcrew's decision to operate in icing conditions near the lower margin of the operating airspeed envelope (with flaps retracted) and Comair's failure to establish and adequately disseminate unambiguous minimum airspeed values for flap configurations and for flight in icing conditions.
Final Report:
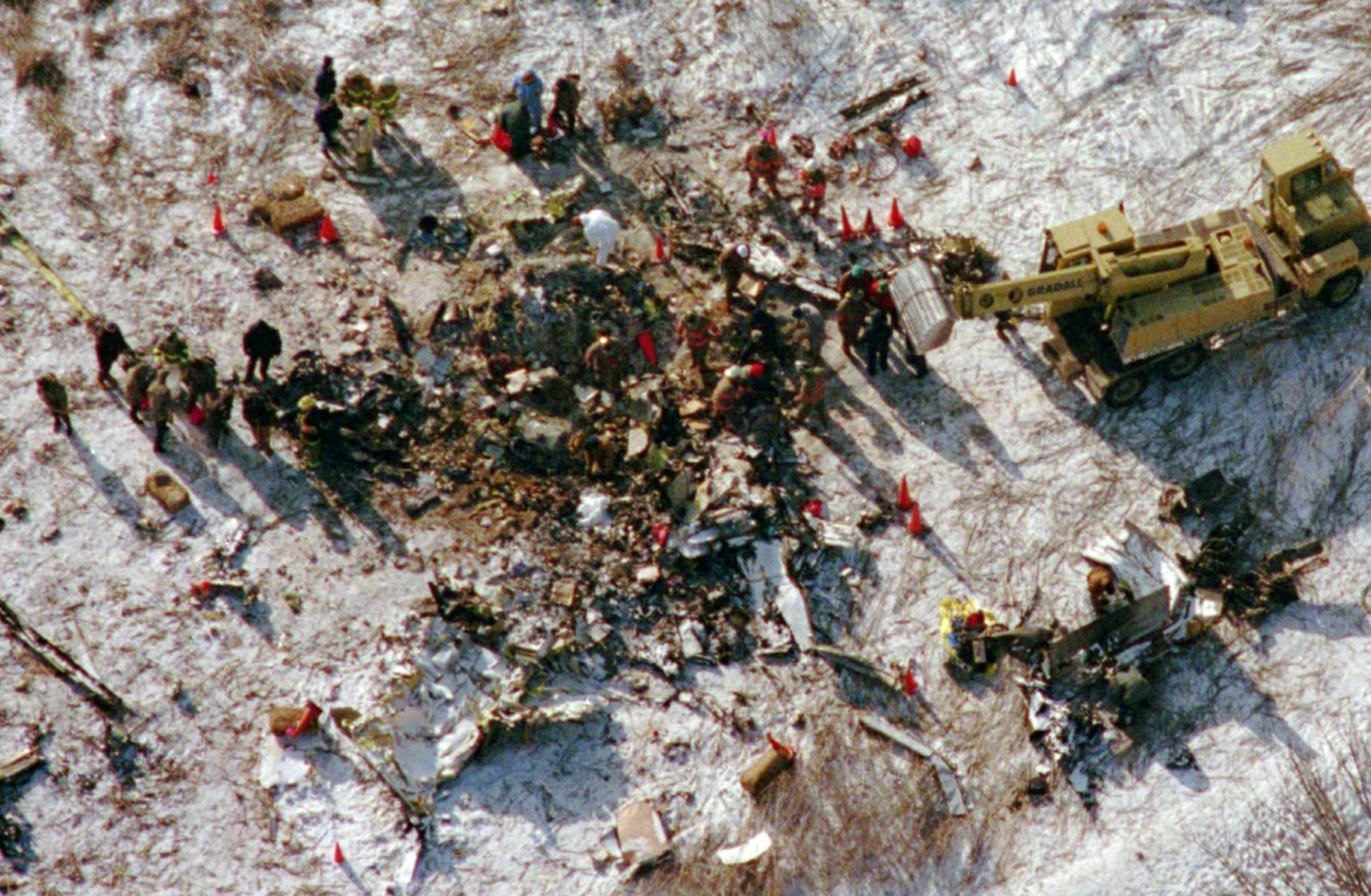
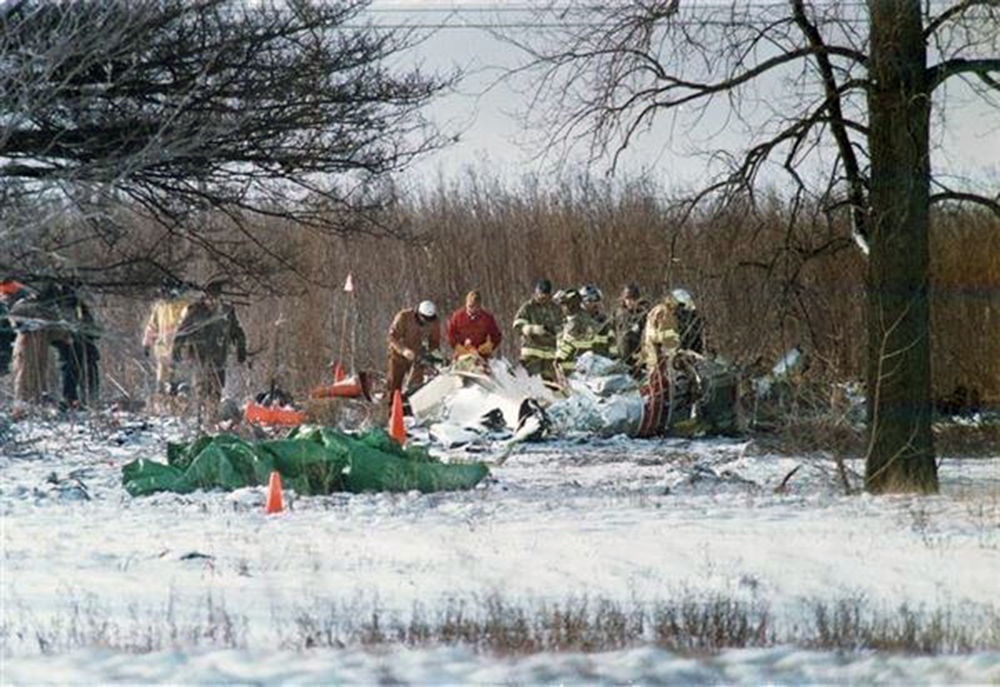
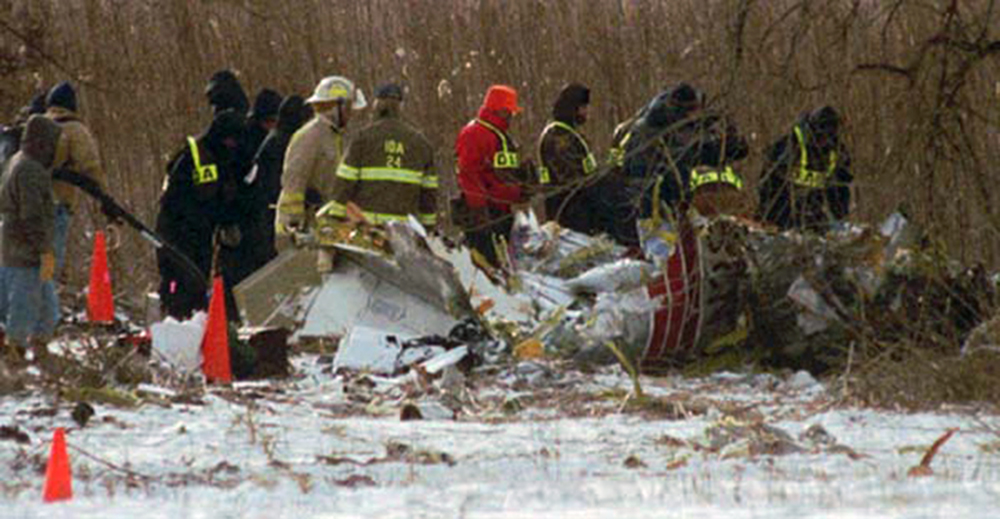




Crash of an Embraer EMB-120RT Brasília in Carrollton: 8 killed
Date & Time:
Aug 21, 1995 at 1253 LT
Registration:
N256AS
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Atlanta - Gulfport
MSN:
120-122
YOM:
1989
Flight number:
EV529
Crew on board:
3
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
26
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
8
Captain / Total hours on type:
7374.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
363
Aircraft flight hours:
17151
Aircraft flight cycles:
18171
Circumstances:
Atlantic Southeast Airline Flight 529 was climbing through 18,000 feet, when a blade from the left propeller separated. This resulted in distortion of the left engine nacelle, excessive drag, loss of wing lift, and reduced directional control. The degraded performance resulted in a forced landing. While landing, the airplane passed through trees, impacted the ground, and was further damaged by post impact fire. An exam of the left propeller revealed the blade had failed due to a fatigue crack that originated from multiple corrosion pits in the taper bore surface of the blade spar. The crack had propagated toward the outside of the blade and around both sides of the taper bore. Due to 2 previous blade failures (separations), a borescope inspection procedure had been developed by Hamilton Standard to inspect returned blades (that had rejectable ultrasonic indications) for evidence of cracks, pits and corrosion. The accident blade was one of 490 rejected blades that had been sent to Hamilton Standard for further evaluation and possible repair. Maintenance technicians, who inspected the blade, lacked proper NDI familiarization training and specific equipment to identify the corrosion that resulted in fatigue. The captain and seven passengers were killed.
Probable cause:
The in-flight fatigue fracture and separation of a propeller blade resulting in distortion of the left engine nacelle, causing excessive drag, loss of wing lift, and reduced directional control of
the airplane. The fracture was caused by a fatigue crack from multiple corrosion pits that were not discovered by Hamilton Standard because of inadequate and ineffective corporate inspection and repair techniques, training, documentation, and communications. Contributing to the accident was Hamilton Standard's and FAA's failure to require recurrent on-wing ultrasonic inspections of the affected propellers. Contributing to the severity of the accident was the overcast cloud ceiling at the accident site.
the airplane. The fracture was caused by a fatigue crack from multiple corrosion pits that were not discovered by Hamilton Standard because of inadequate and ineffective corporate inspection and repair techniques, training, documentation, and communications. Contributing to the accident was Hamilton Standard's and FAA's failure to require recurrent on-wing ultrasonic inspections of the affected propellers. Contributing to the severity of the accident was the overcast cloud ceiling at the accident site.
Final Report:
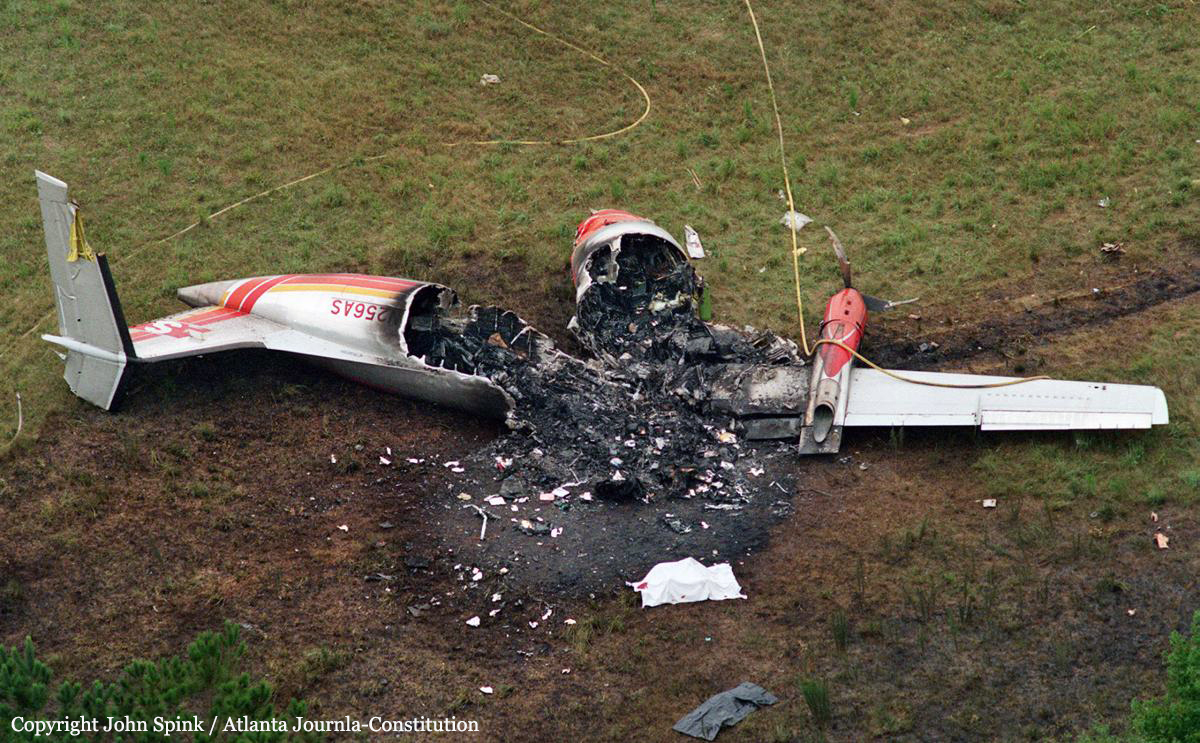
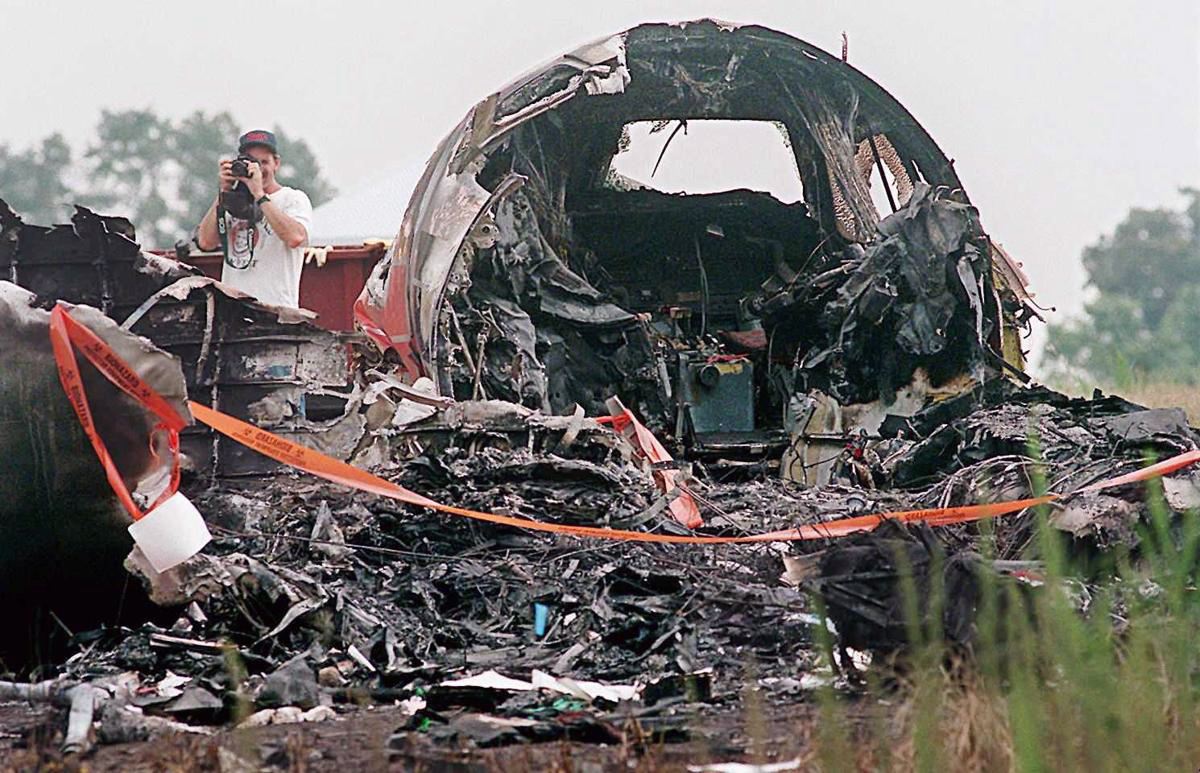
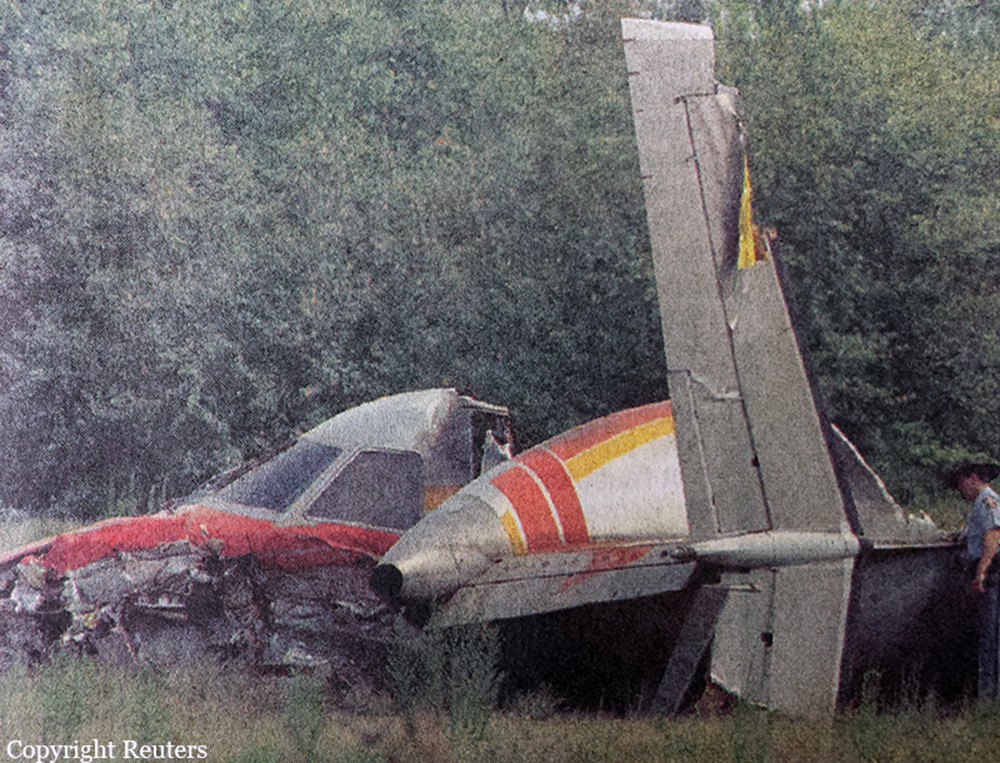
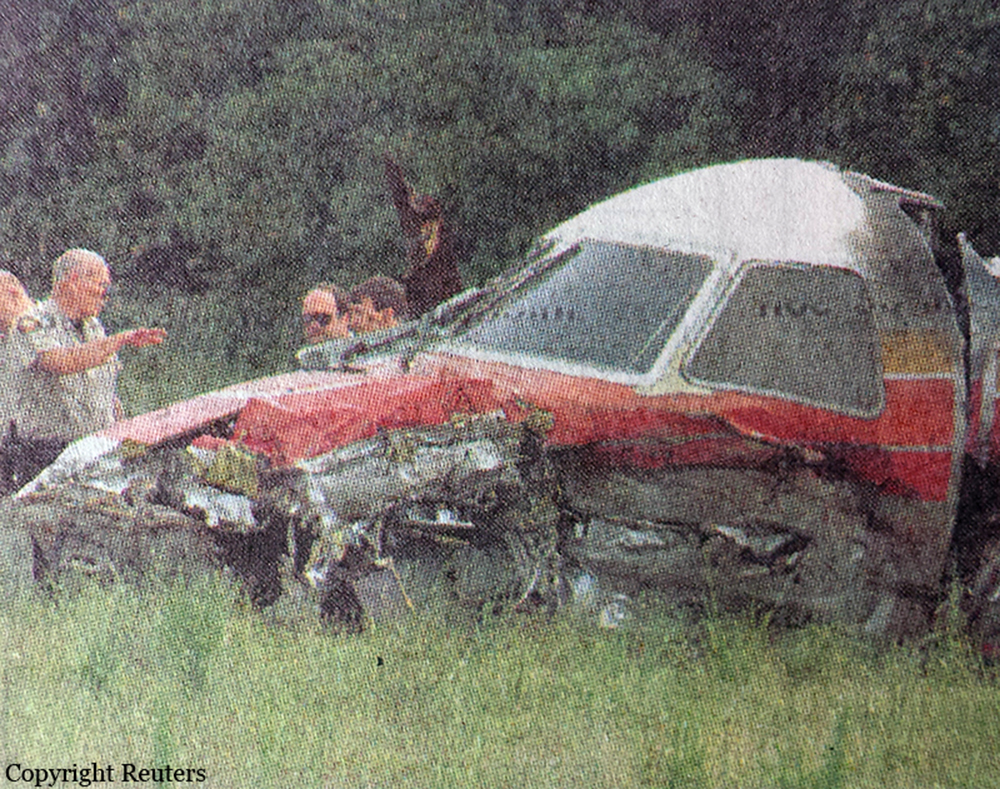






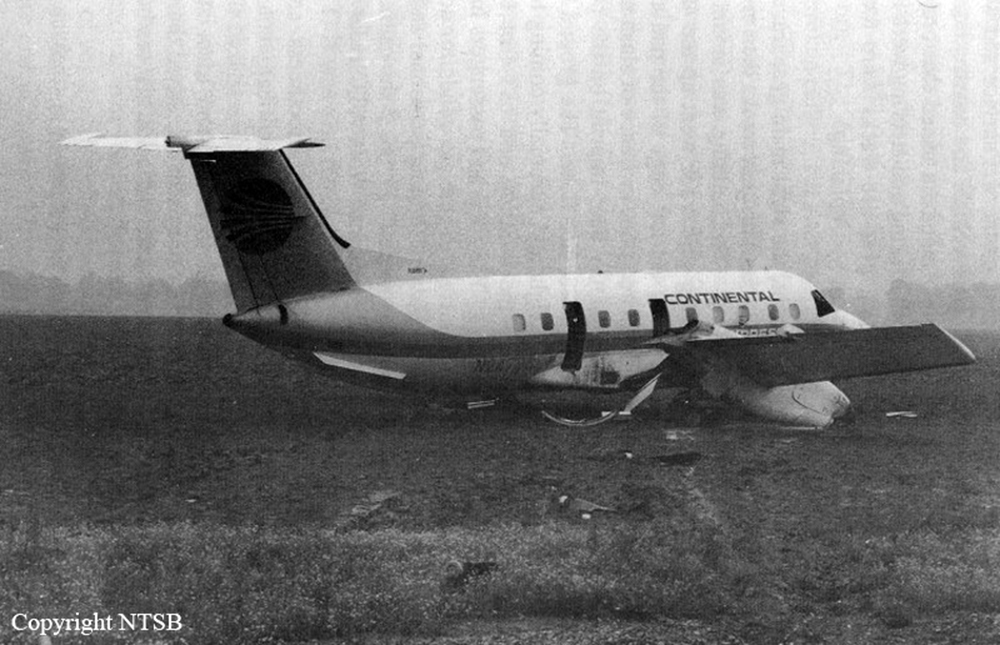
Crash of an Embraer EMB-120RT Brasília in Pine Bluff
Date & Time:
Apr 29, 1993 at 1555 LT
Registration:
N24706
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Little Rock - Houston
MSN:
120-093
YOM:
1988
Flight number:
CA2733
Crew on board:
3
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
27
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Captain / Total hours on type:
2600.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
700
Aircraft flight hours:
10398
Circumstances:
In climb, captain (pic) increased pitch, when flight attendant (f/a) entered cockpit and suggested faster climb, so she could begin cabin service. Autoflight was set in pitch and heading modes, contrary to company policy. Pic and f/a had non- pertinent conversation for 4.5 min, while 1st officer (f/o) was making log entries. Airplane stalled in IMC at 17,400 feet. Initial recovery was at 6,700 feet after f/o lower gear, then due to improper recovery, 2nd stall occurred and recovery was at 5,500 feet. Left propeller shed 3 blades, left engine cowling separated, left engine was shut down in descent. Level flight could not be maintained and forced landing was made at closed airport. Pic overshot final turn due to controllability problems and landed fast with 1,880 feet of wet runway remaining. Airplane hydroplaned off runway and was further damaged. Crew got limited sleep during 3 day trip, though rest periods available. Freezing level near 11,500 feet, clouds tops to 21,000 feet with potential for icing to 19,000 feet. No pre-accident malfunction was found.
Probable cause:
The captain's failure to maintain professional cockpit discipline, his consequent inattention to flight instruments and ice accretion, and his selection of an improper autoflight vertical mode, all of which led to an aerodynamic stall, loss of control, and a forced landing. Factors contributing to the accident were: poor crew discipline, including flightcrew coordination before the stall and the flightcrew's inappropriate actions to recover from the loss of control. Also contributing to the accident was fatigue induced by the flightcrew's failure to properly manage provided rest periods.
