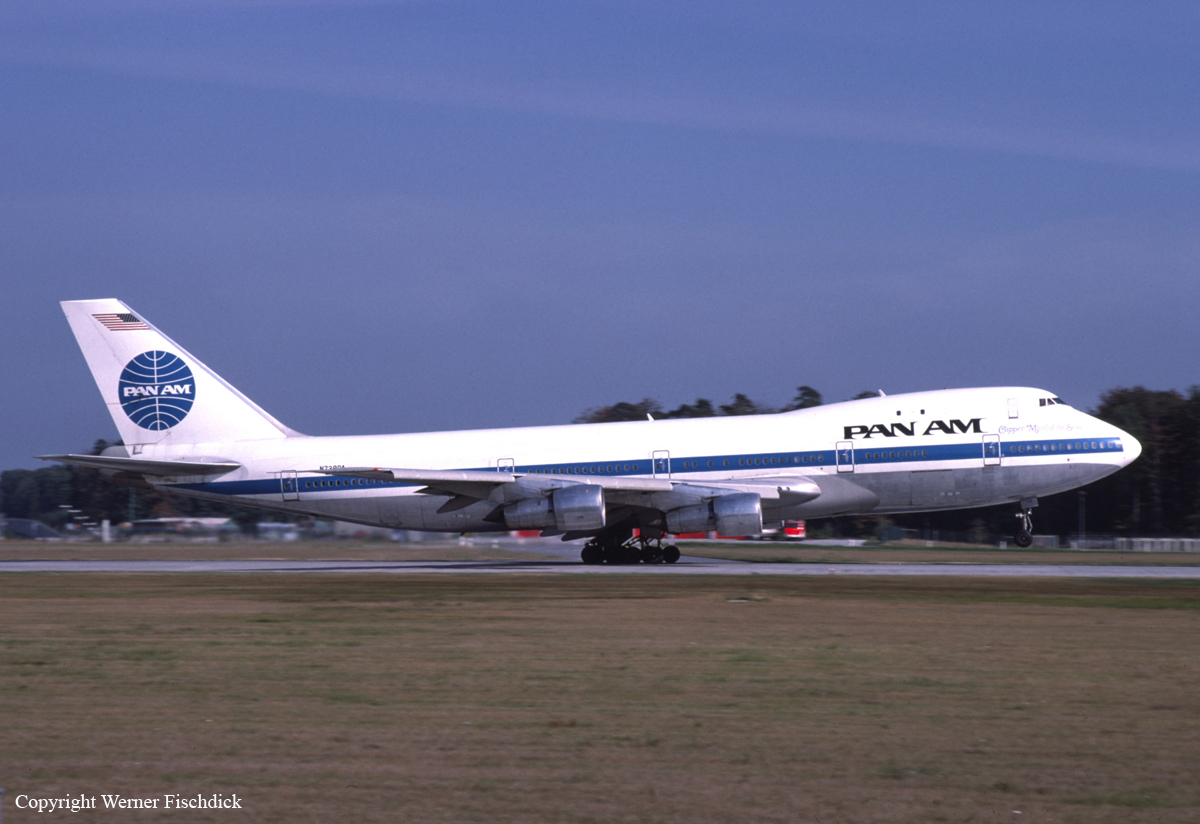
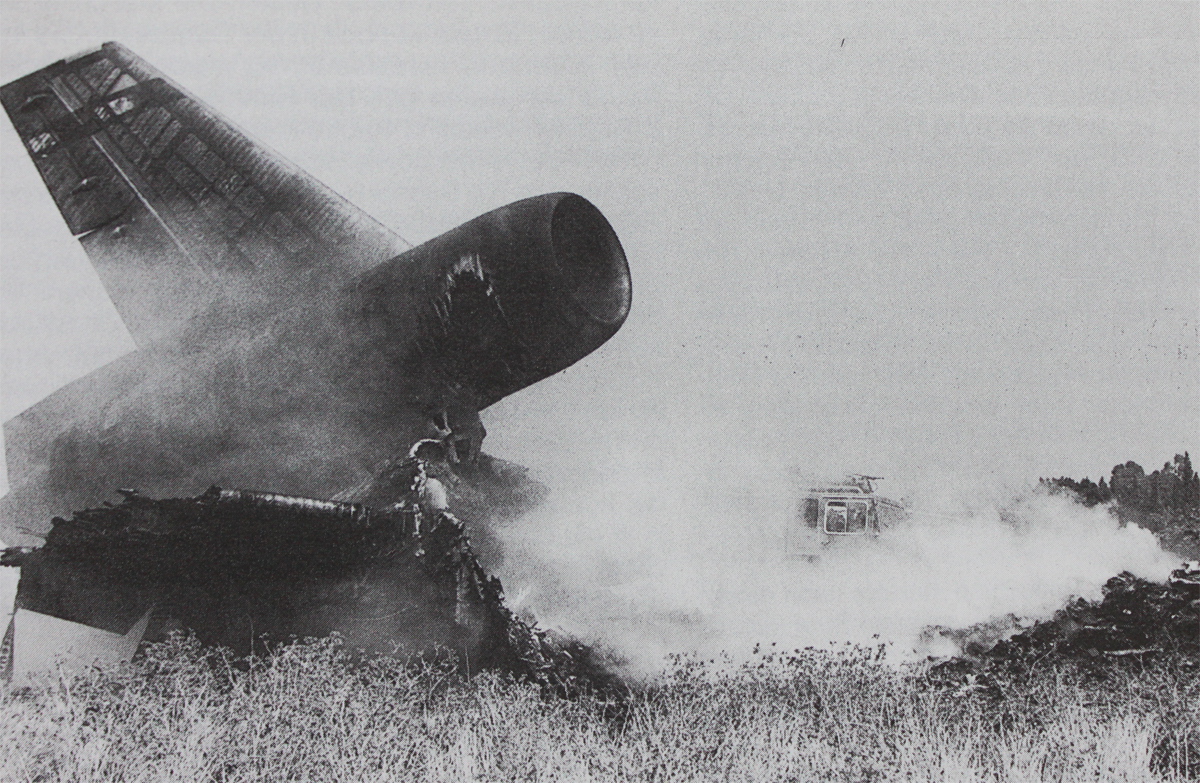
Crash of a Boeing 747-121A in Lockerbie: 270 killed
Date & Time:
Dec 21, 1988 at 1903 LT
Registration:
N739PA
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
London - New York
MSN:
19646
YOM:
1970
Flight number:
PA103
Crew on board:
16
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
243
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
270
Captain / Total hours on type:
4107.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
5517
Aircraft flight hours:
72464
Aircraft flight cycles:
16497
Circumstances:
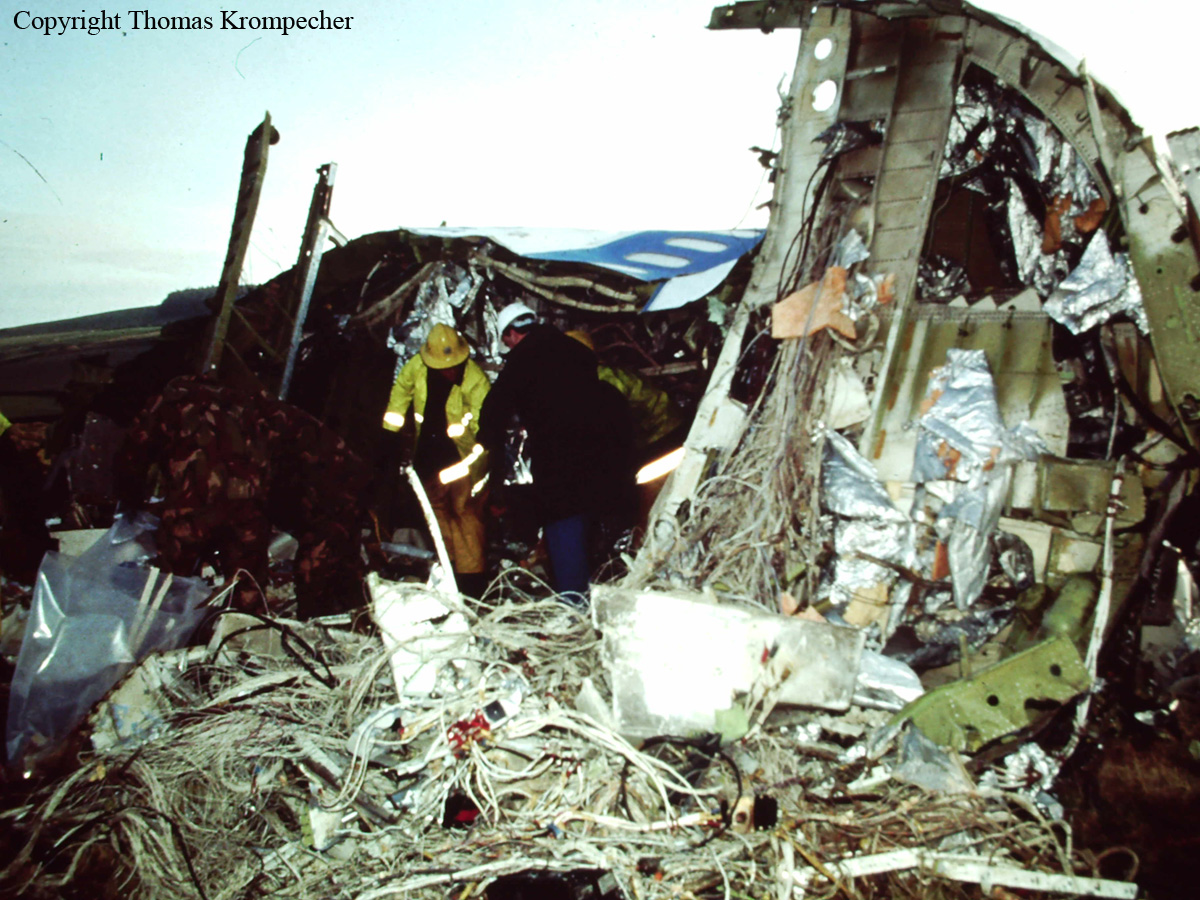
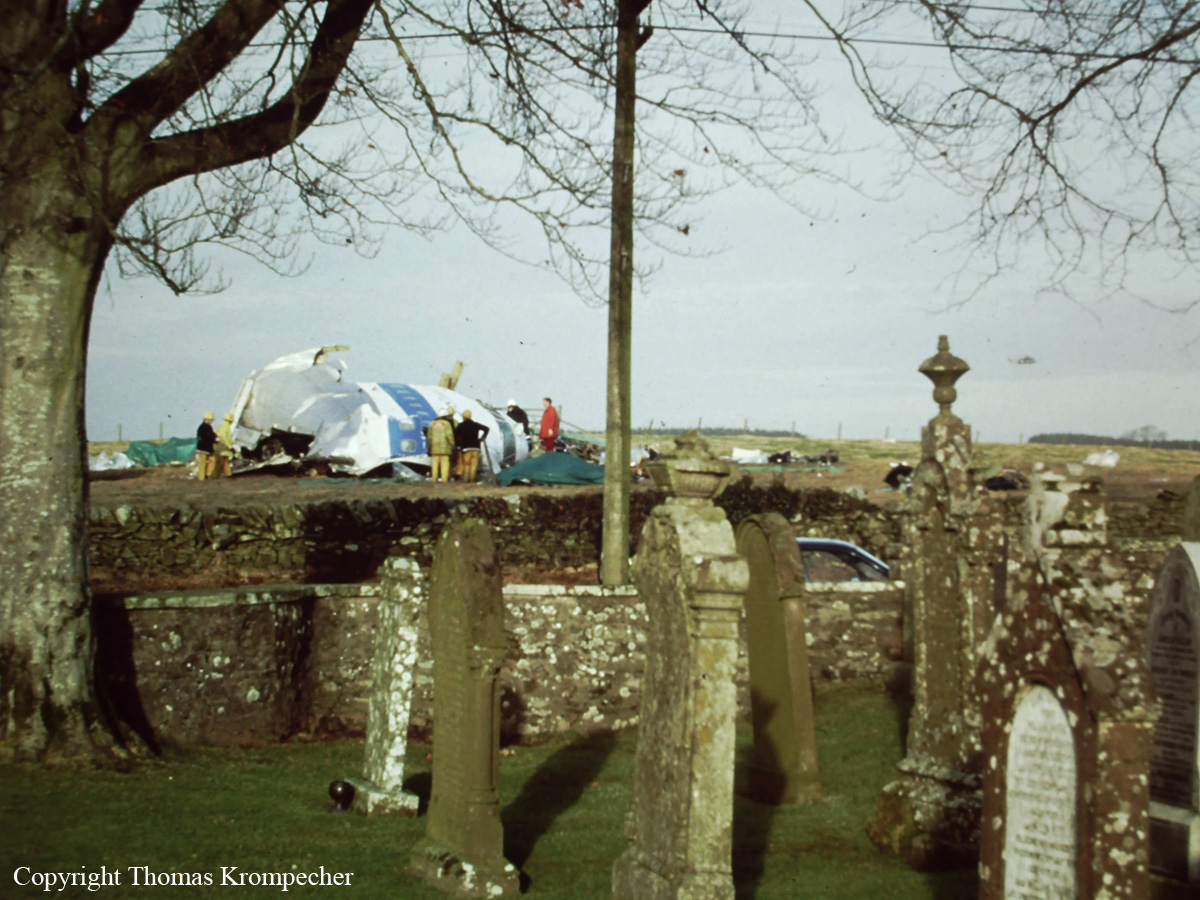
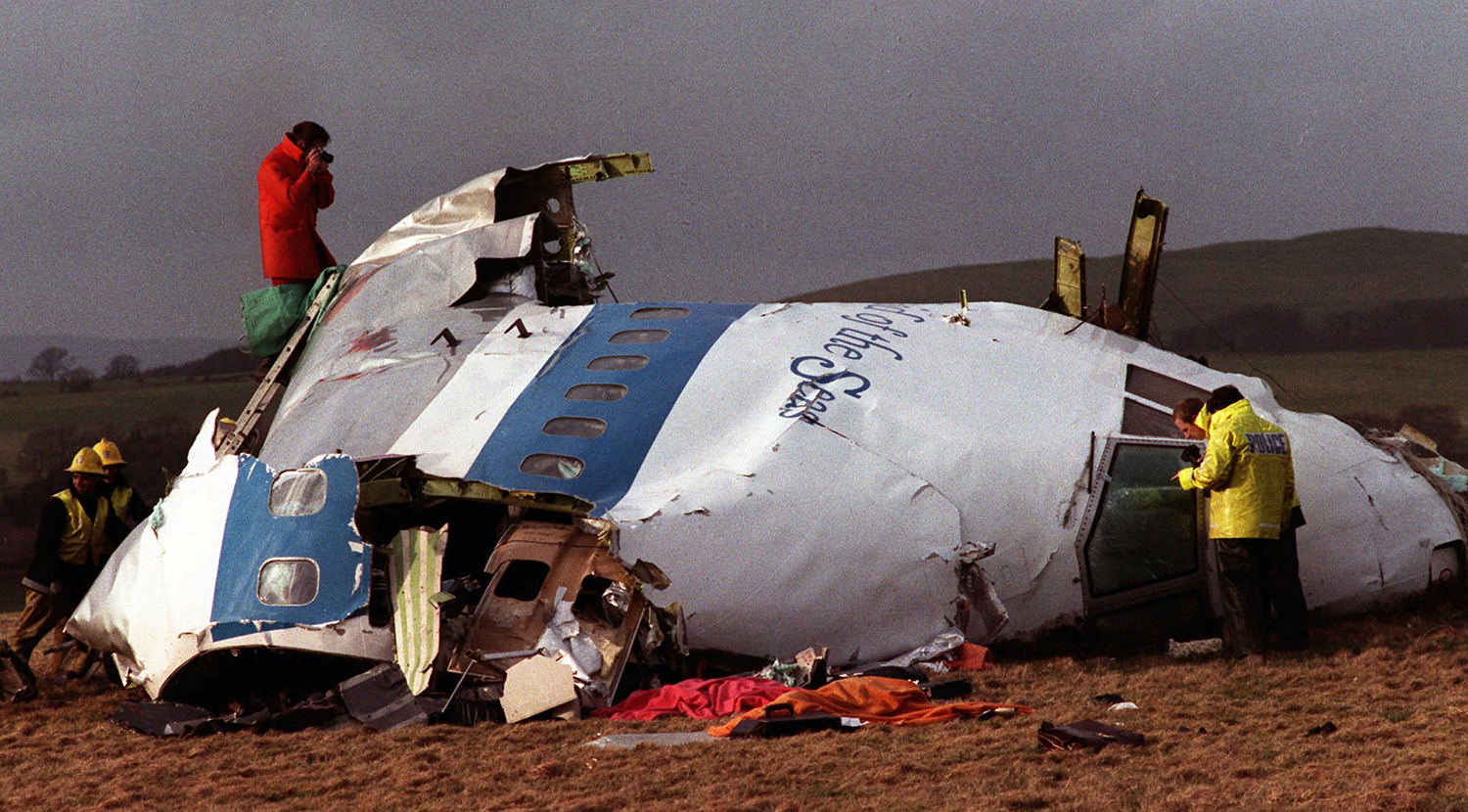
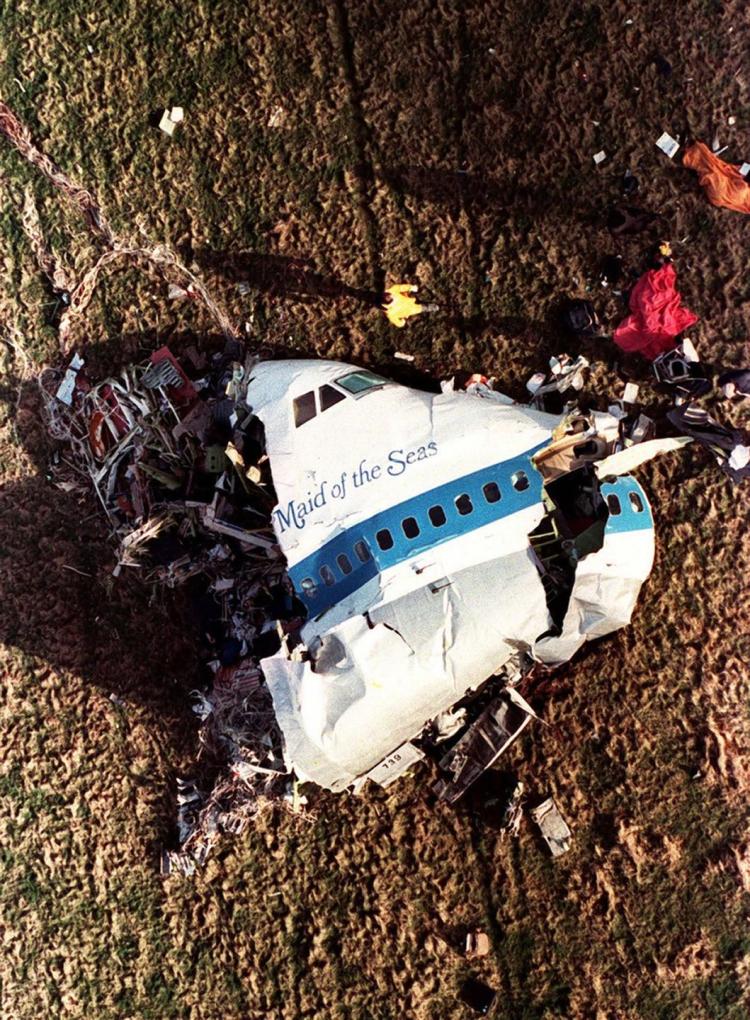
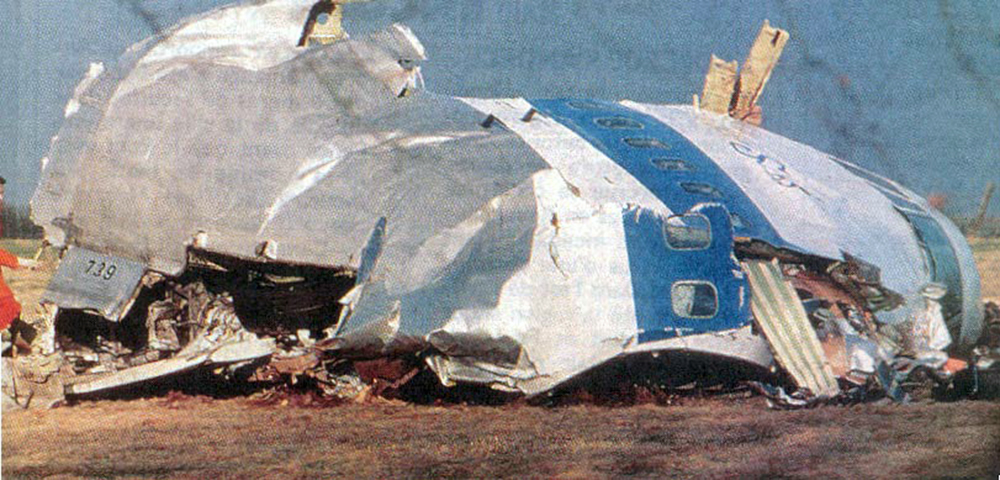
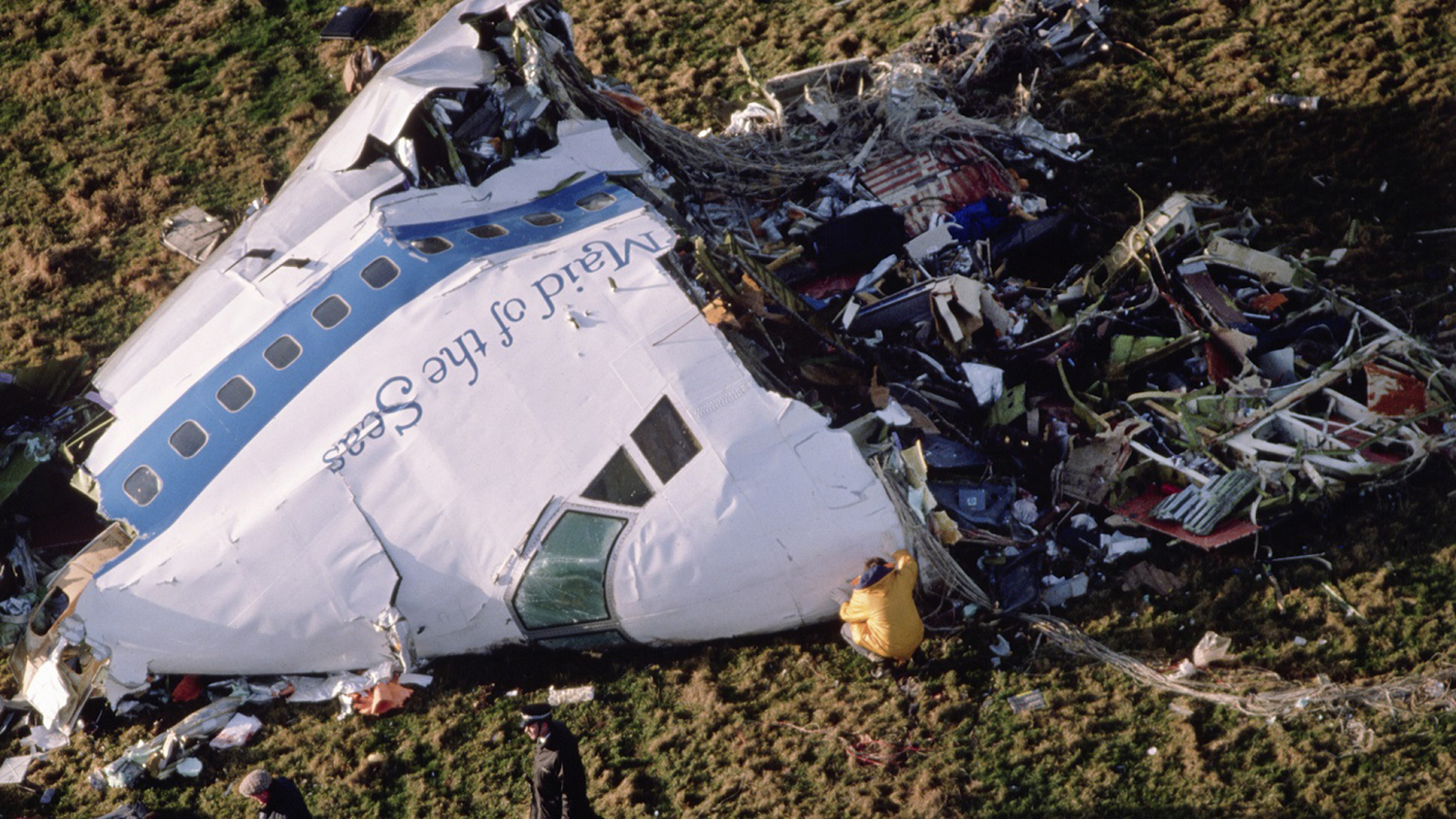
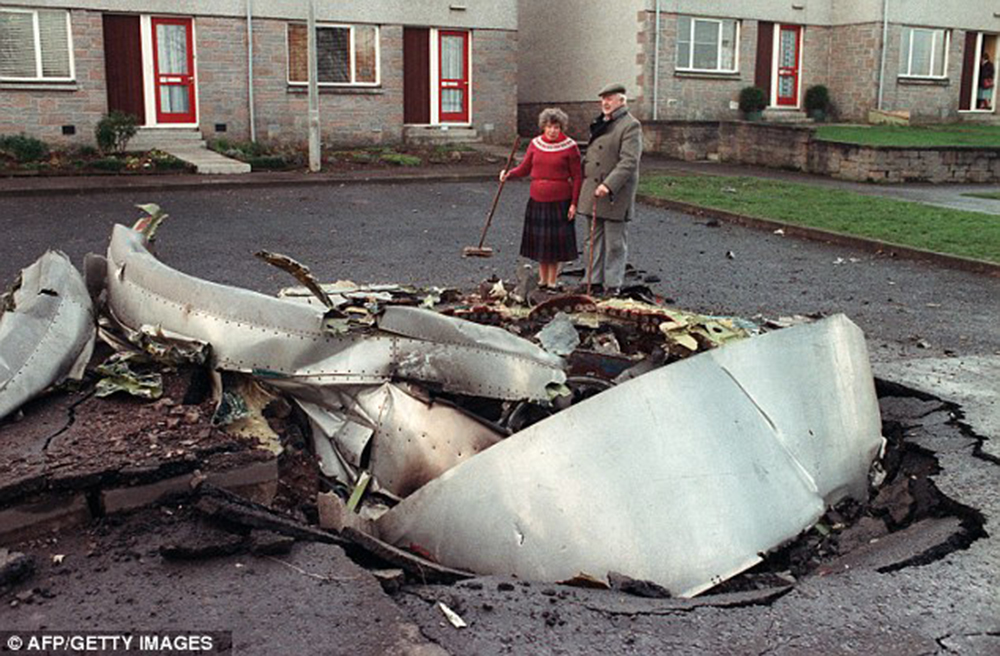
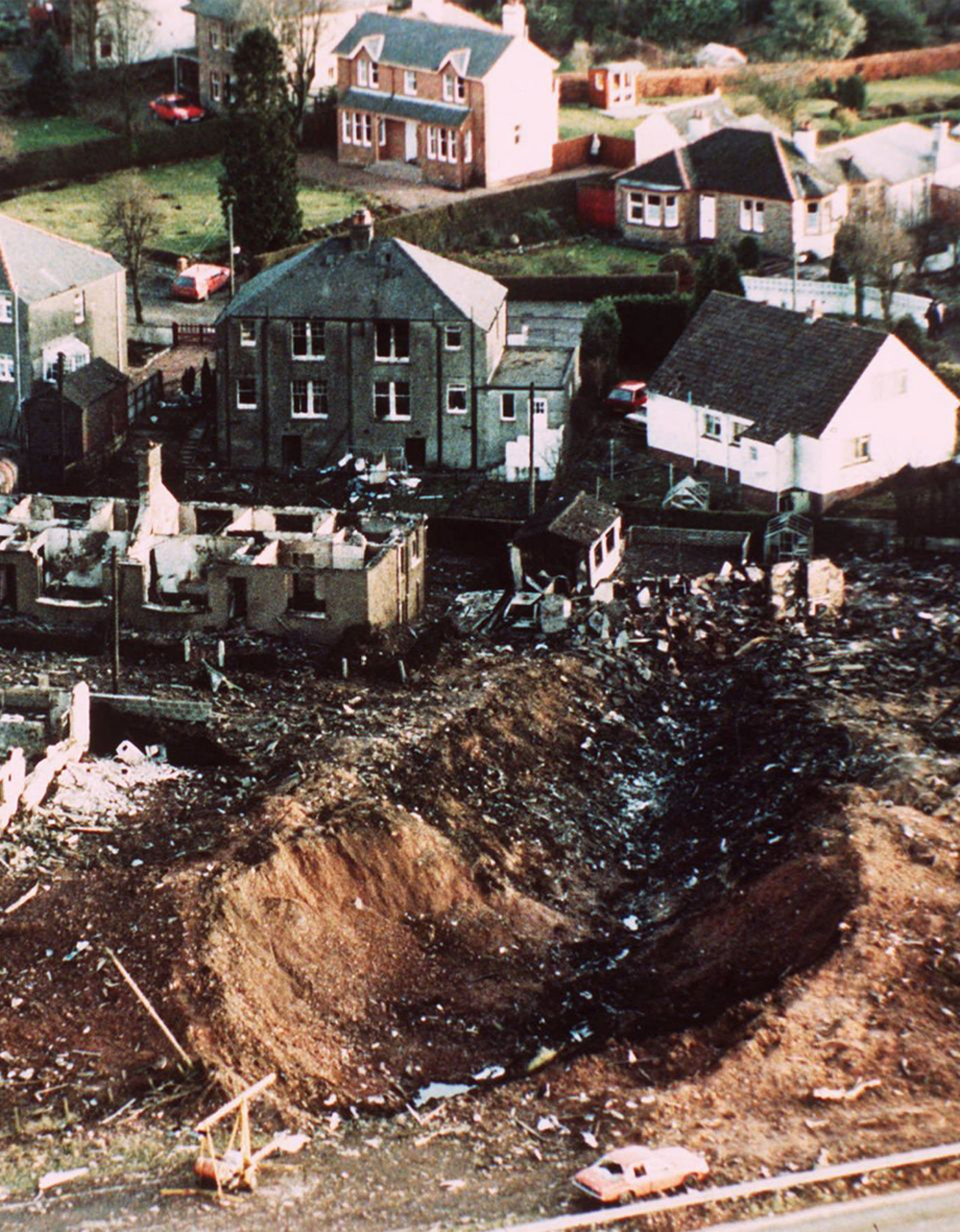
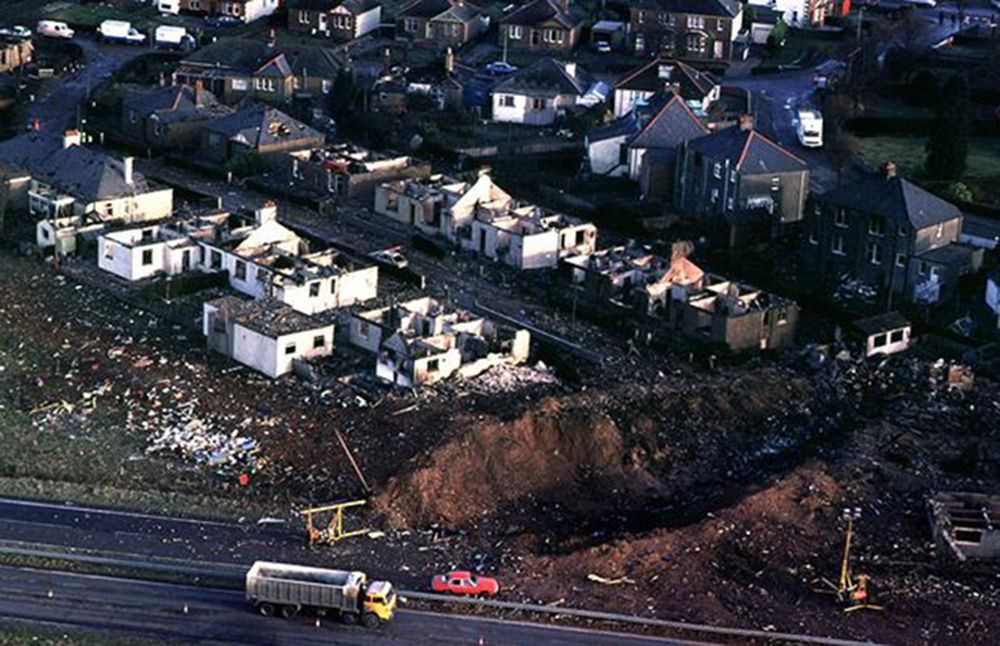
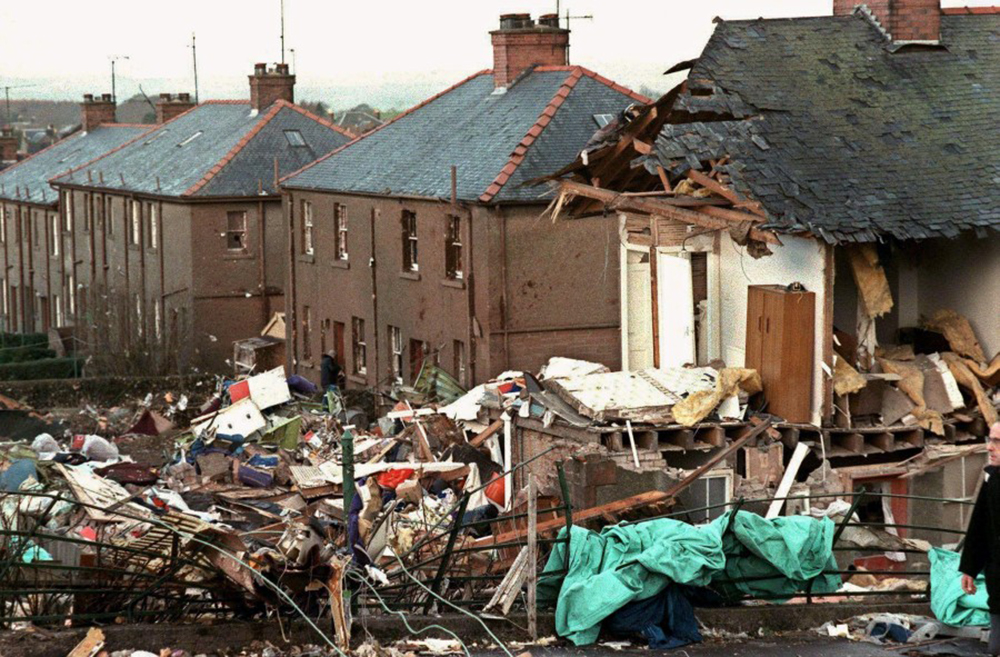
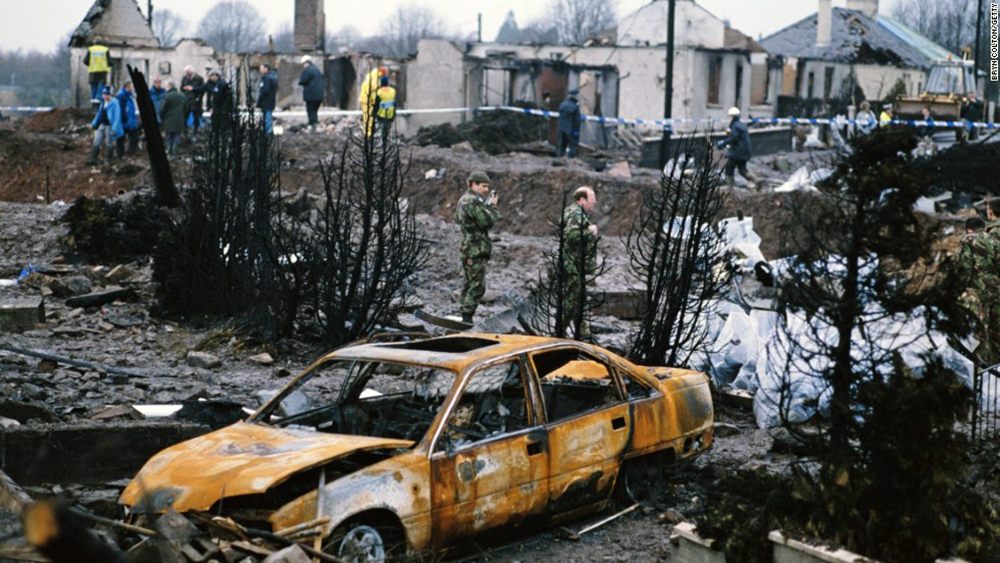
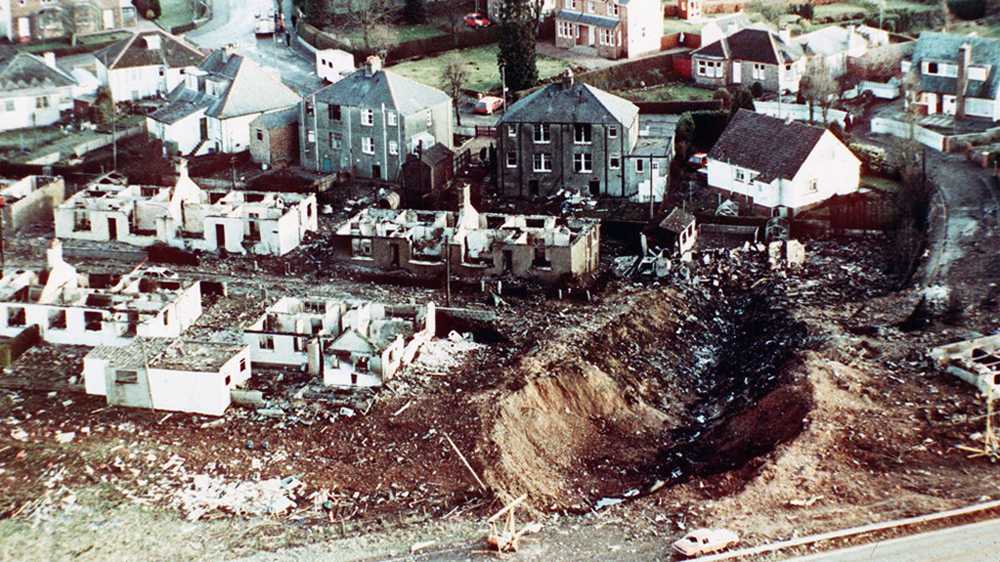
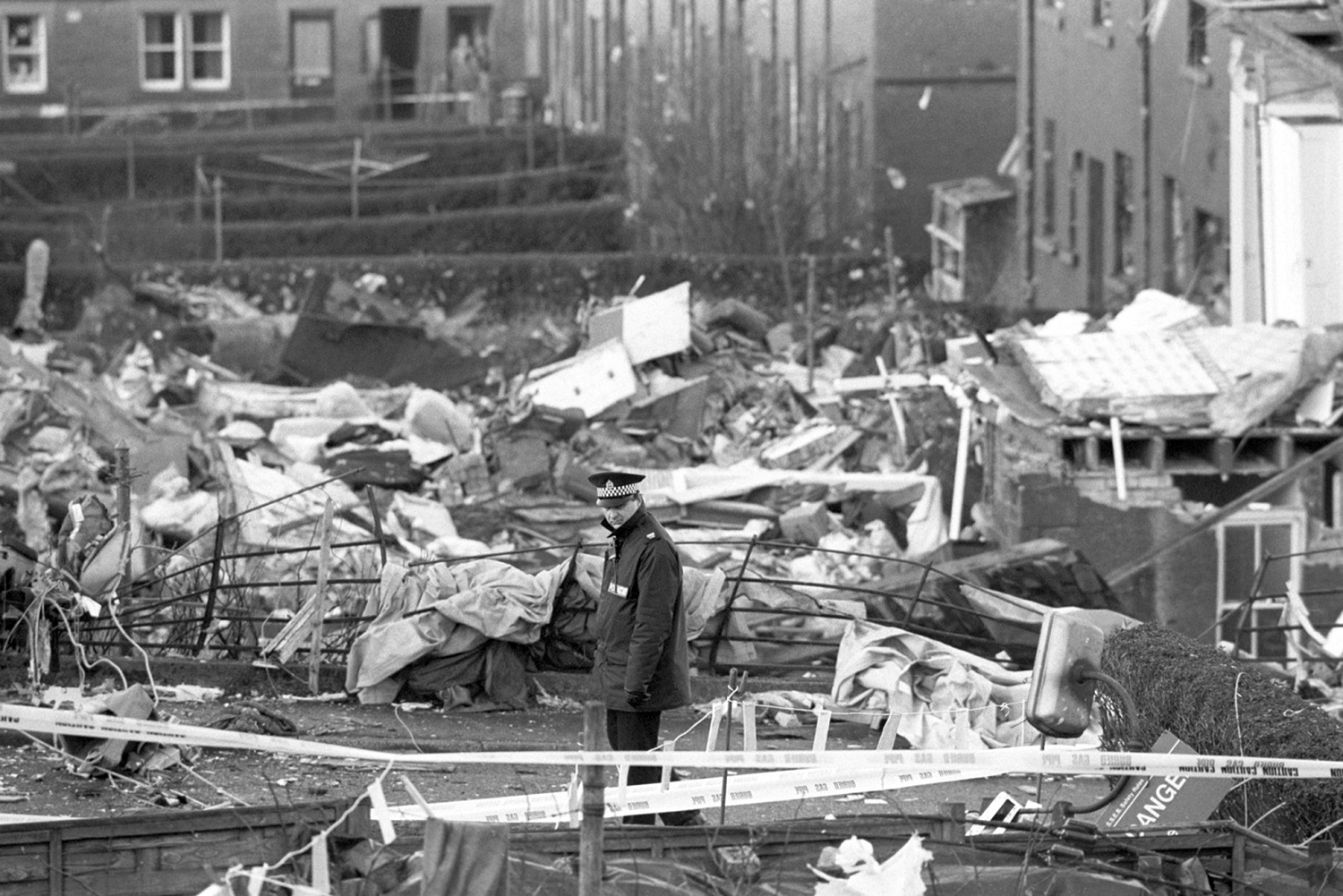
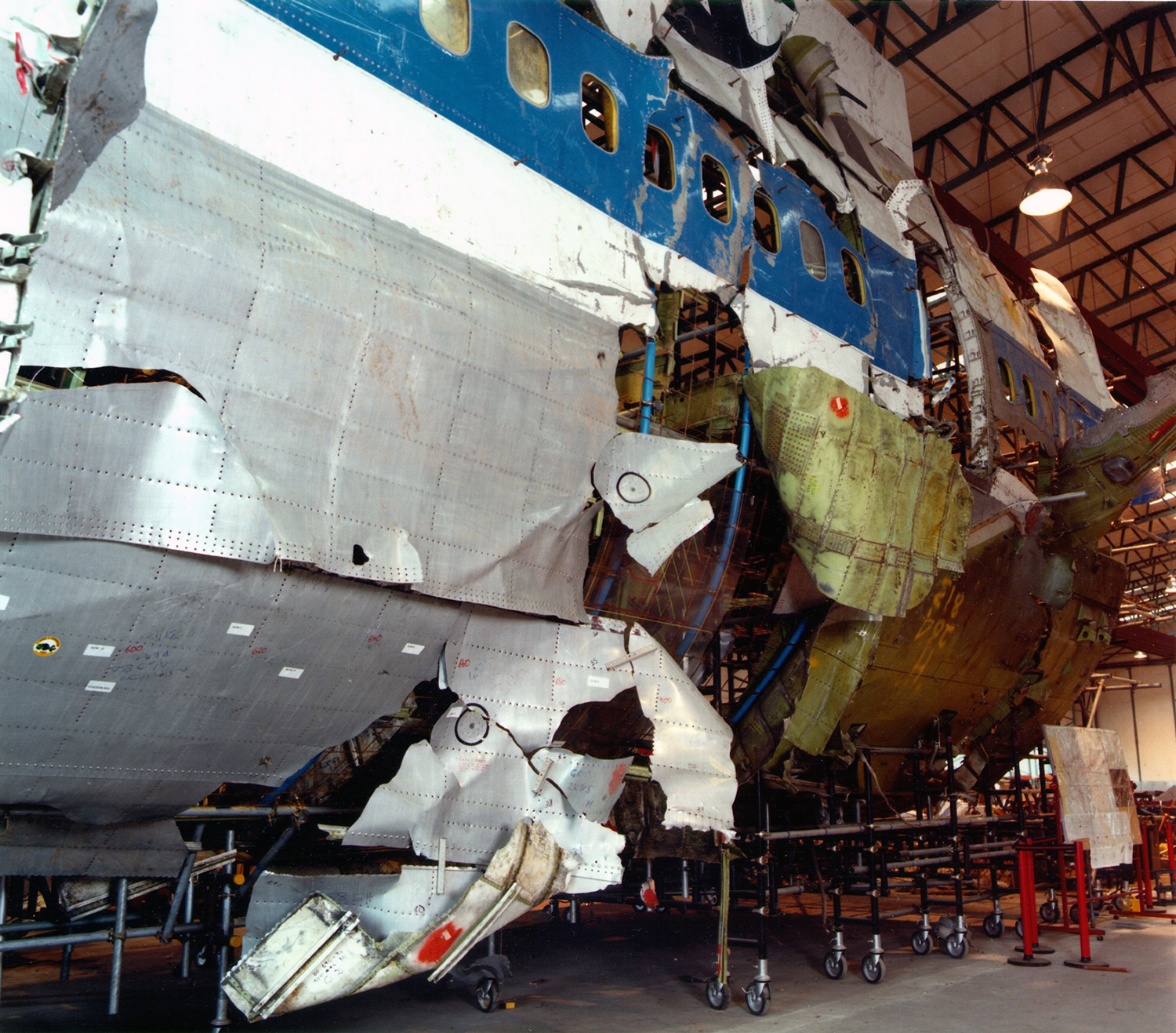
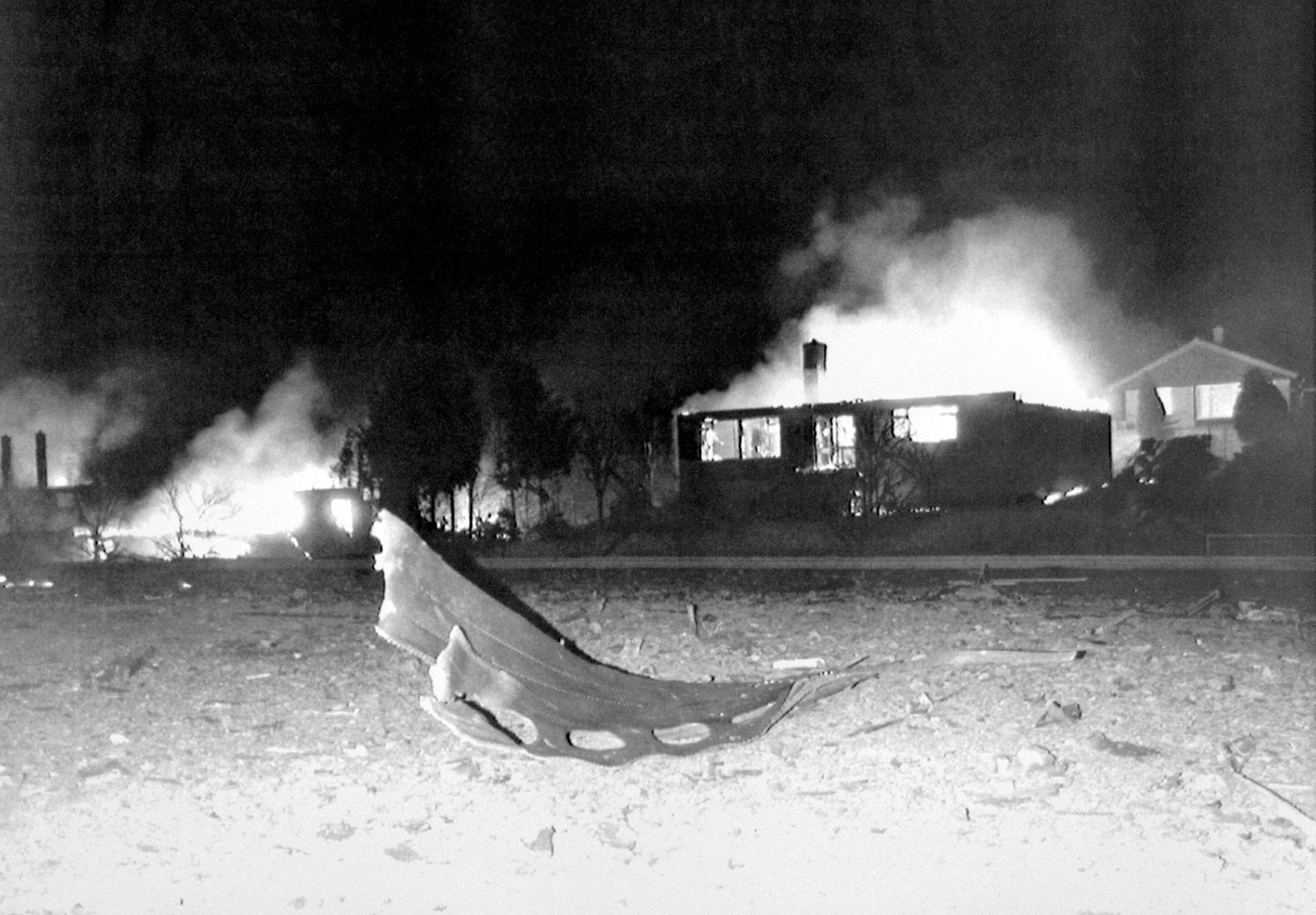
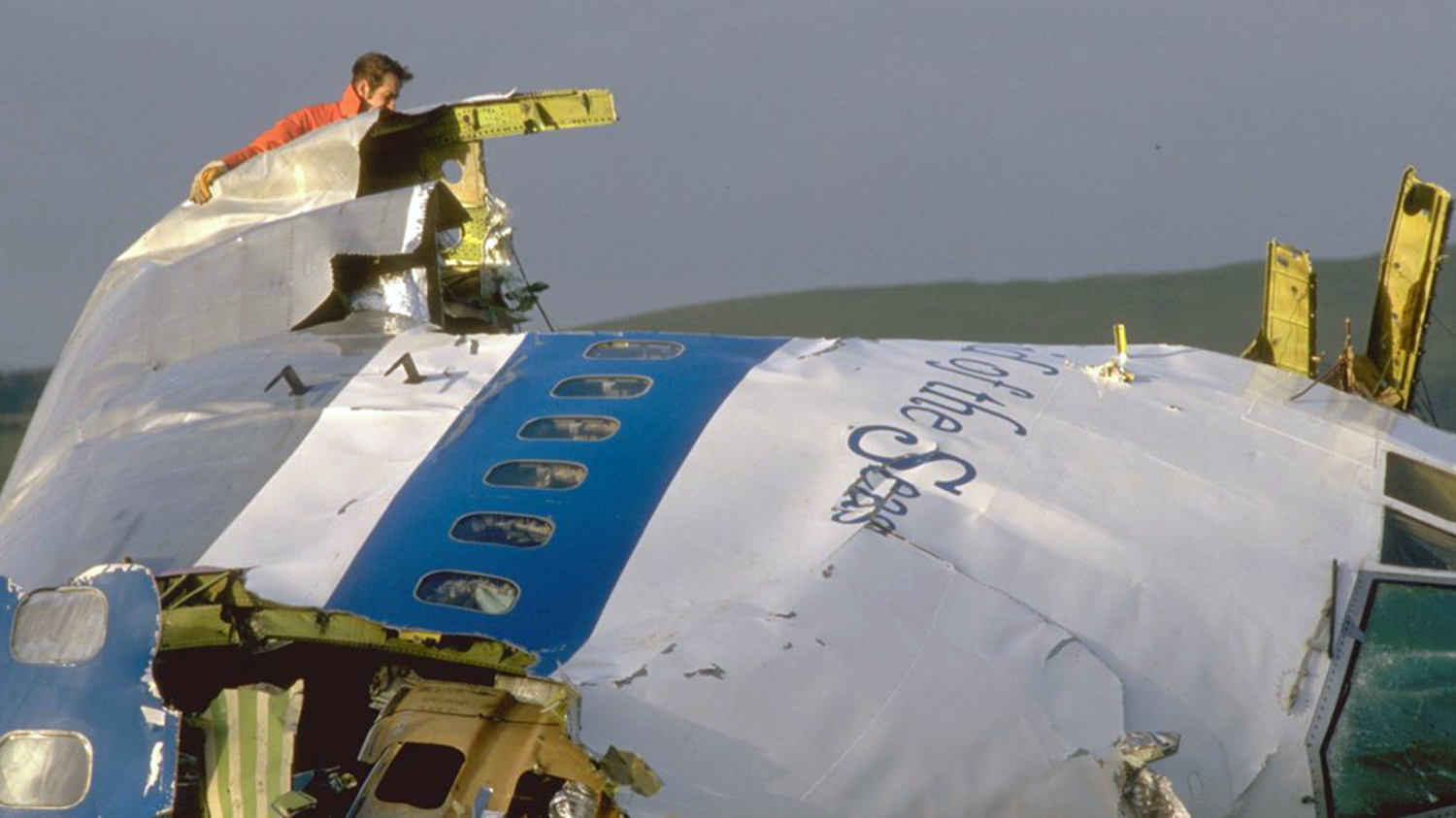
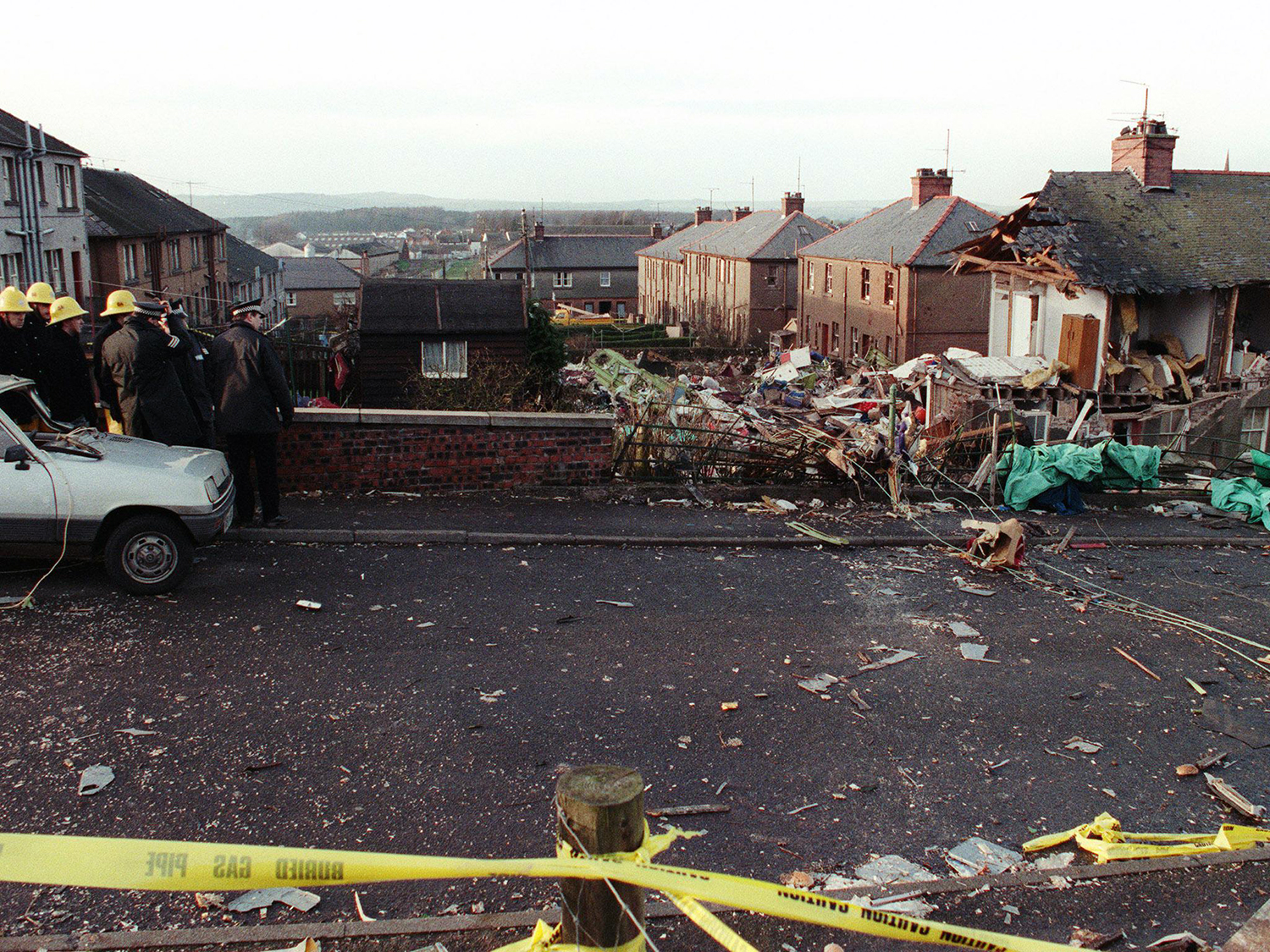
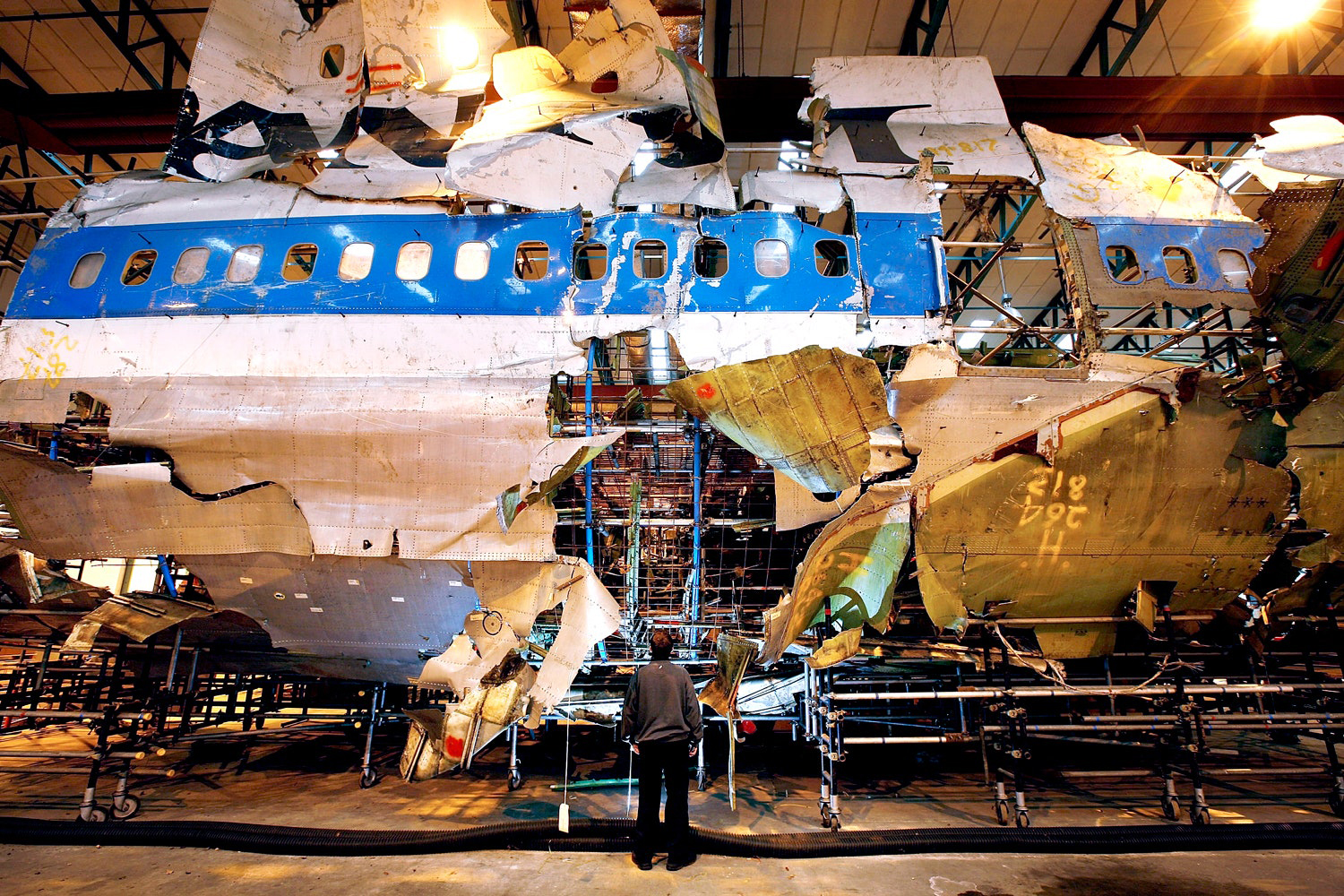
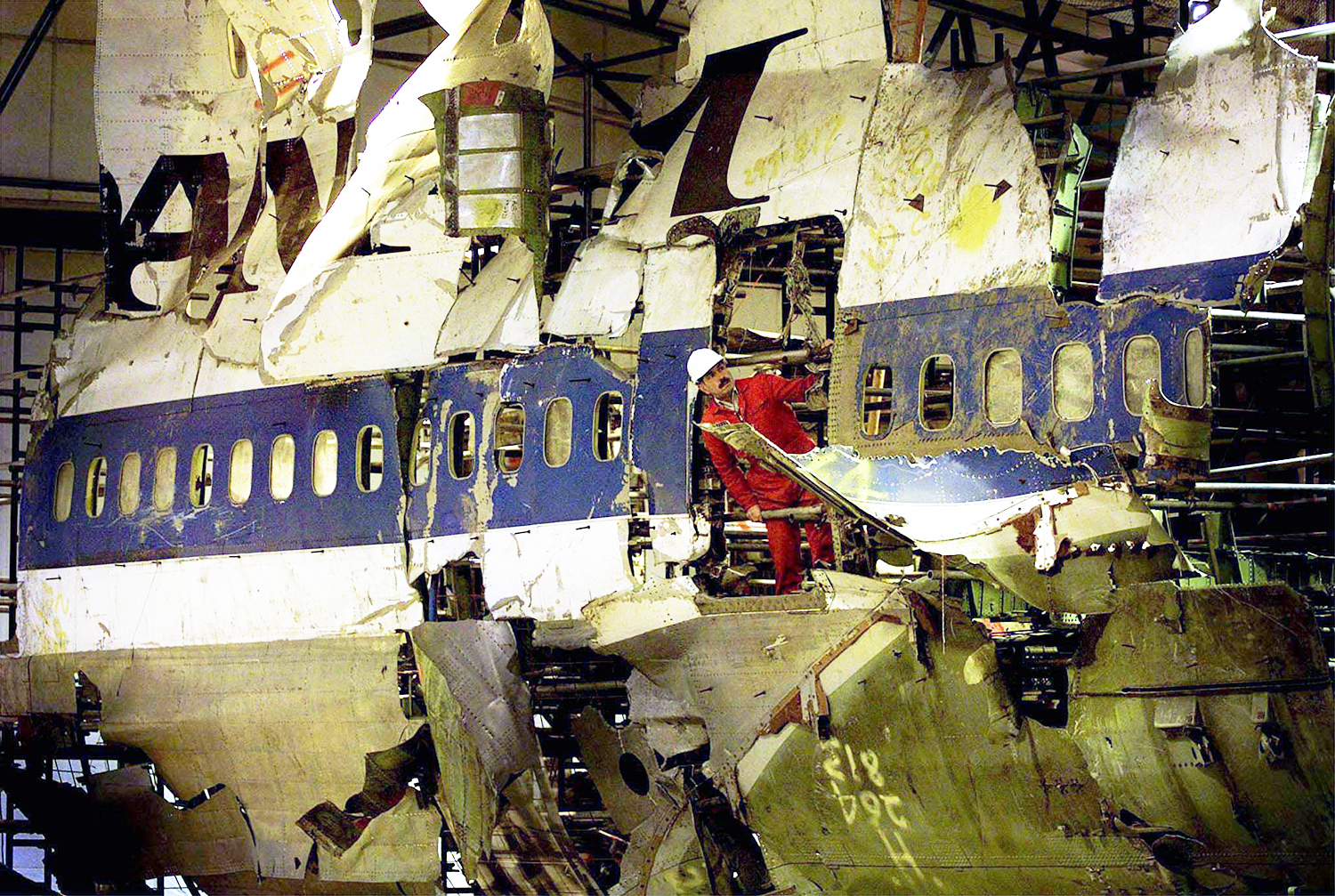
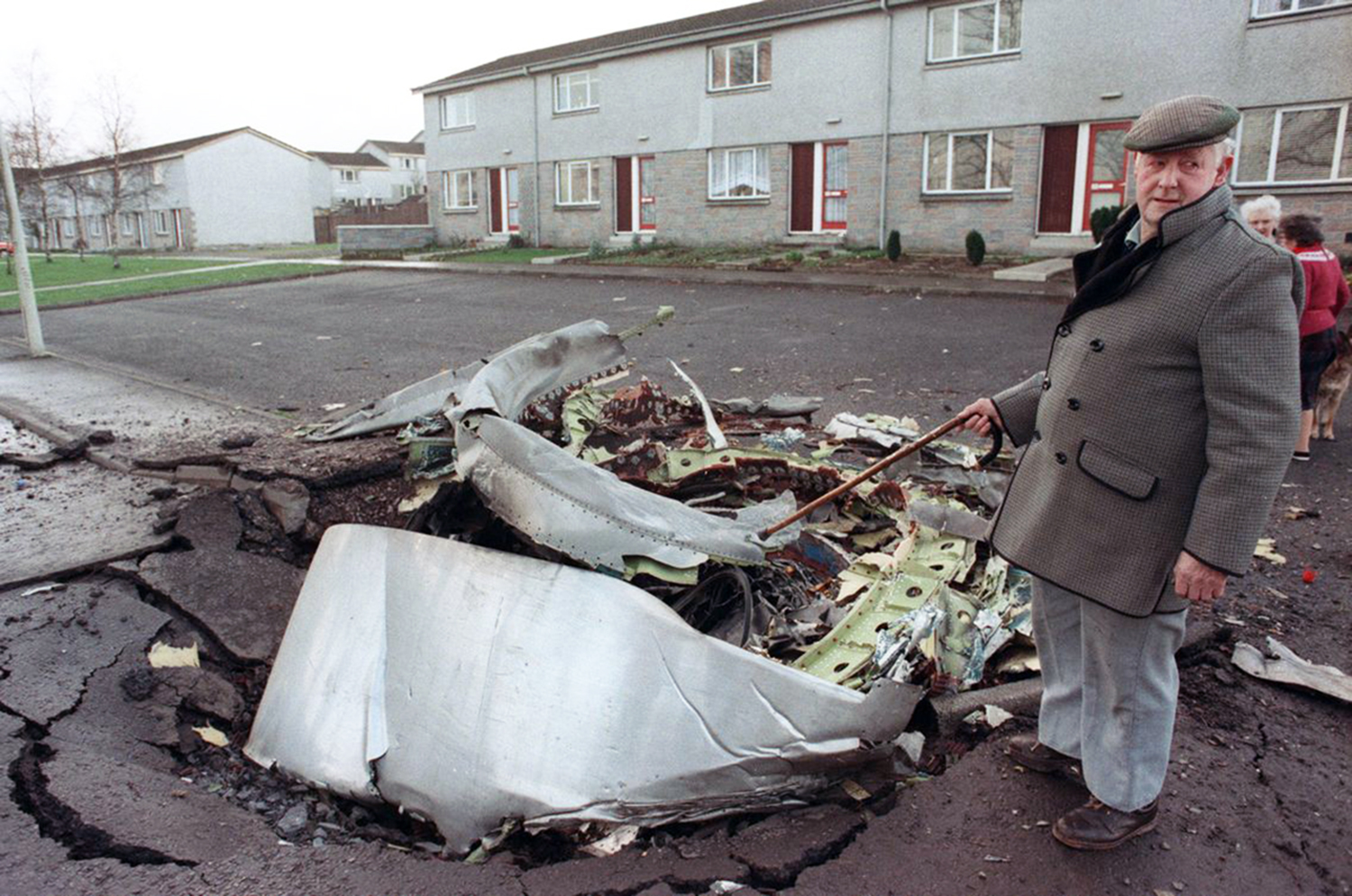
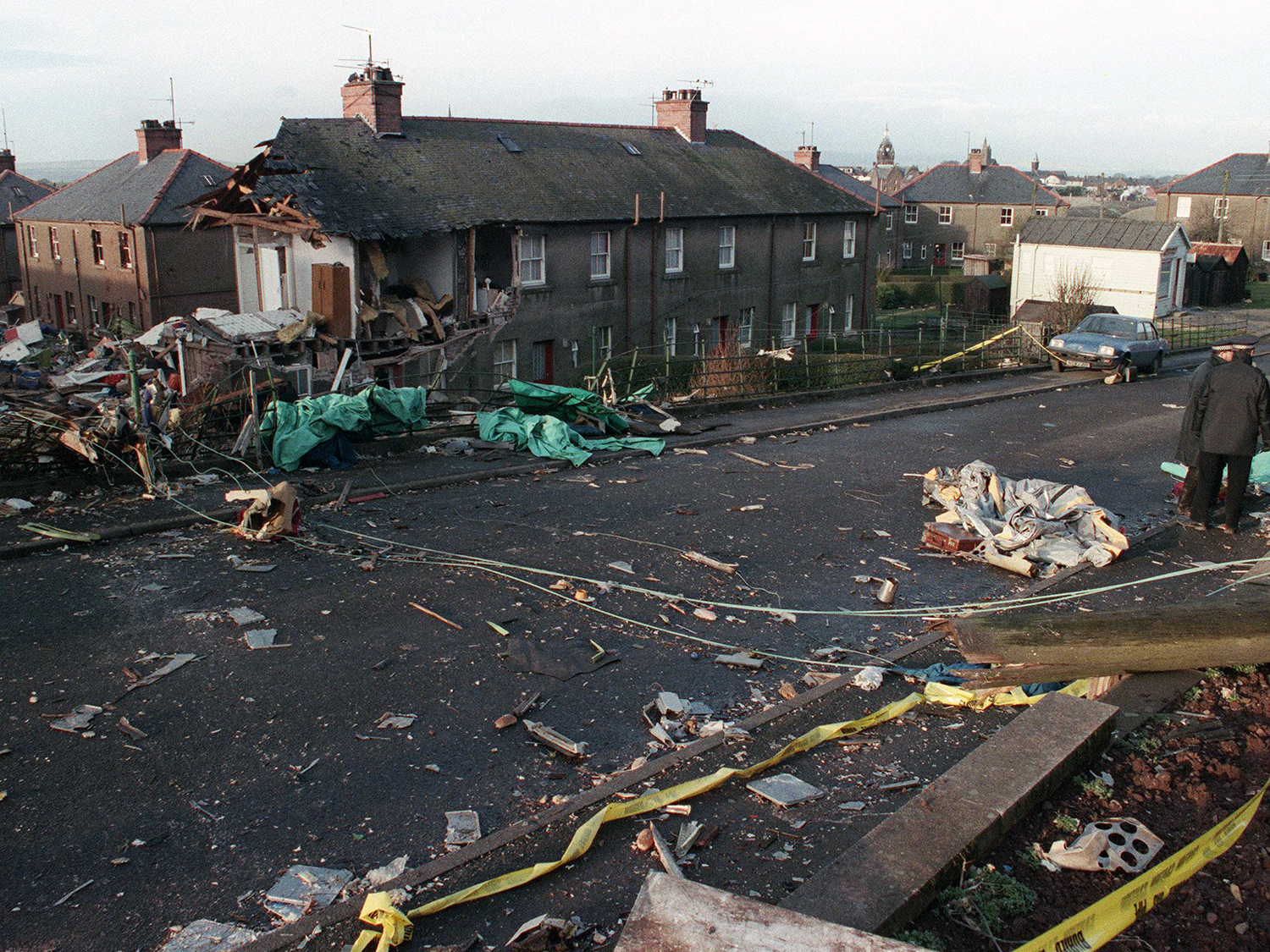
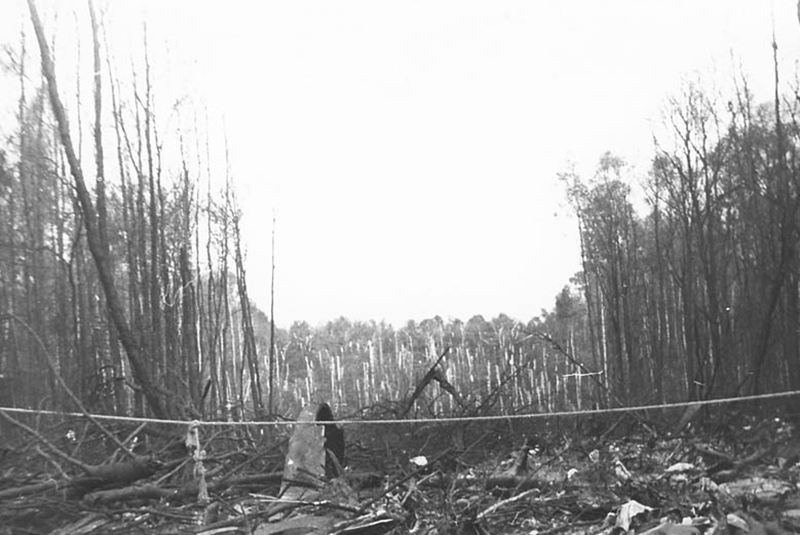
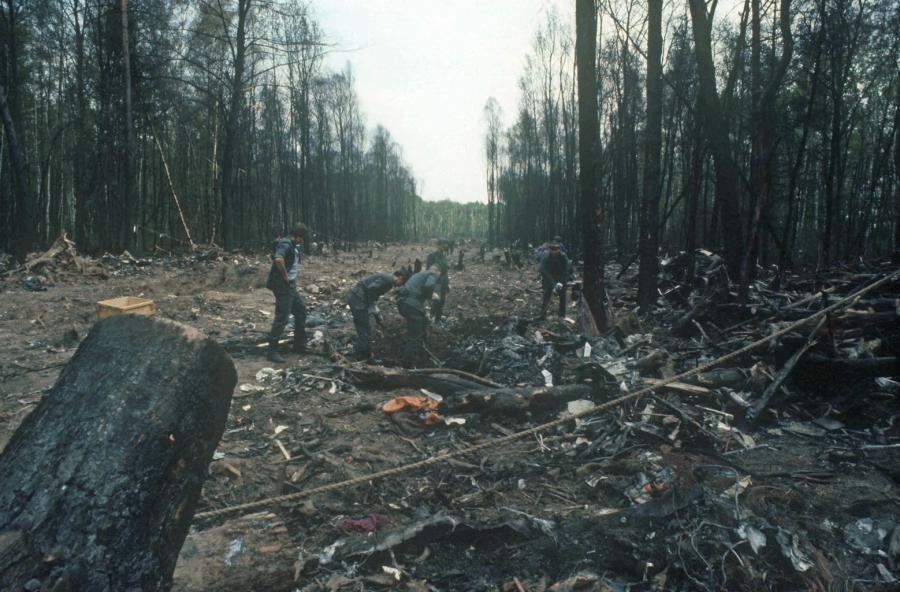
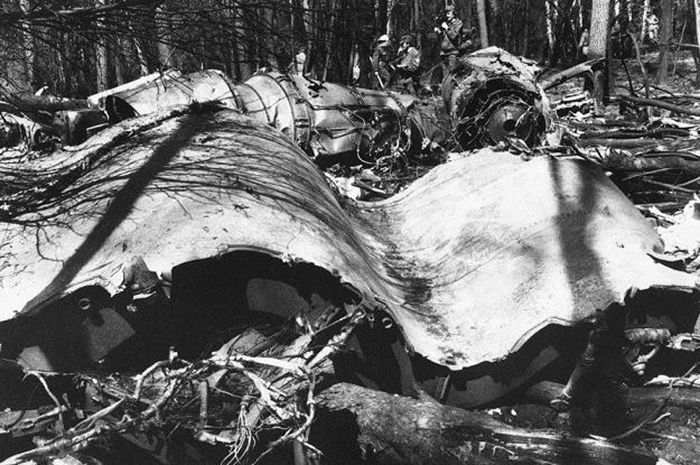
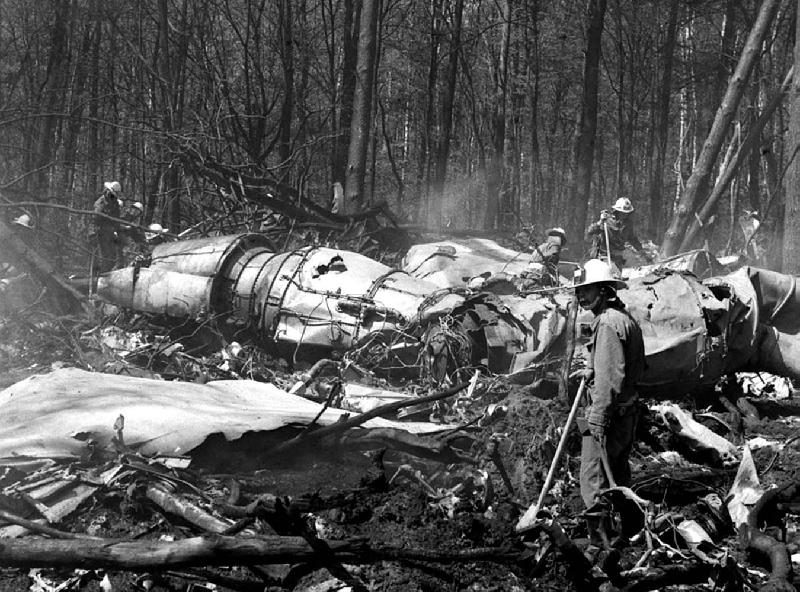
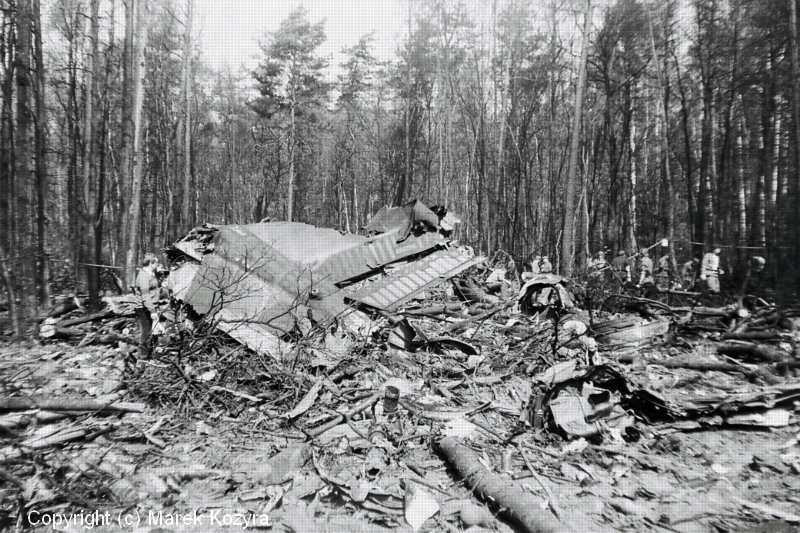
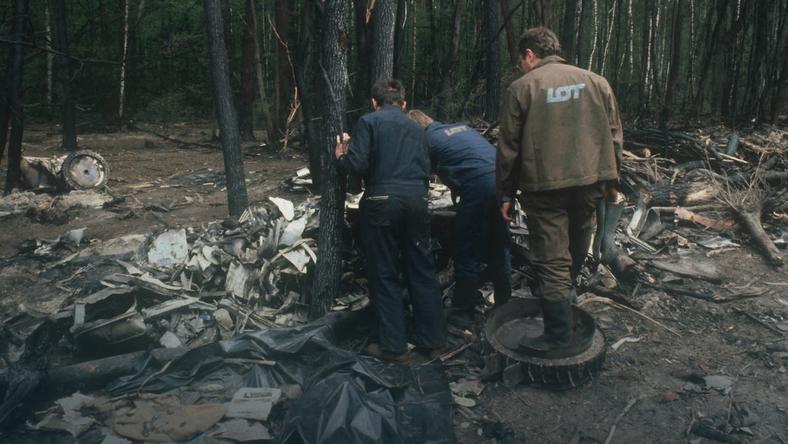
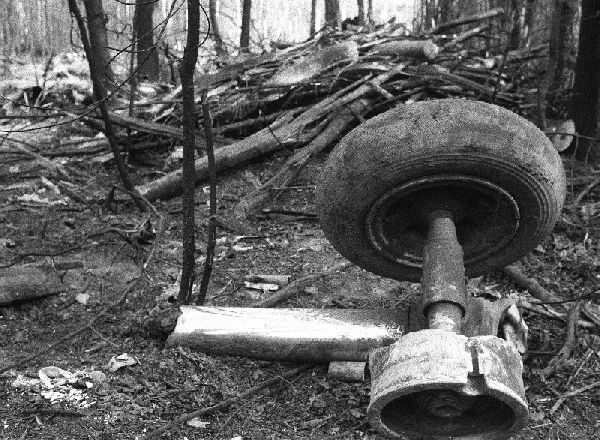
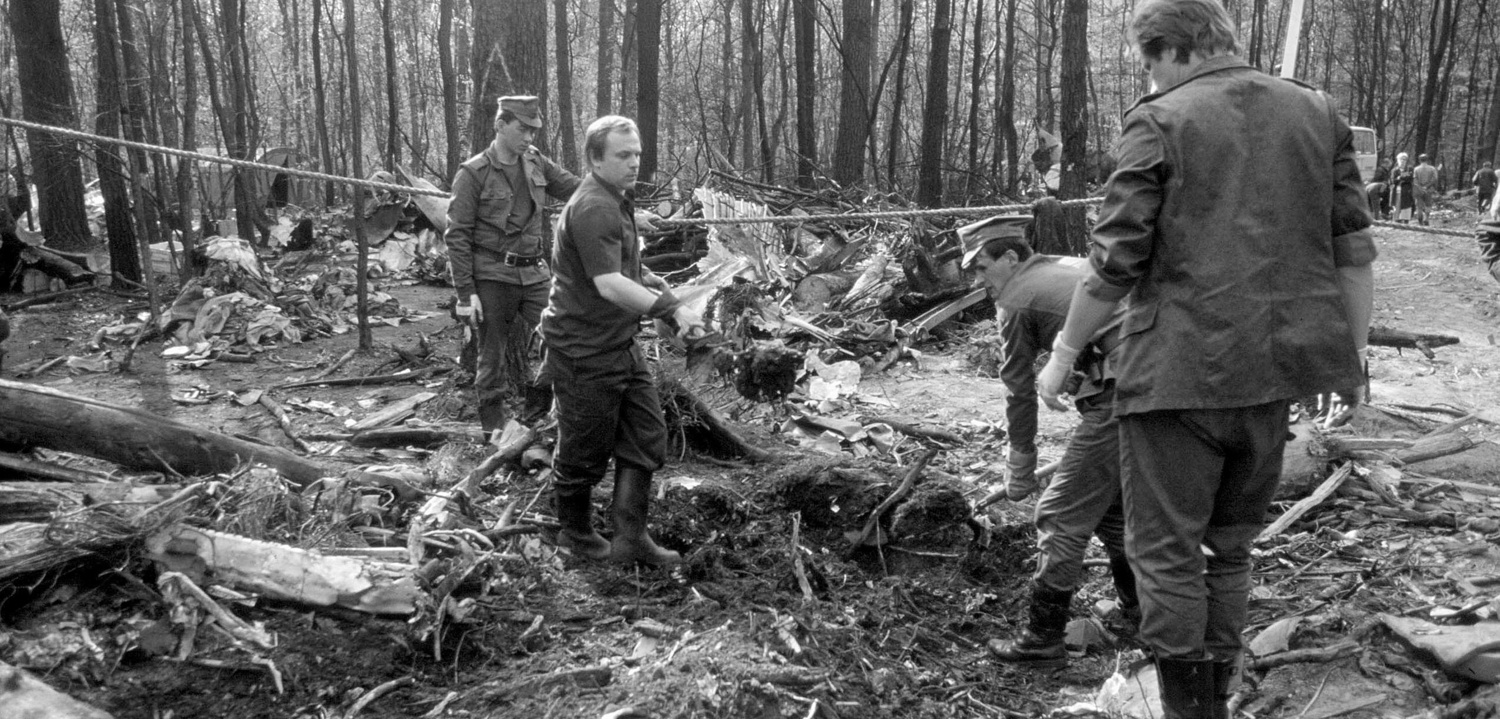
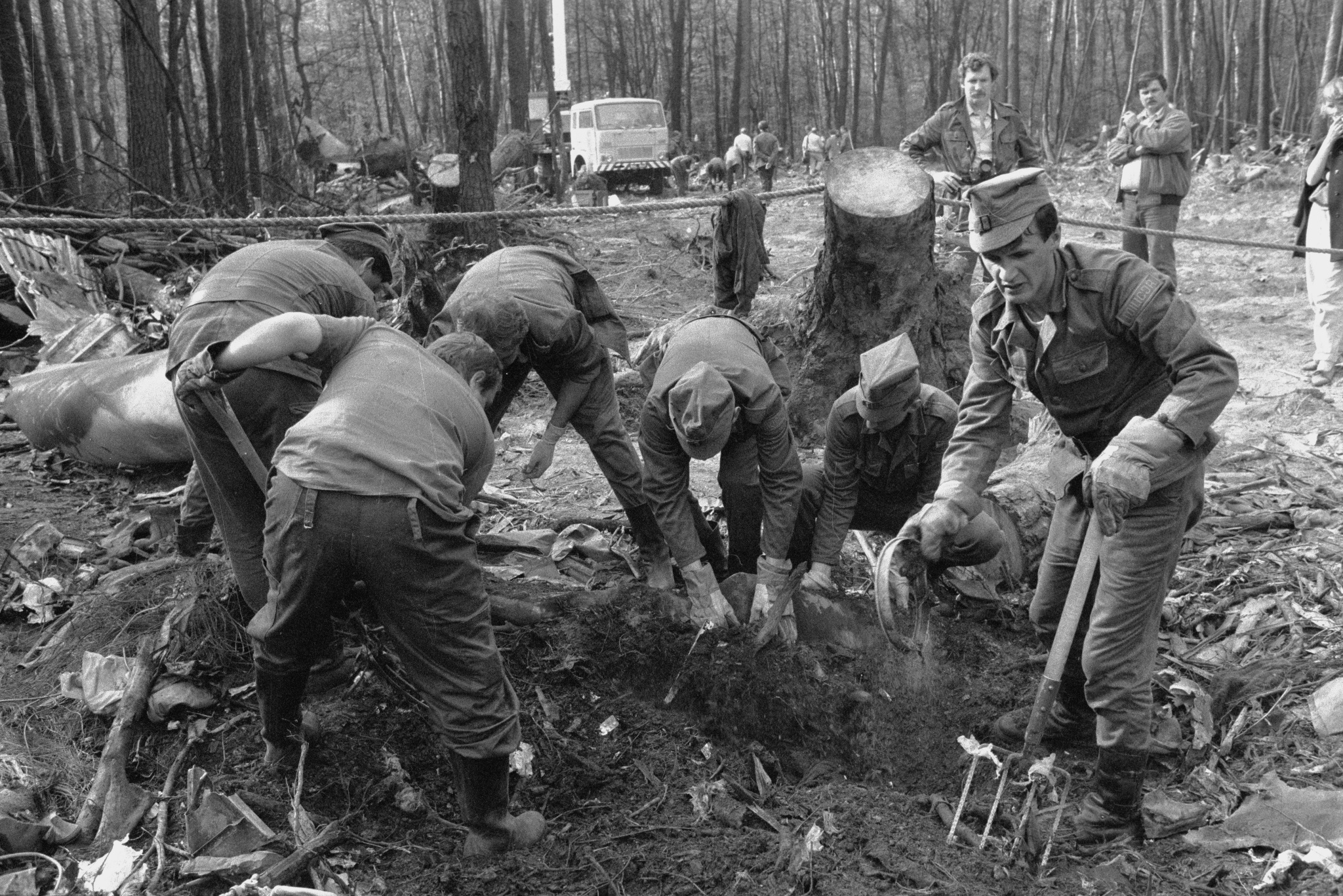
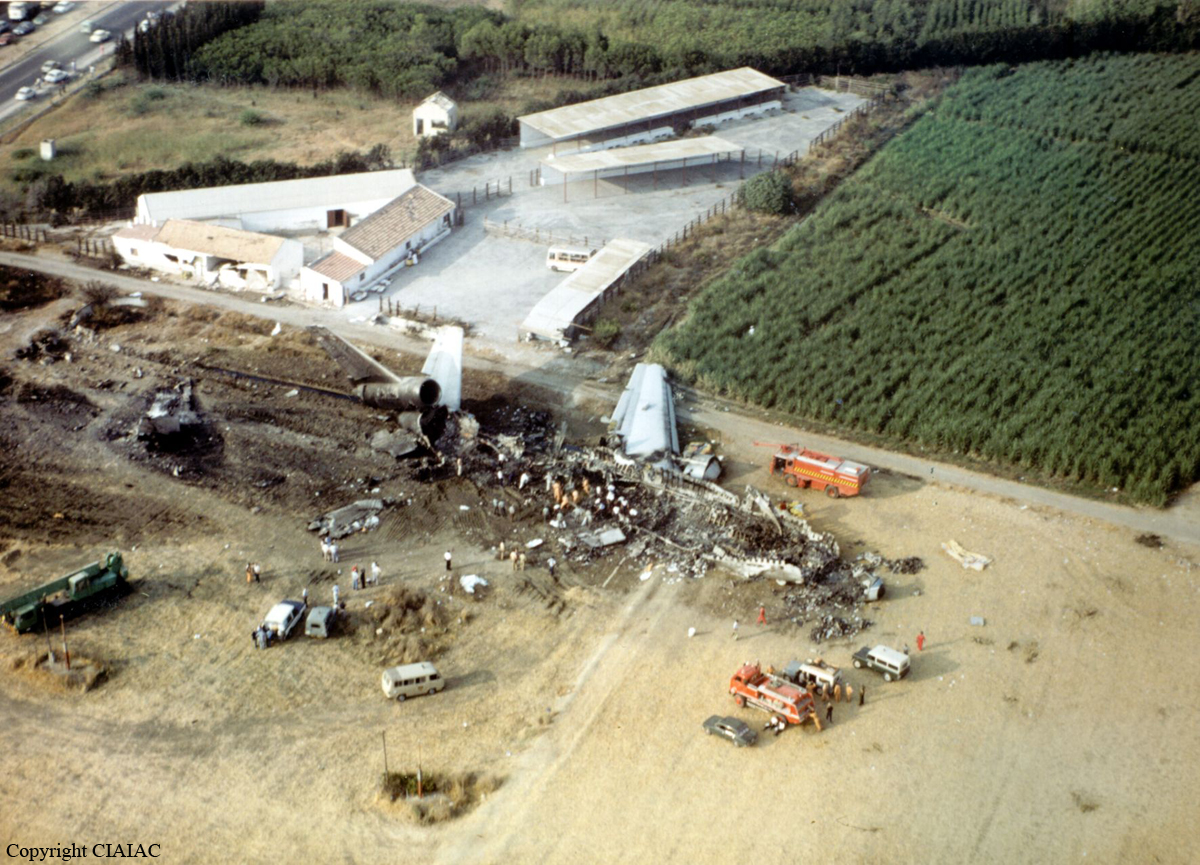
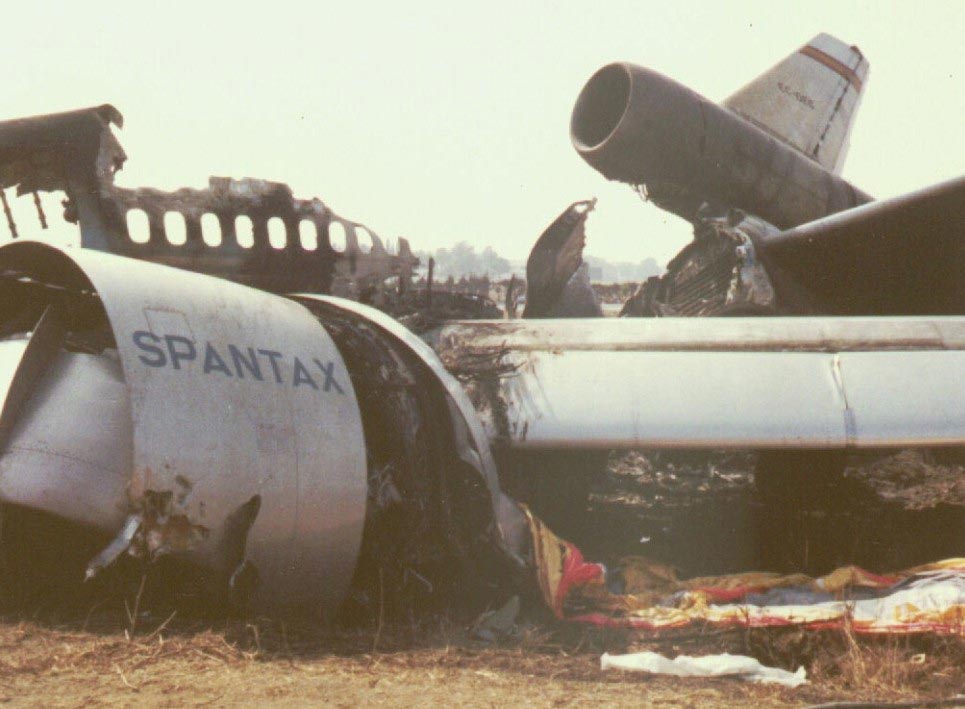
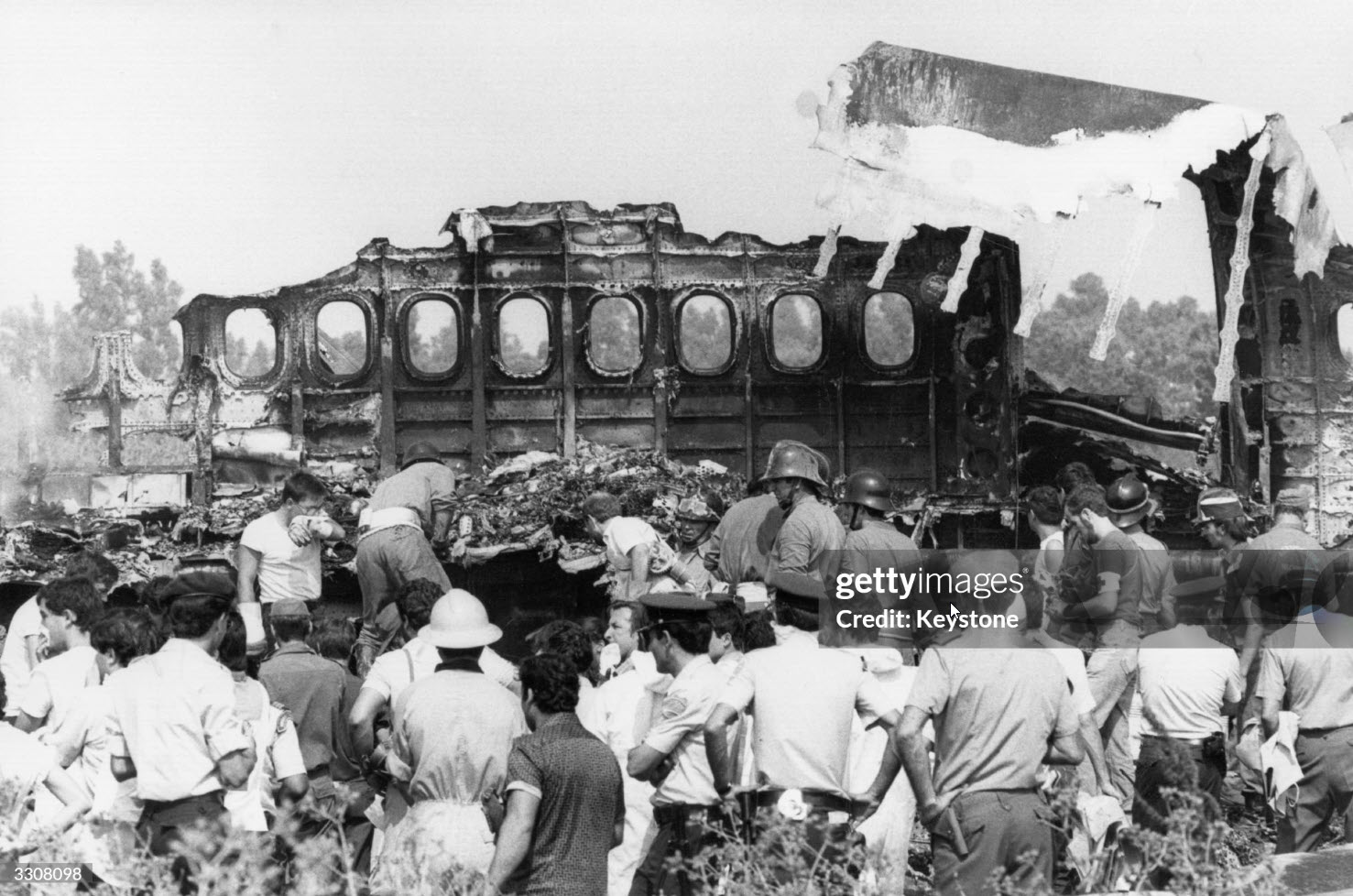
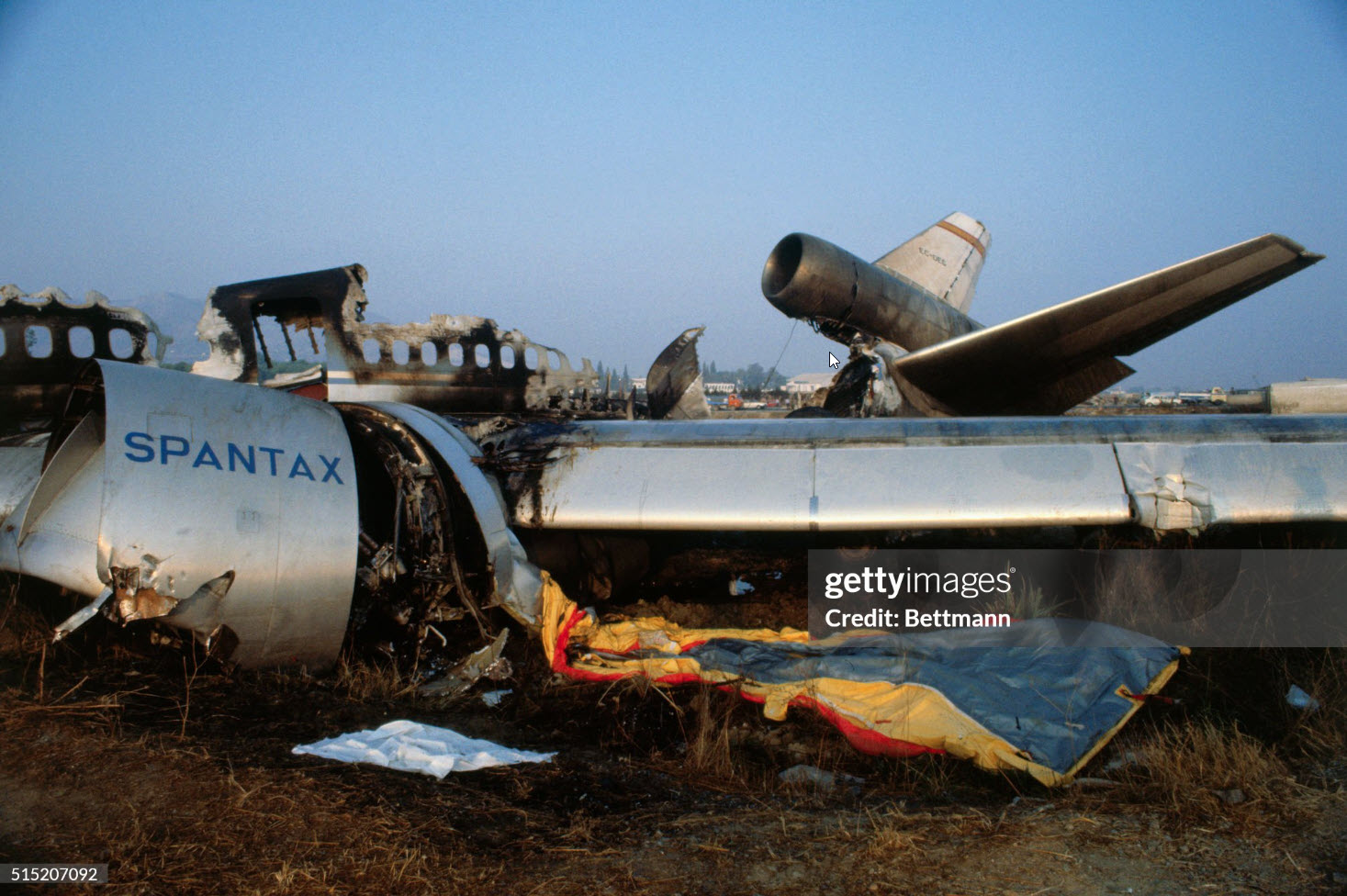
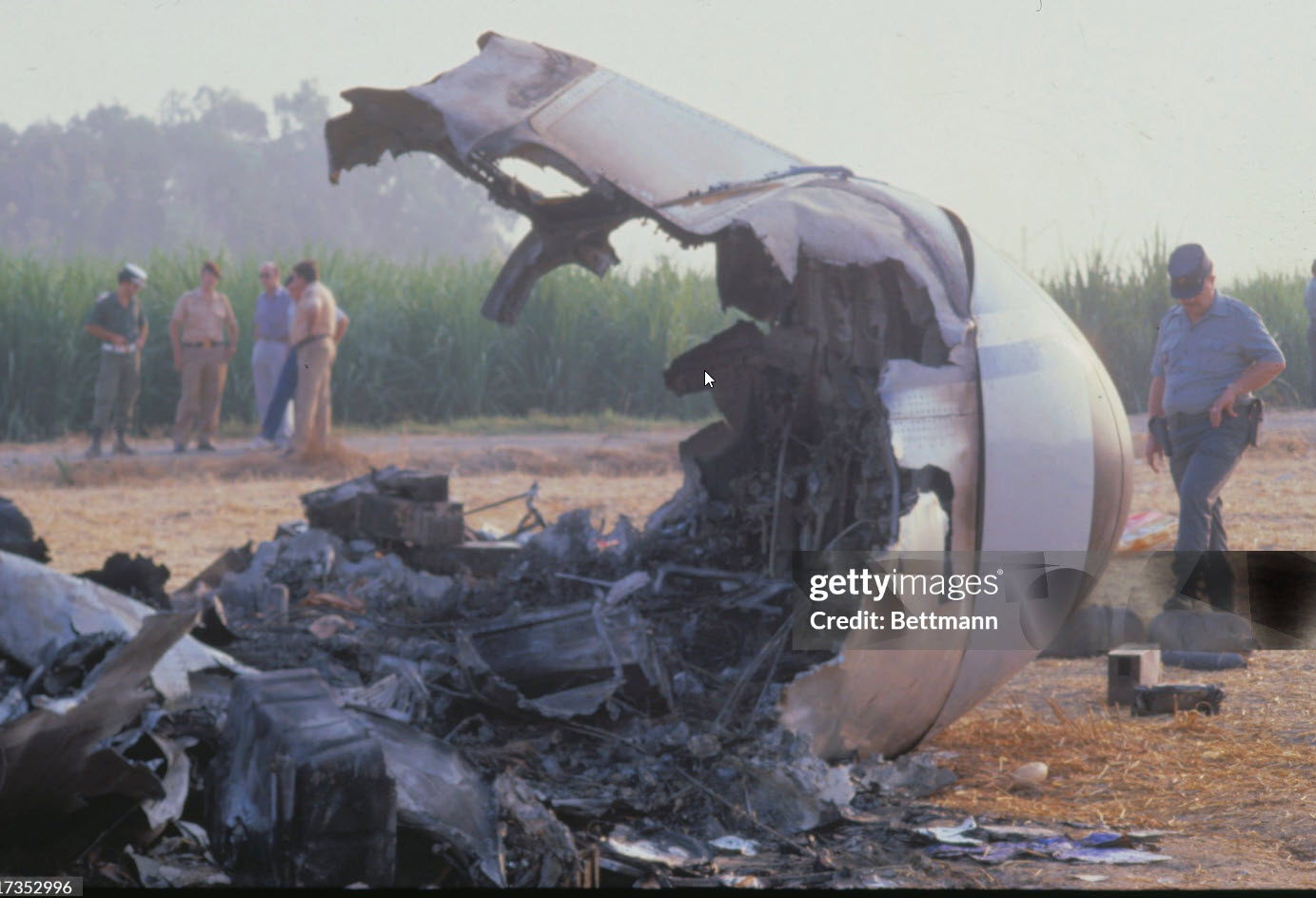
Flight PA103 departed London-Heathrow runway 27R for New York at 18:25. The aircraft levelled off at FL310, 31 minutes later. At 19:03 Shanwick Oceanic Control transmitted an oceanic clearance. At that time an explosion occurred in the aircraft's forward cargo hold at position 4L. The explosive forces produced a large hole in the fuselage structure and disrupted the main cabin floor. Major cracks continued to propagate from the large hole while containers and items of cargo ejected through the hole, striking the empennage, left- and right tail plane. The forward fuselage and flight deck area separated when the aircraft was in a nose down and left roll attitude, peeling away to the right at Station 800. The nose section then knocked the no. 3 engine off its pylon. The remaining aircraft disintegrated while it was descending nearly vertically from 19000 feet to 9000 feet. A section of cabin floor and baggage hold (from approx. Station 1241-1920) fell onto housing at Rosebank Terrace, Lockerbie. The main wing structure struck the ground with a high yaw angle at Sherwood Crescent, Lockerbie causing a massive fire. The Semtex bomb which caused the explosion had probably been hidden in a radio cassette player and was transferred to PA103 from a Pan Am Boeing 727 flight, arriving from Frankfurt. After a three-year joint investigation by the Dumfries and Galloway Constabulary and the U.S. Federal Bureau of Investigation indictments for murder were issued on November 13, 1991, against Abdel Basset Ali al-Megrahi, a Libyan intelligence officer and the head of security for Libyan Arab Airlines (LAA), and Lamin Khalifah Fhimah, the LAA station manager in Luqa Airport, Malta. United Nations sanctions against Libya and protracted negotiations with the Libyan leader Colonel Muammar al-Gaddafi secured the handover of the accused on April 5, 1999. On January 31, 2001, Megrahi was convicted of murder by a panel of three Scottish judges, and sentenced to 27 years in prison. Fhimah was acquitted.
Probable cause:
The in-flight disintegration of the aircraft was caused by the detonation of an improvised explosive device located in a baggage container positioned on the left side of the forward cargo hold at aircraft station 700.
Final Report: