Circumstances:
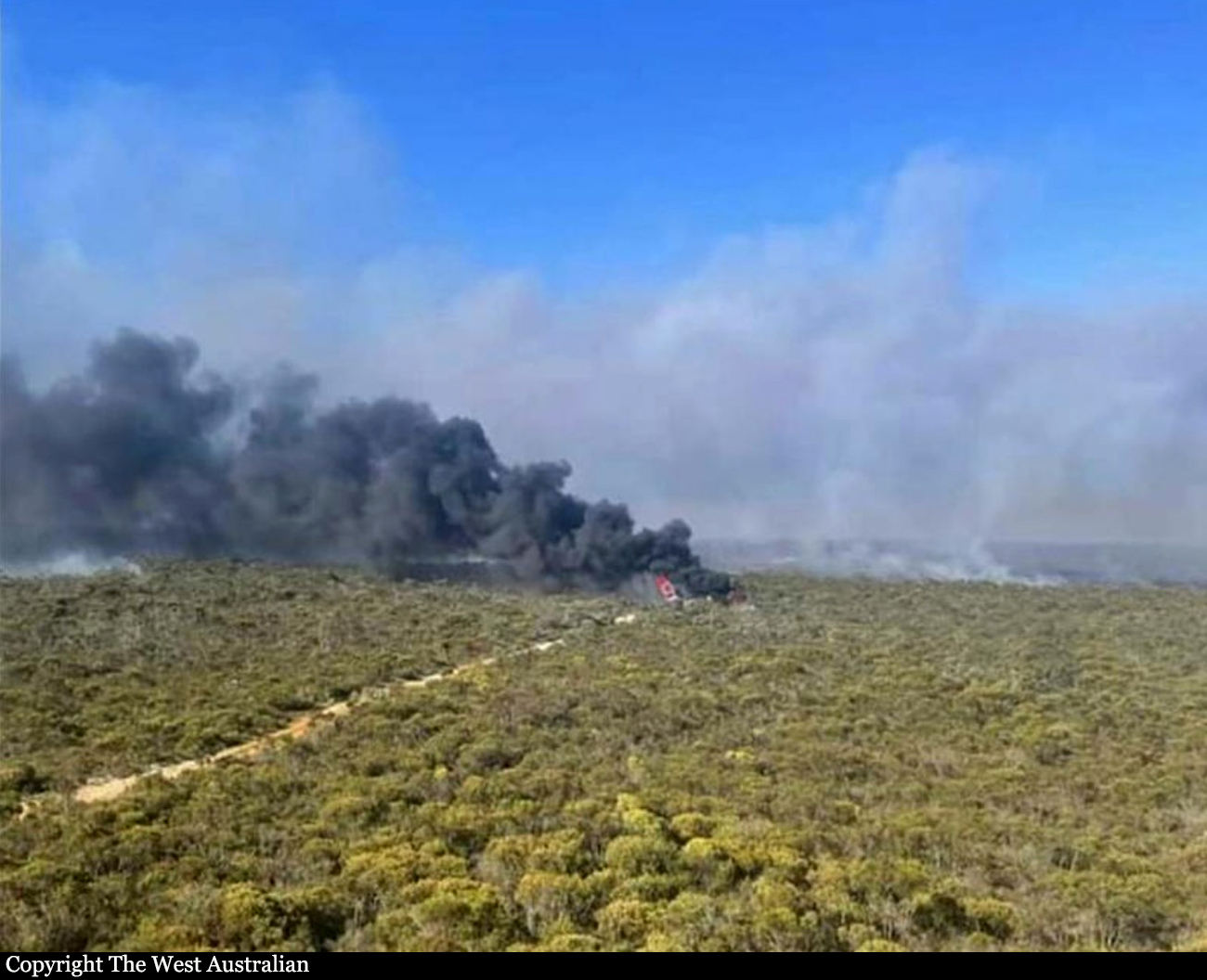
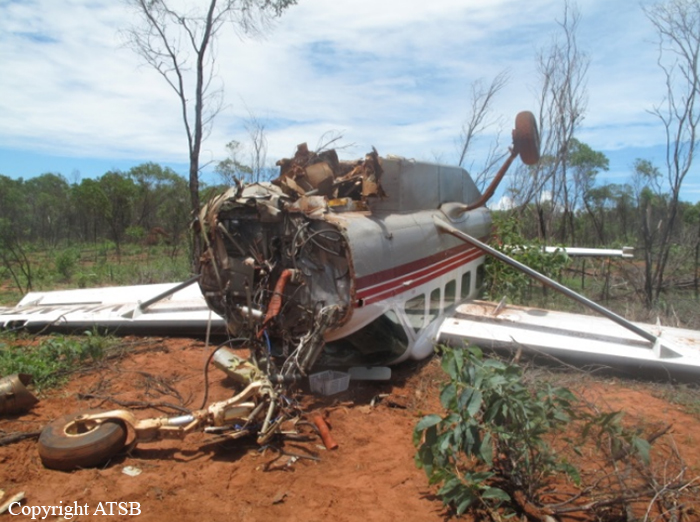
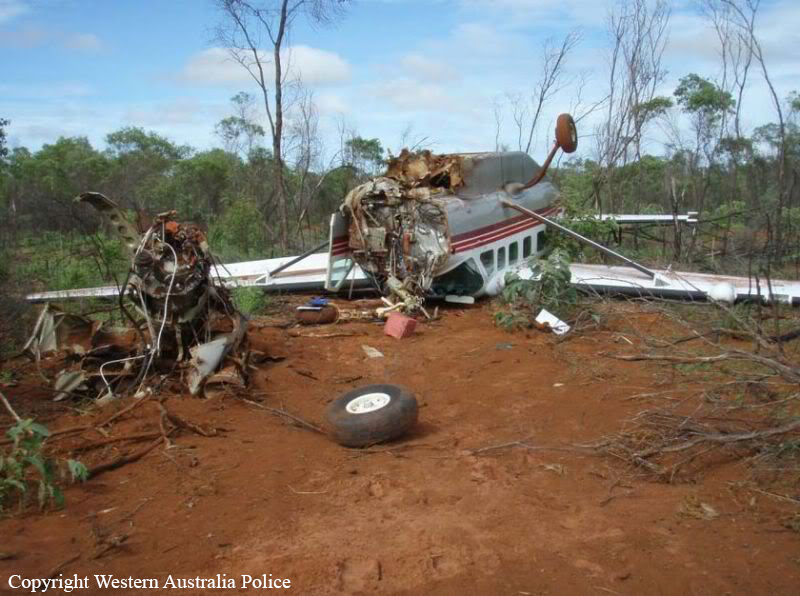
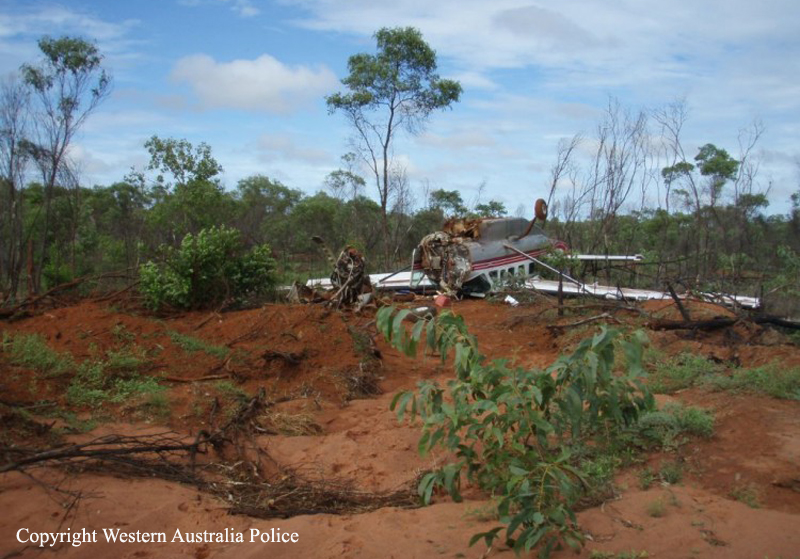
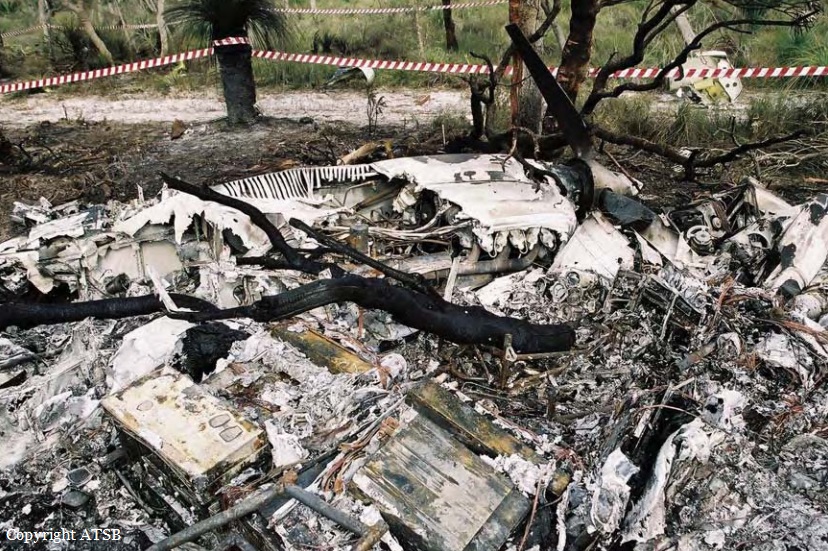
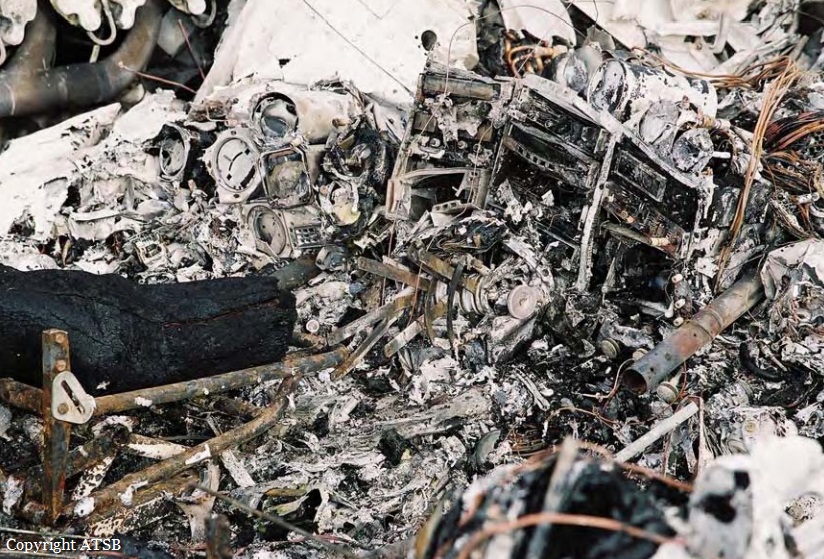
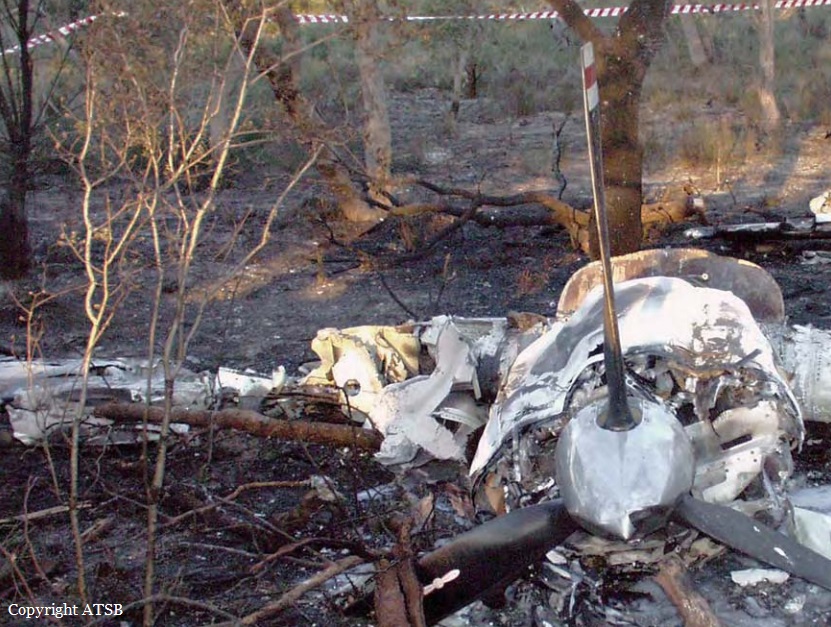
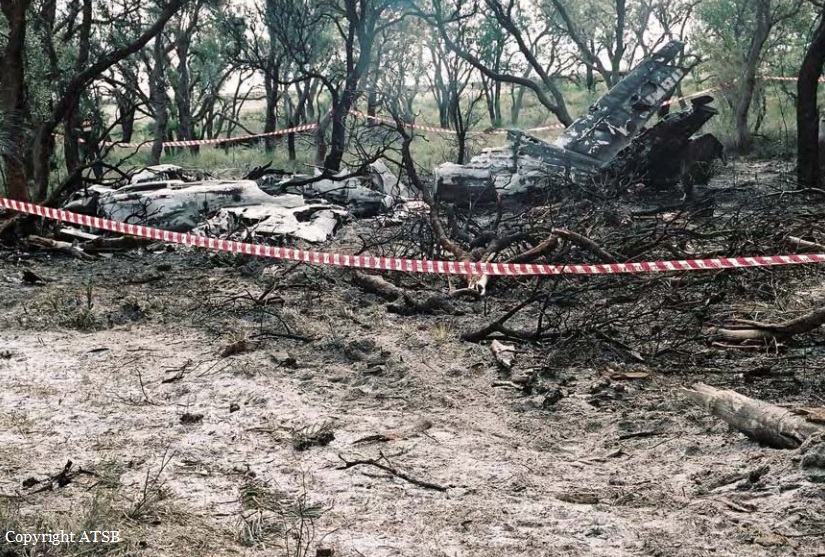
On 22 April 2017, a Gippsland Aeronautics GA-8 aircraft, registered VH-AJZ, was being used to conduct incendiary bombing aerial work operations in the Prince Regent River area of northern Western Australia (WA). On board were a pilot, a navigator seated in the co-pilot seat and a bombardier in the rear of the aircraft cabin. While conducting the incendiary bombing operations, the bombardier advised the pilot that he was suffering from motion sickness. The pilot elected to land at Gibb River aircraft landing area (ALA), WA, to take a lunch break and provide the bombardier with time to recover from the motion sickness. At about 1255 Western Standard Time (WST), the aircraft landed on runway 07 at Gibb River. During the landing roll, the engine failed. The aircraft had sufficient momentum to enable the pilot to turn the aircraft around on the runway and begin to taxi to the parking area at the western end of runway 07. Shortly after turning around, the aircraft came to rest on the runway. The pilot attempted to restart the engine, but the engine did not start. The pilot waited about 10–20 seconds before again attempting to restart the engine. While attempting the second restart of the engine, the pilot heard a loud noise similar to that of a backfire. The navigator then observed flames and smoke coming from around the front of the engine and immediately notified the pilot. After being notified of the fire, the pilot immediately shut down the engine and switched off the aircraft electrical system. As the pilot switched off the aircraft electrical system, the navigator located the aircraft fire extinguisher and evacuated from the aircraft through the co-pilot door. After evacuating from the aircraft, the navigator observed fire on the aircraft nose wheel. The navigator had difficulty preparing the fire extinguisher for use and was unable to discharge the fire extinguisher onto the fire. While the navigator was attempting to extinguish the fire, the pilot exited the aircraft through the pilot door and assisted the bombardier to exit the aircraft. After assisting the bombardier, the pilot moved to the front of the aircraft to assist the navigator with the firefighting. The pilot was able to activate the fire extinguisher and extinguished the fire on the nose wheel. The pilot observed fire continuing to burn within the engine compartment. Due to the heat of the fire, the pilot was unable to access the engine compartment to extinguish this fire. The pilot determined that no more could be done to contain the fire, and therefore, the pilot, navigator and bombardier moved clear of the aircraft to a safe location as the fire continued. The crew members were not injured. As a result of the fire, the aircraft was destroyed.
Probable cause:
These findings should not be read as apportioning blame or liability to any particular organisation or individual.
- The cause of the engine failure and fire could not be determined.
- After the fire was identified, two steps in the emergency procedure were omitted. This included not closing the fuel shutoff valve, which likely resulted in the fire not being extinguished and subsequently intensifying.