Final Report:


Crash of an Embraer EMB-120RT Brasília in Eagle Lake: 14 killed
Date & Time:
Sep 11, 1991 at 1003 LT
Registration:
N33701
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Laredo - Houston
MSN:
120-077
YOM:
1987
Flight number:
CO2574
Crew on board:
3
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
11
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
14
Captain / Total hours on type:
2468.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
1066
Aircraft flight hours:
7229
Aircraft flight cycles:
10009
Circumstances:
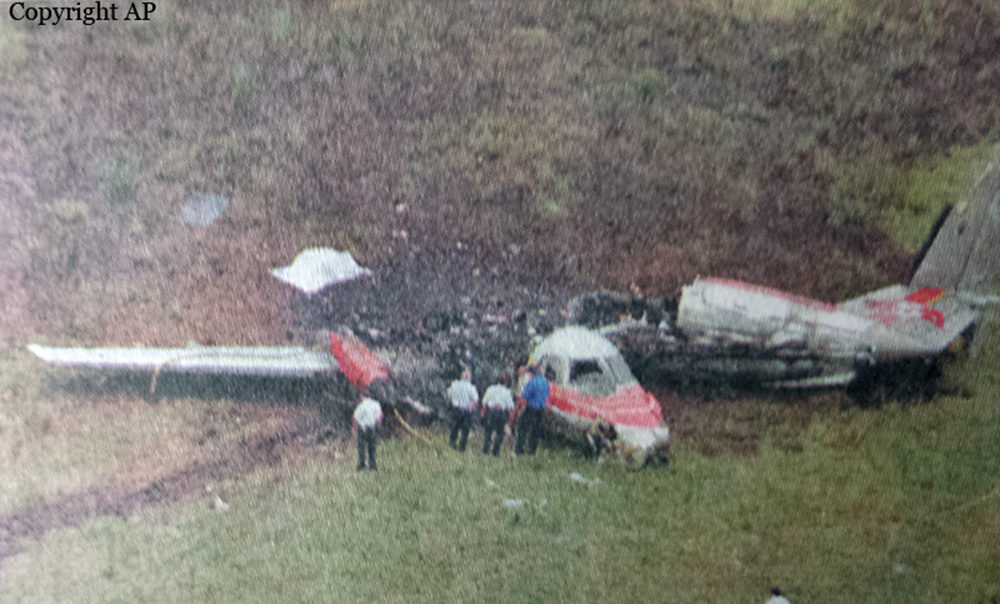
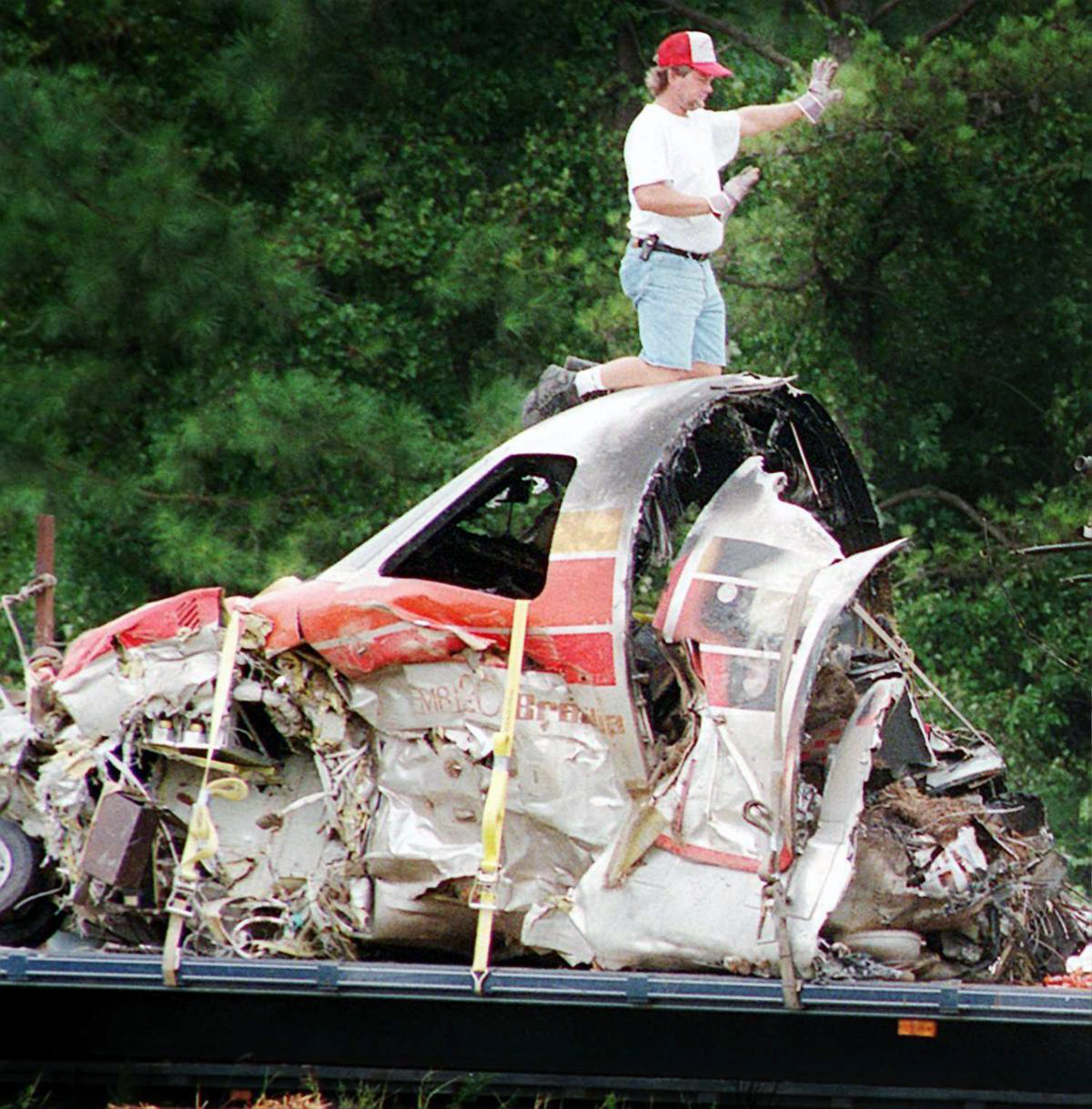
The airplane broke up in flight while descending from FL240. The horizontal stabilizer, or top of the T-type tail, had separated from the fuselage before ground impact. Examination revealed that the 47 screw fasteners that would have attached the upper surface of the leading edge assembly for the left side of the horizontal stabilizer were missing. They had been removed the night before during scheduled maintenance. Investigation revealed that there was a lack of compliance with the FAA-approved general maintenance manual procedures by the mechanics, inspectors, and supervisors responsible for assuring the airworthiness of the airplane the night before the accident. In addition, routine surveillance of the continental express maintenance department by the FAA was inadequate and did not detect deficiencies, such as those that led to this accident. All 14 occupants were killed.
Probable cause:
The failure of continental express maintenance and inspection personnel to adhere to proper maintenance and quality assurance procedures for the airplane's horizontal stabilizer deice boots that led to the sudden in-flight loss of the partially secured left horizontal stabilizer leading edge and the immediate severe nose down pitchover and breakup of the airplane. Contributing to the cause of the accident was the failure of continental express management to ensure compliance with the approved maintenance procedures, and the failure of the faa surveillance to detect and verify compliance with approved procedures.
Final Report:
Crash of an Embraer EMB-120RT Brasilía in Brunswick: 23 killed
Date & Time:
Apr 5, 1991 at 1451 LT
Registration:
N270AS
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Atlanta - Brunswick
MSN:
120-218
YOM:
1990
Flight number:
EV2311
Crew on board:
3
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
20
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
23
Captain / Total hours on type:
5720.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
2795
Aircraft flight hours:
816
Aircraft flight cycles:
845
Circumstances:
Witnesses reported that the airplane suddenly turned or rolled left until the wings were perpendicular to the ground. The airplane then fell in a nose-down attitude. Examination of the left propeller components indicated a blade angle of about 3°, while the left propeller control unit (pcu) ballscrew position was consistent with a commanded blade angle of 79.2°. Extreme wear on the pcu quill spline teeth, which normally engaged the titanium-nitrided splines of the propeller transfer tube, was found. The titanium-nitrided surface was much harder and rougher than the nitrided surface of the quill. Therefore, the transfer tube splines acted like a file and caused abnormal wear of the gear teeth on the quill. Wear of the quill was not considered during the certification of the propeller system. The aircraft was totally destroyed upon impact and all 23 occupants were killed, among them John Goodwin Tower, Senator of Texas and the astronaut Manley Sonny Carter.
Probable cause:
The loss of control in flight as a result of a malfunction of the left engine propeller control unit which allowed the propeller blade angles to go below the flight idle position. Contributing to the accident was the deficient design of the propeller control unit by hamilton standard and the approval of the design by the federal aviation administration. The design did not correctly evaluate the failure mode that occurred during this flight, which resulted in an uncommanded and uncorrectable movement of the blades of the airplane's left propeller below the flight idle position.
Final Report: