Circumstances:
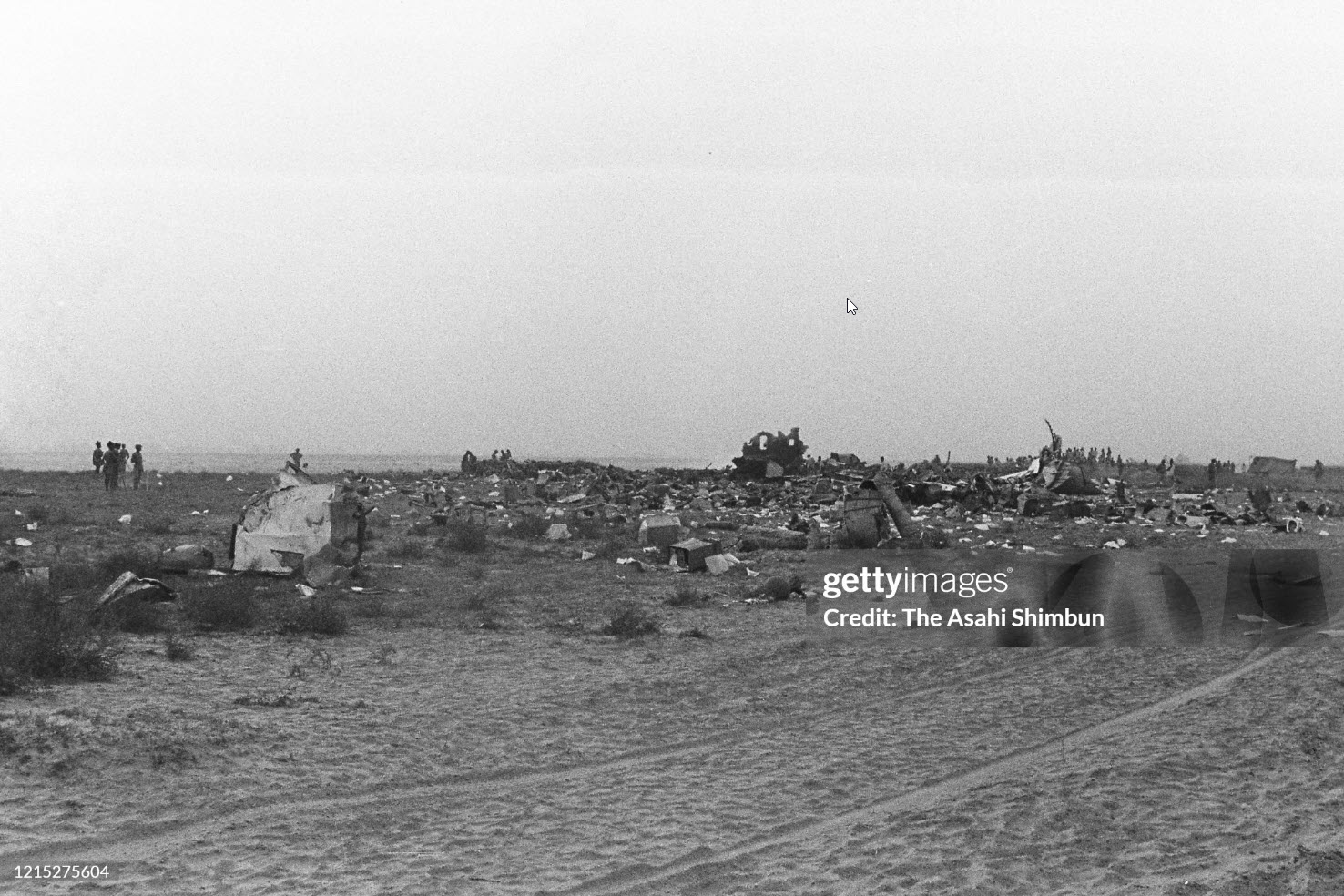
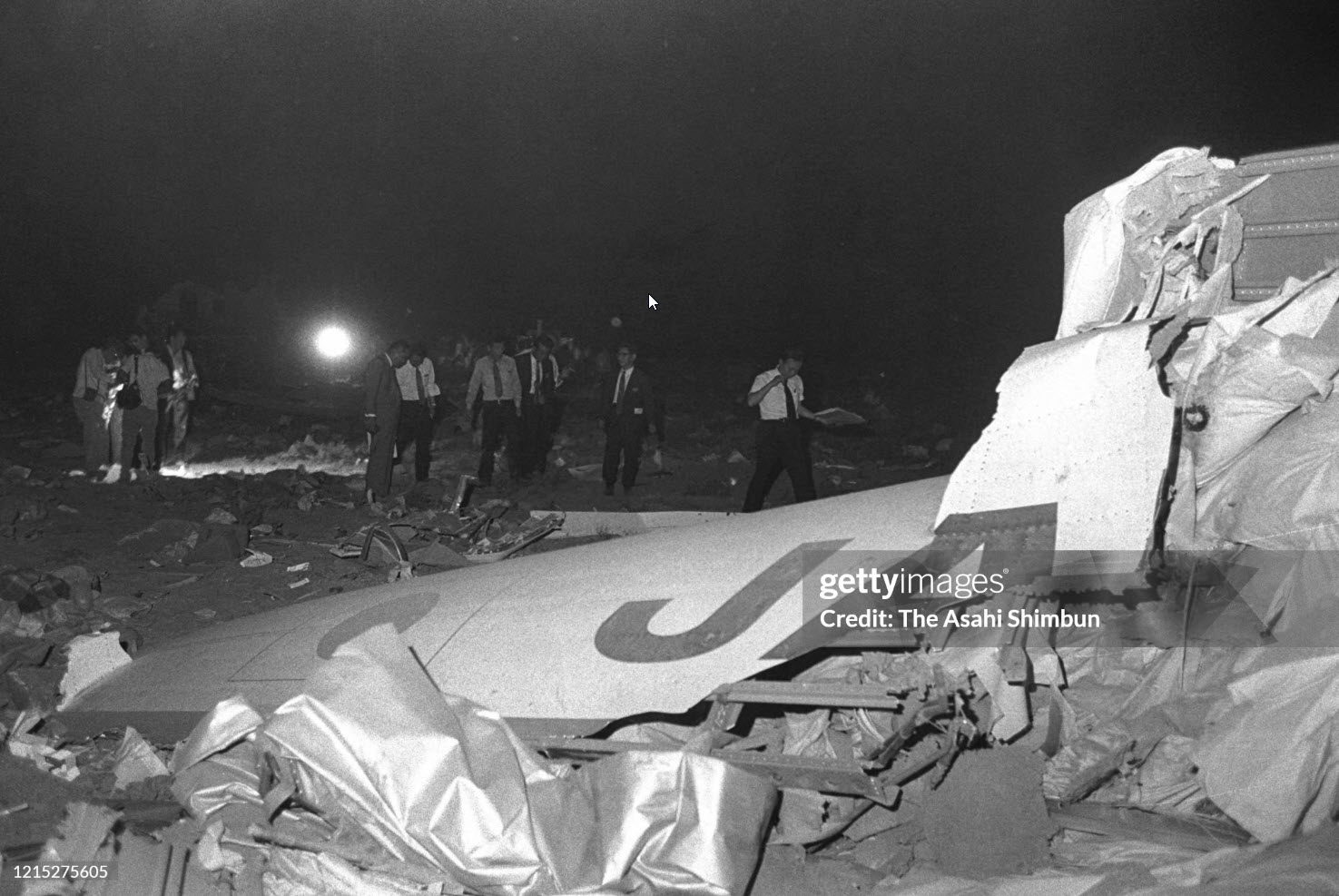
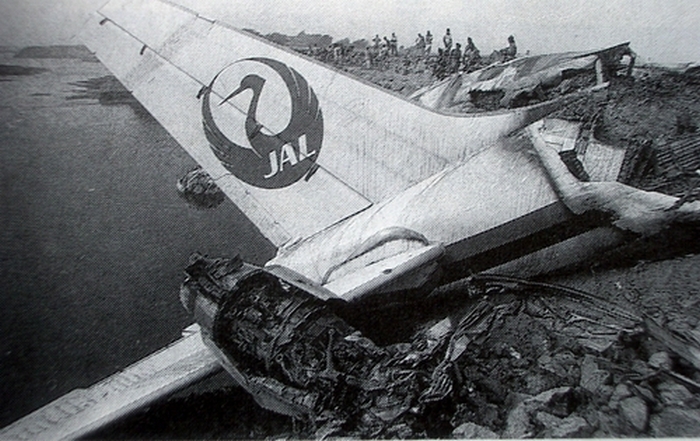
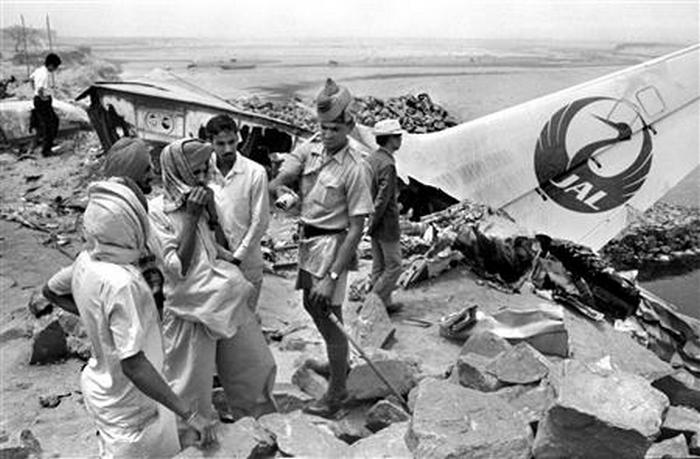
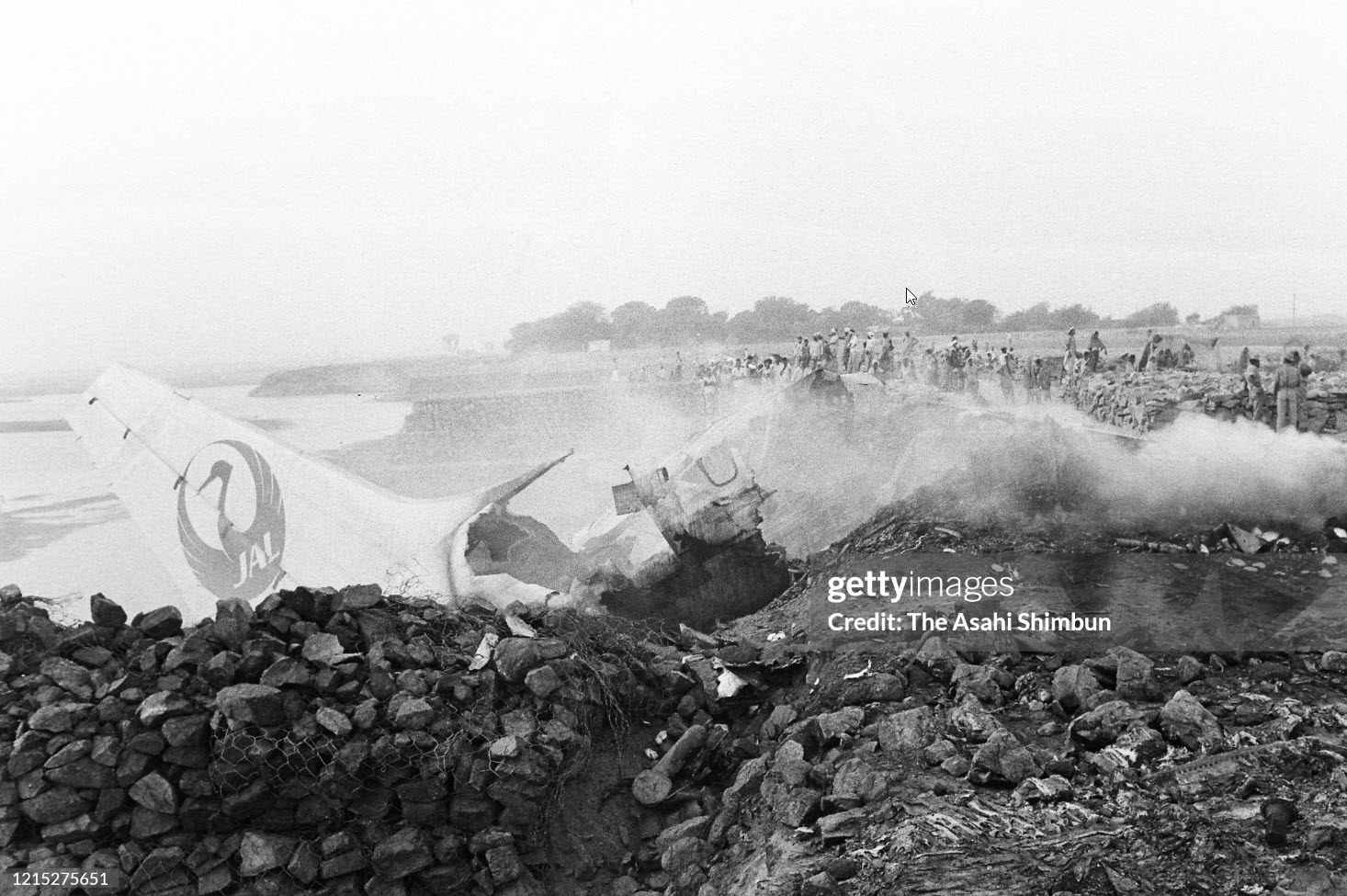
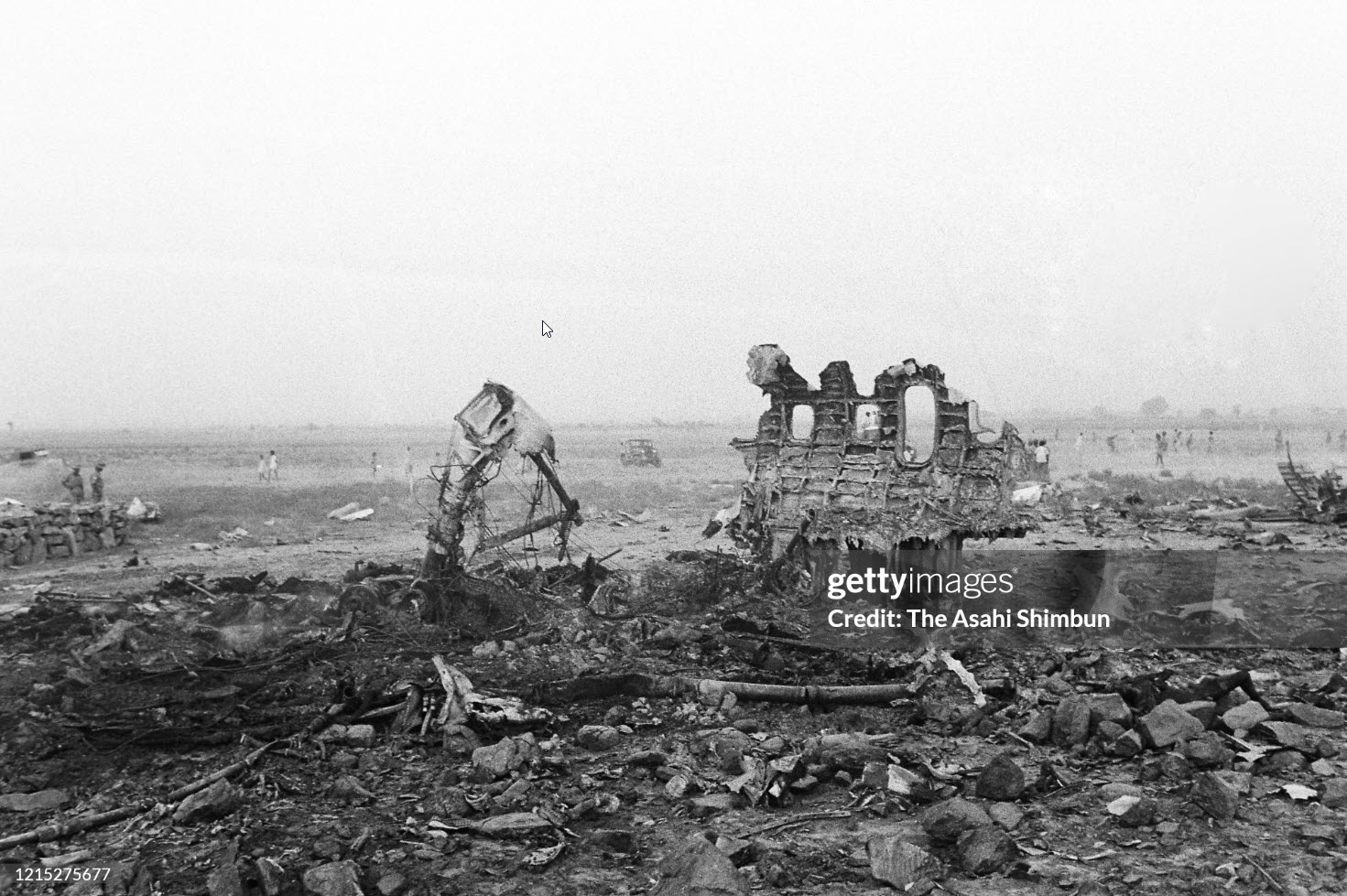
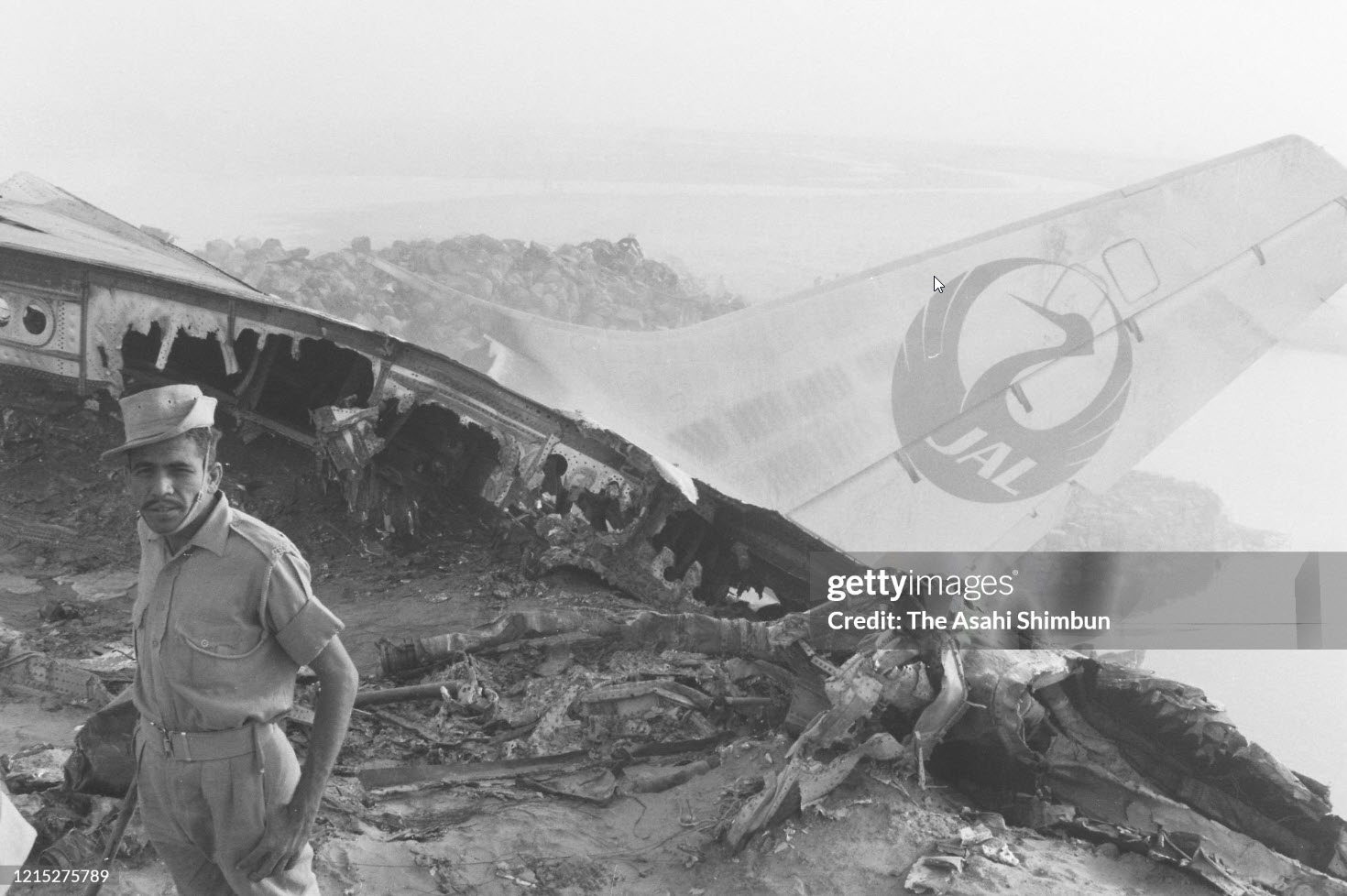
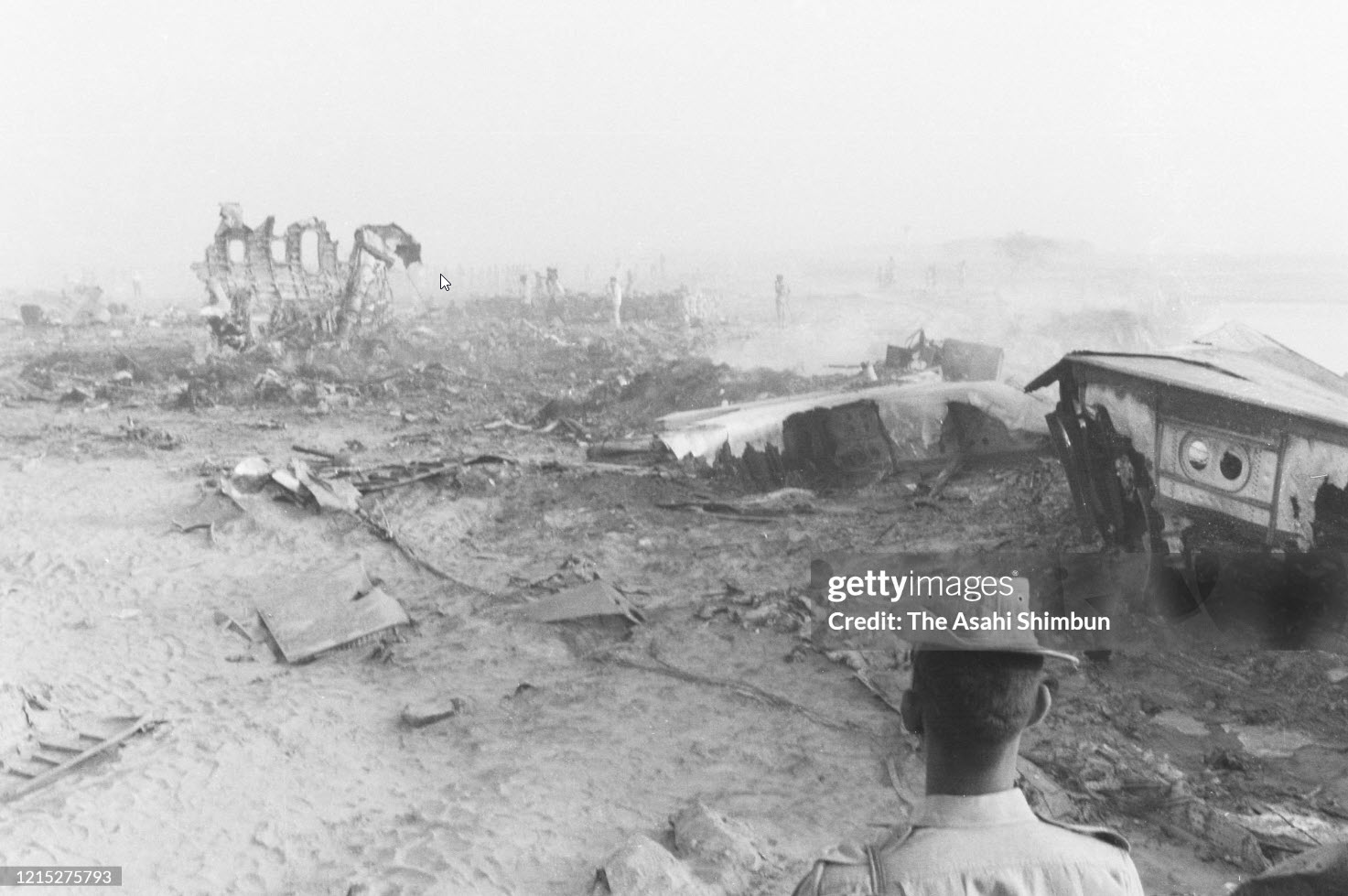
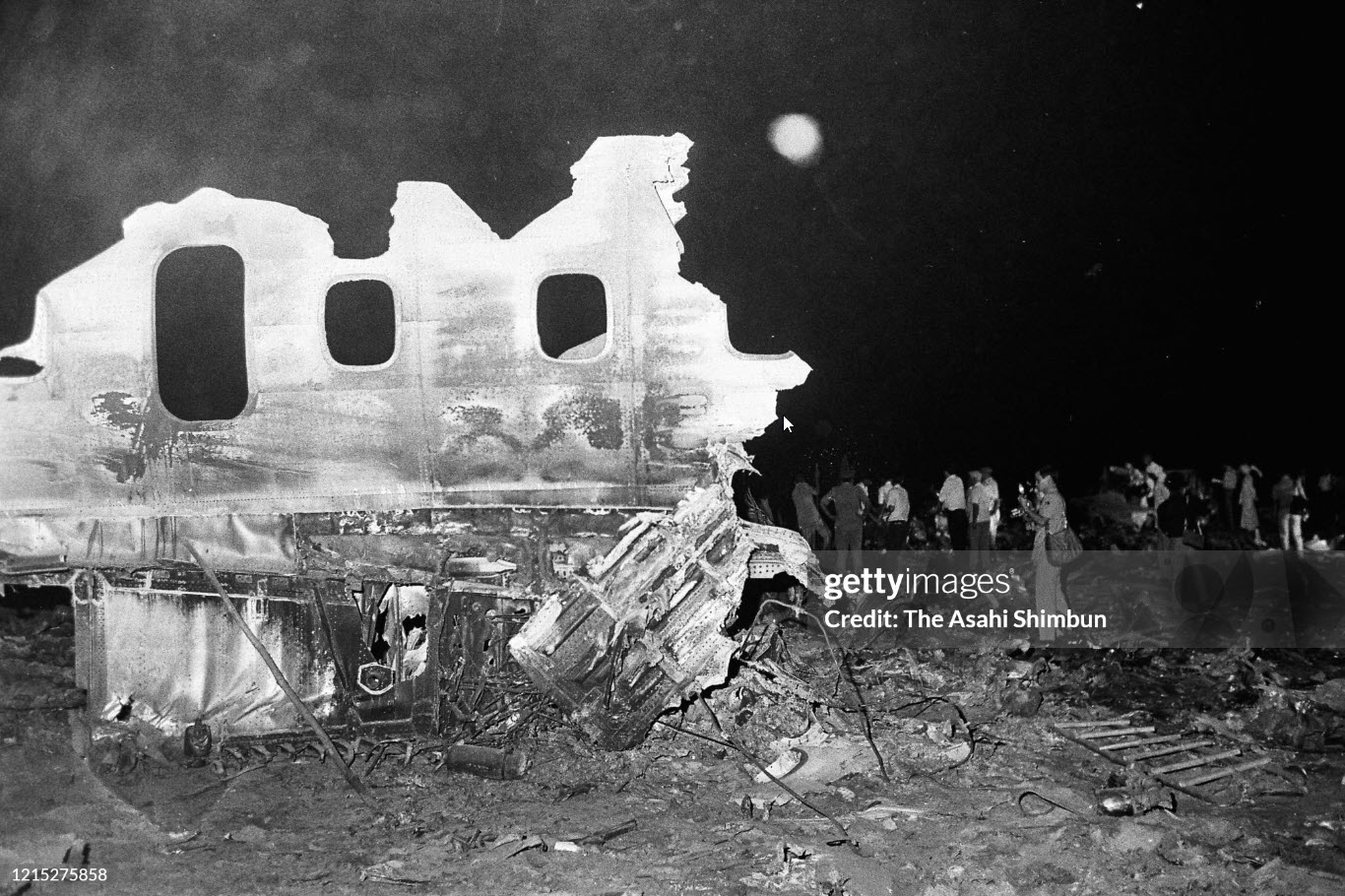
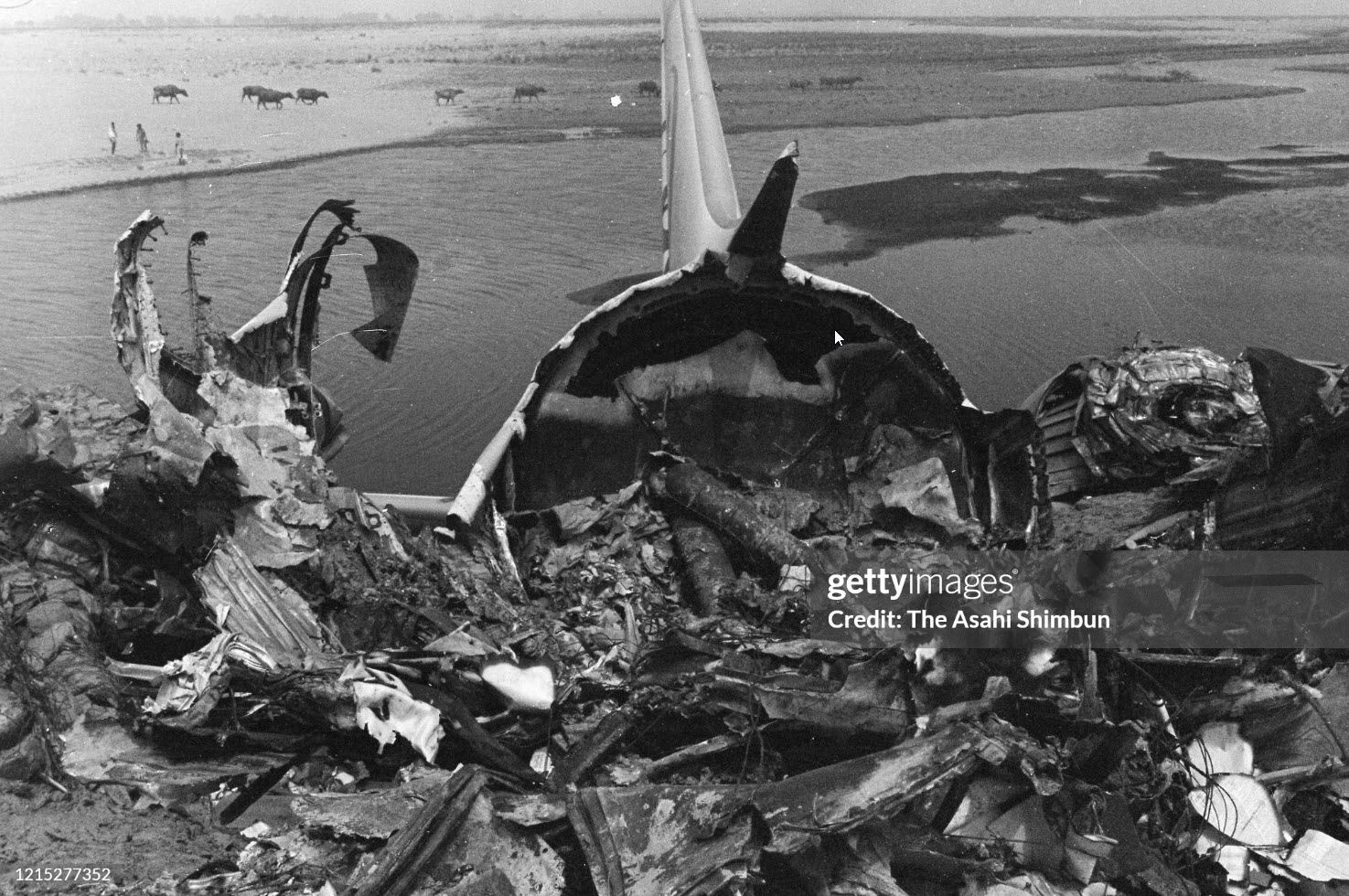
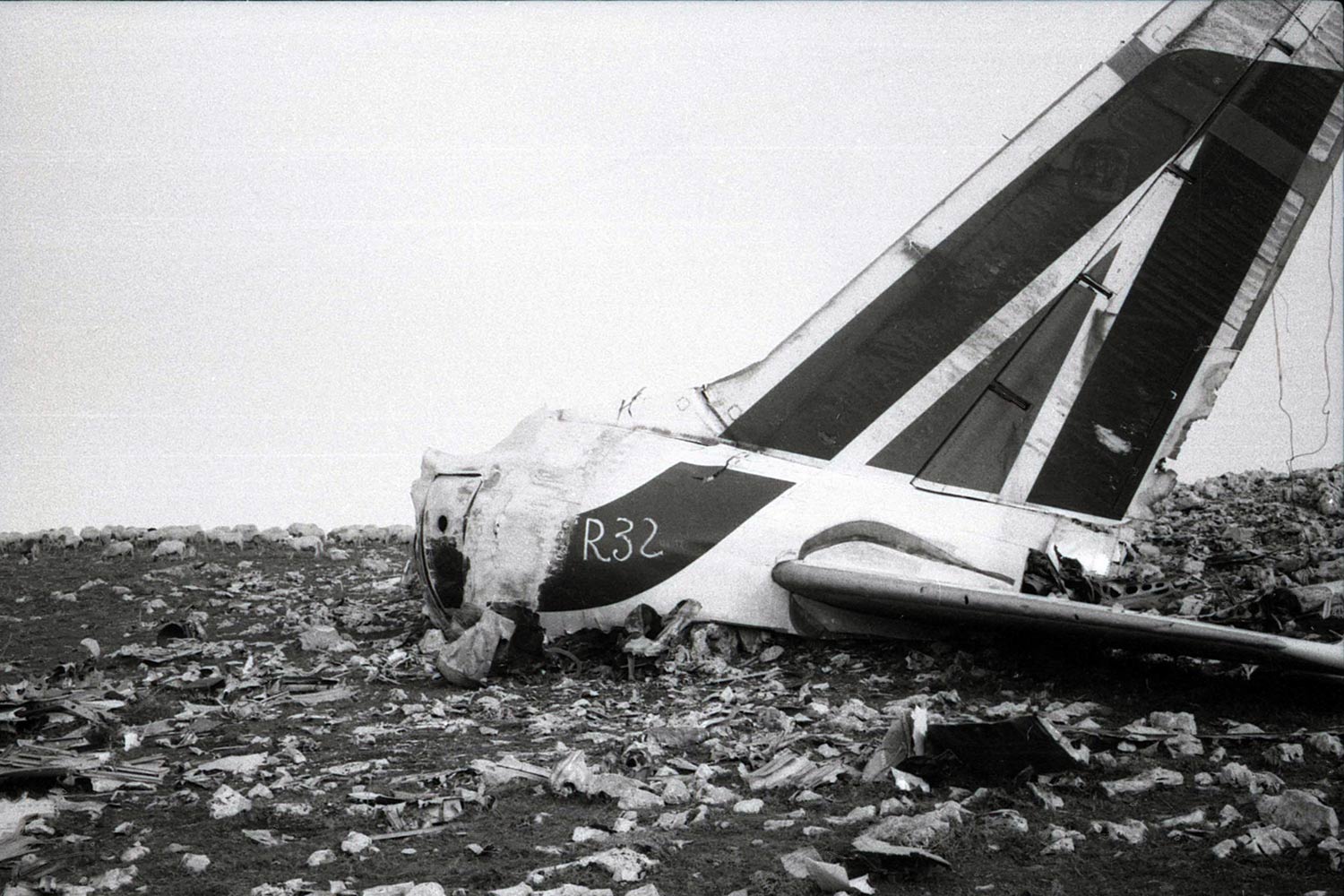
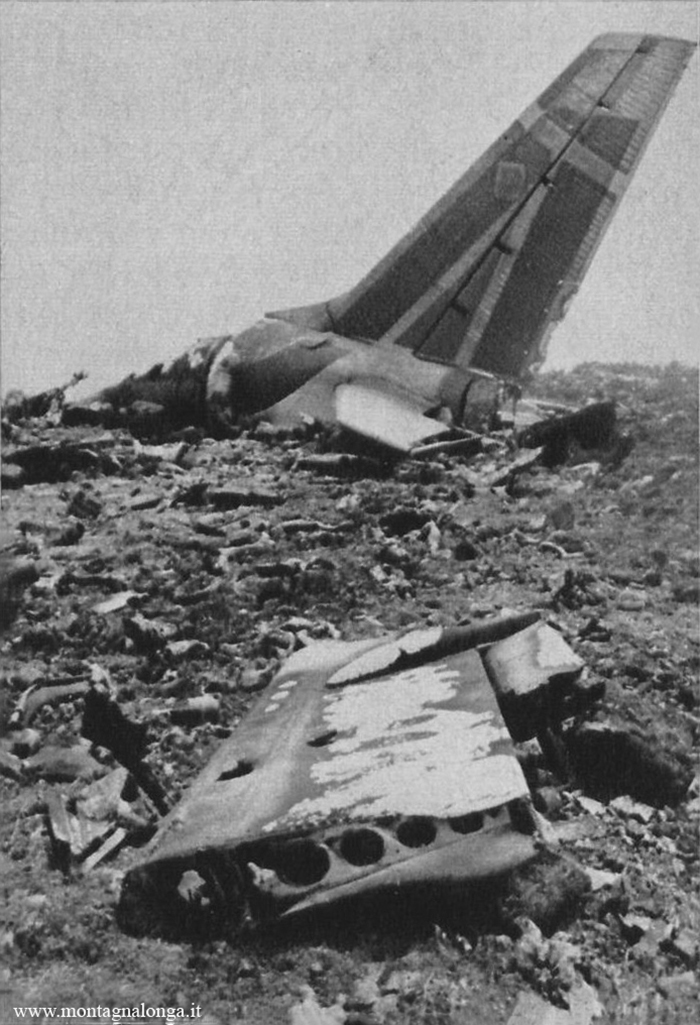
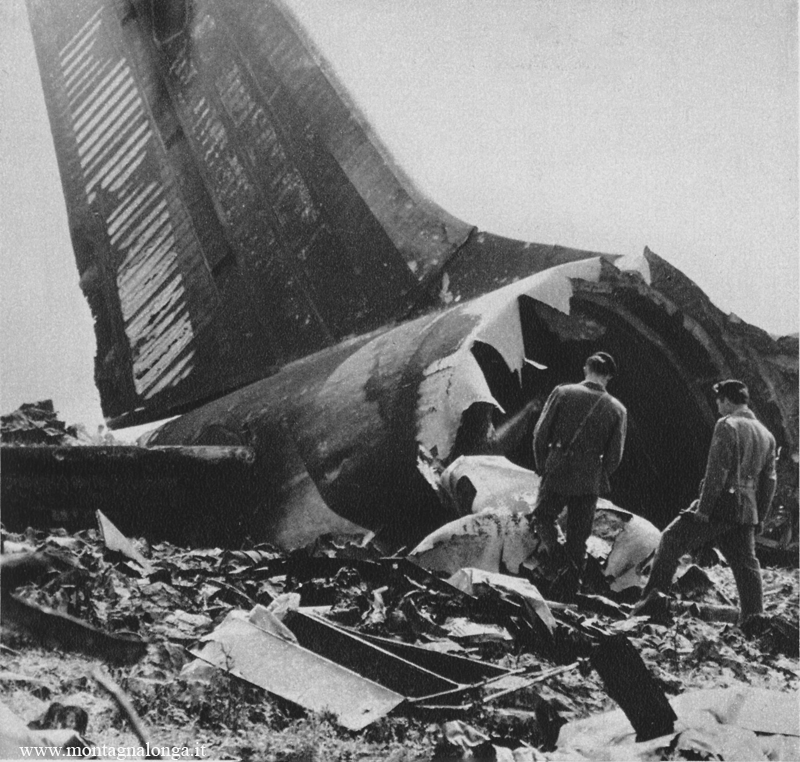
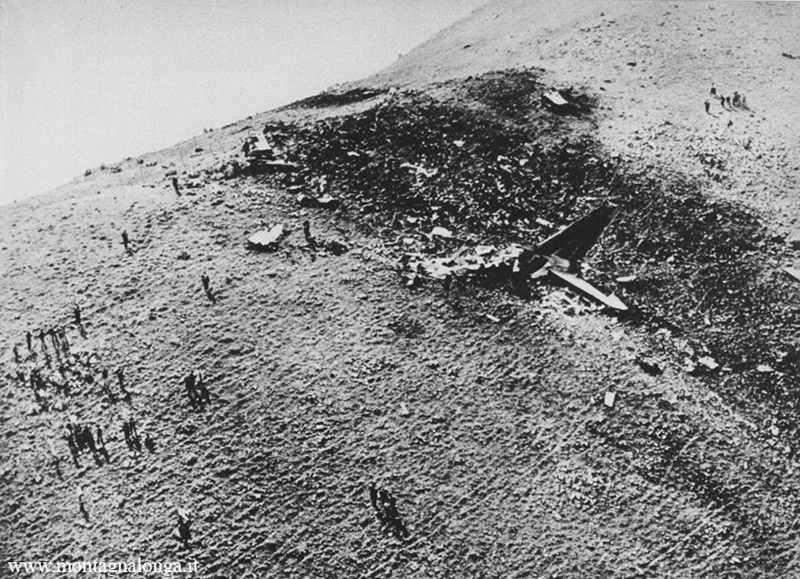
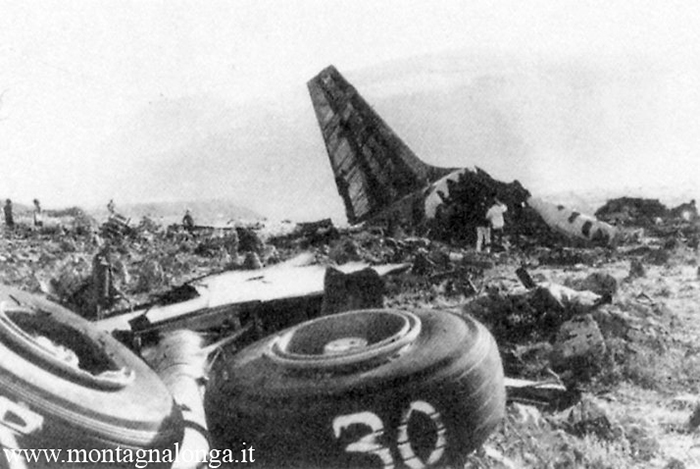
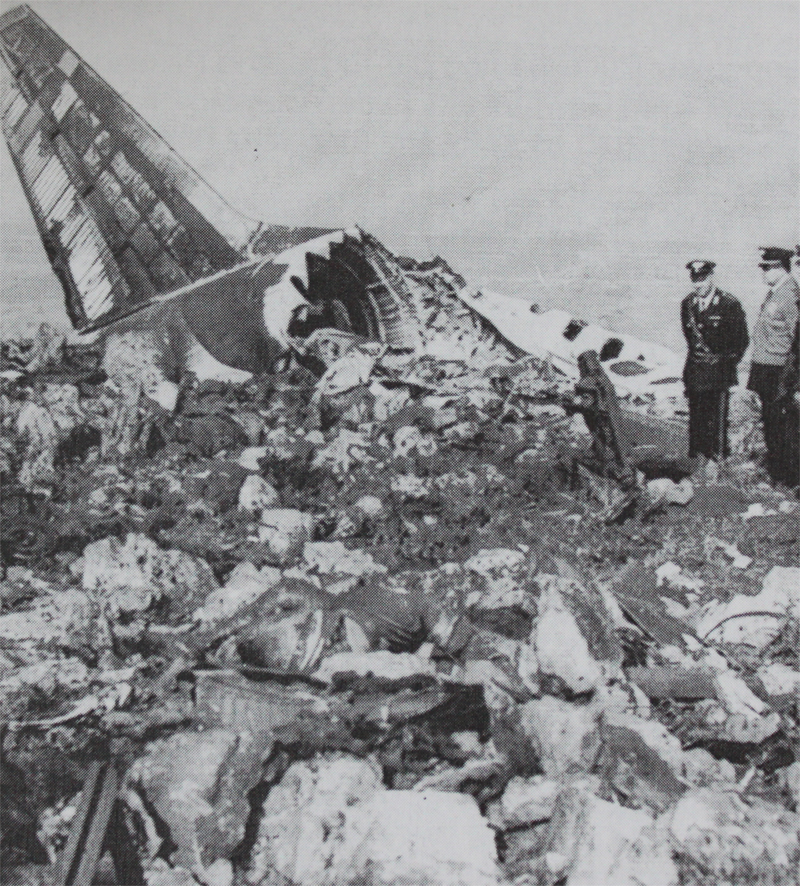
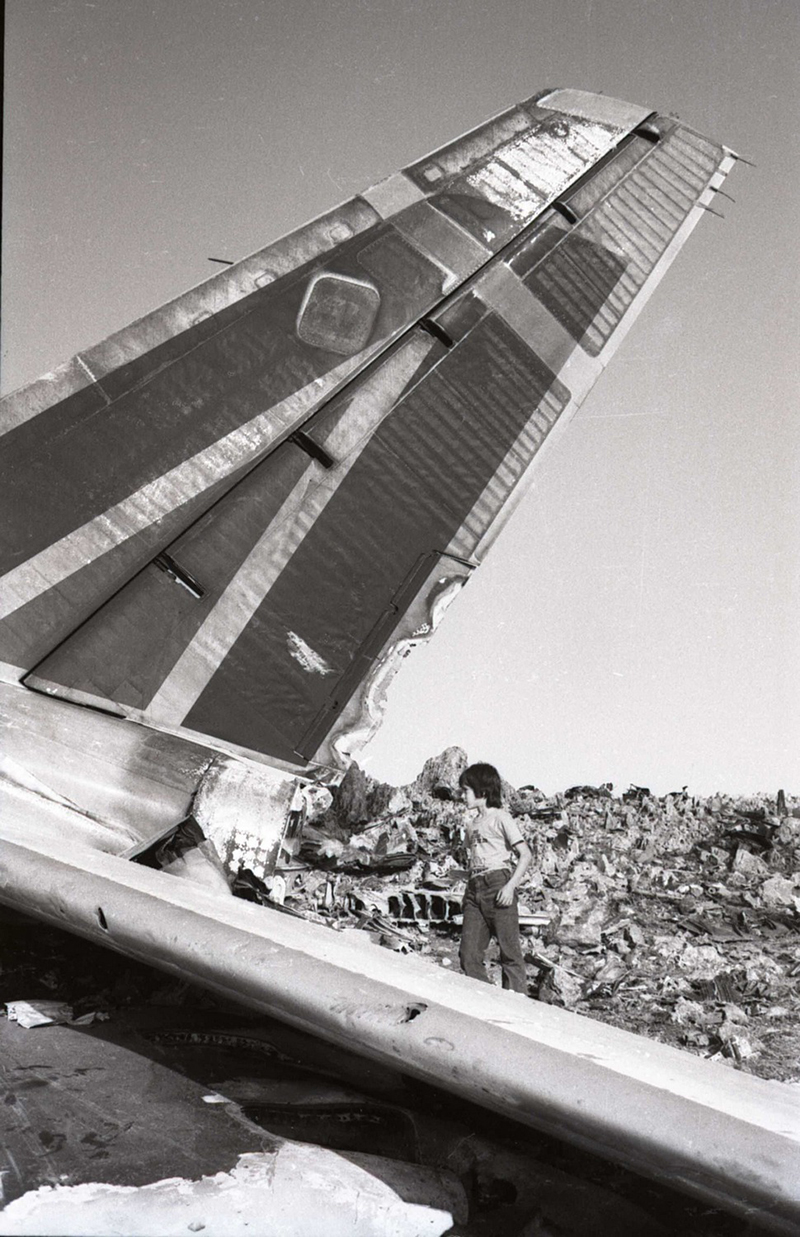
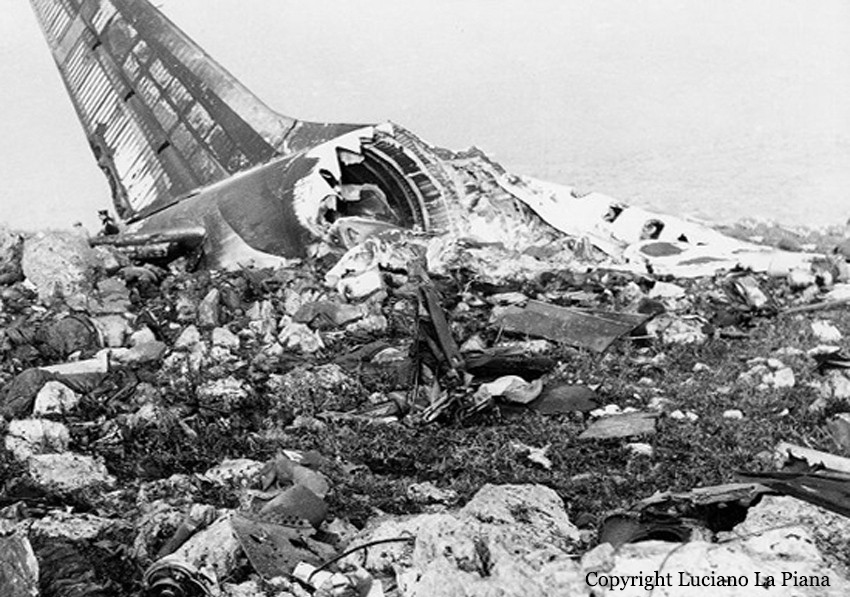
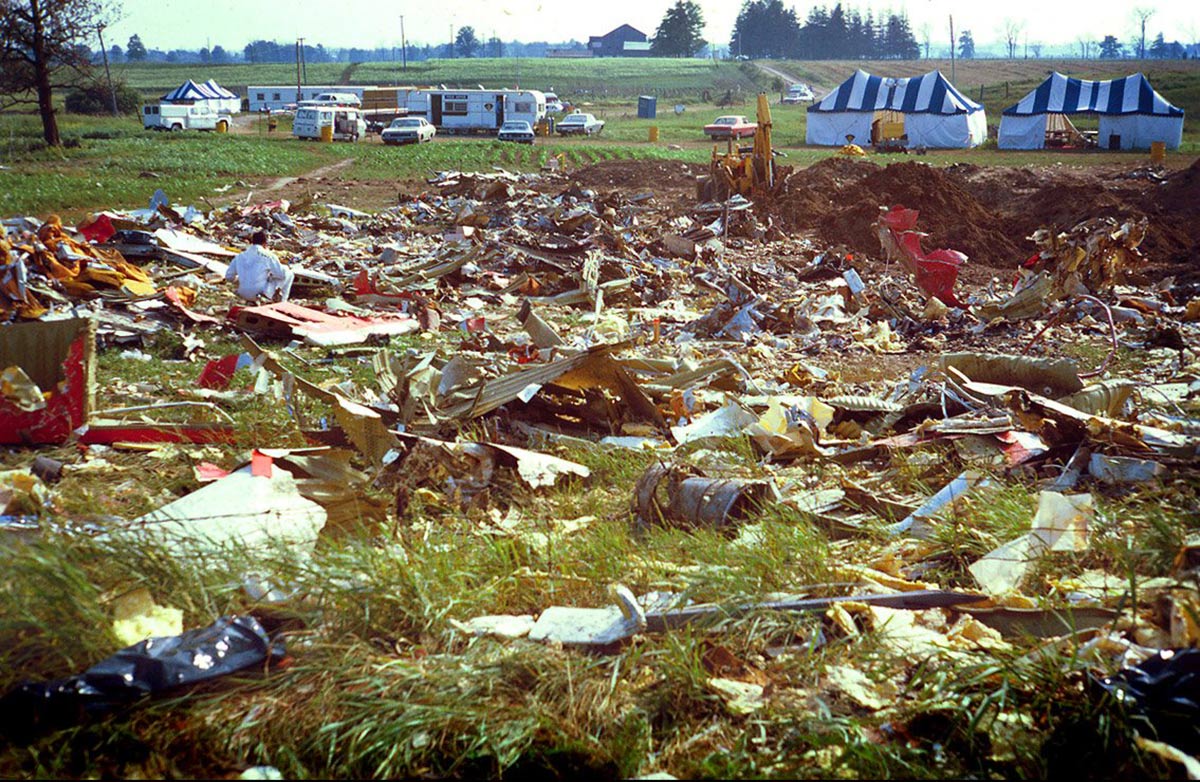
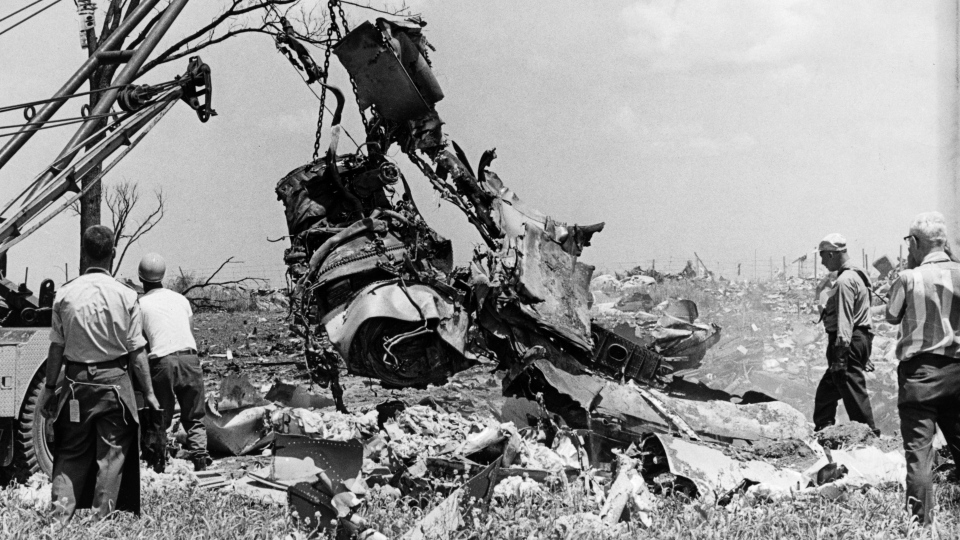
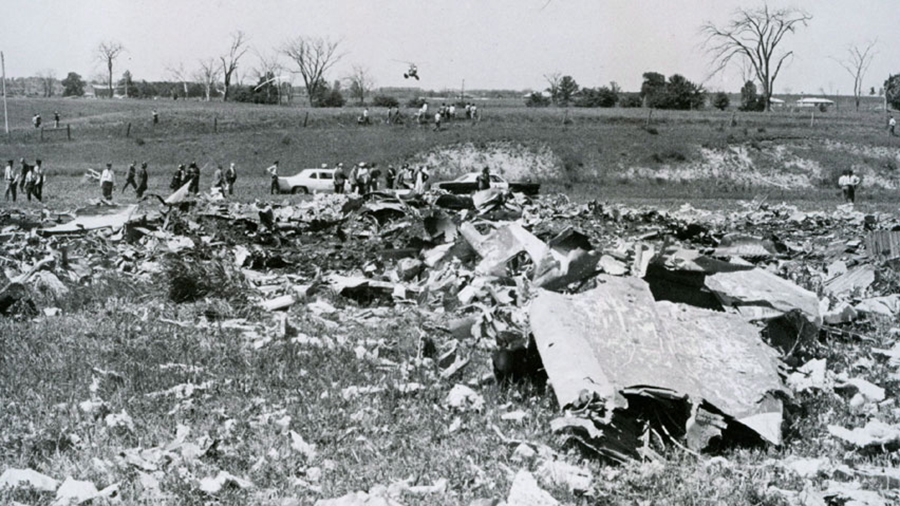
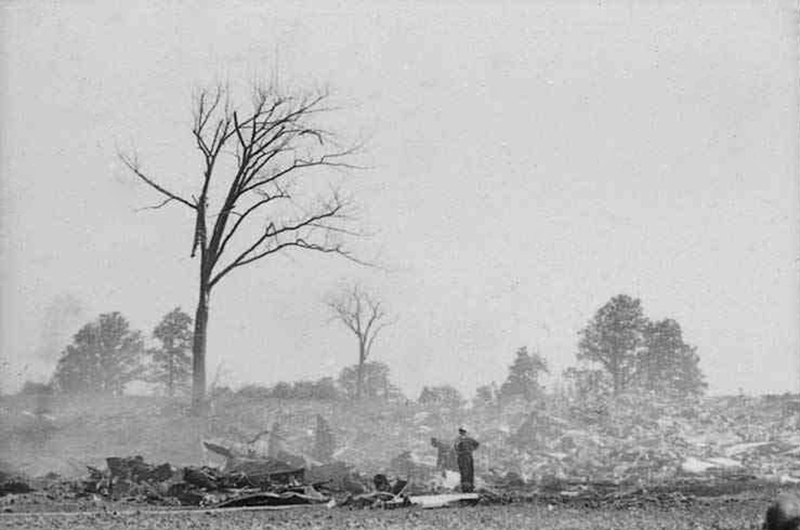
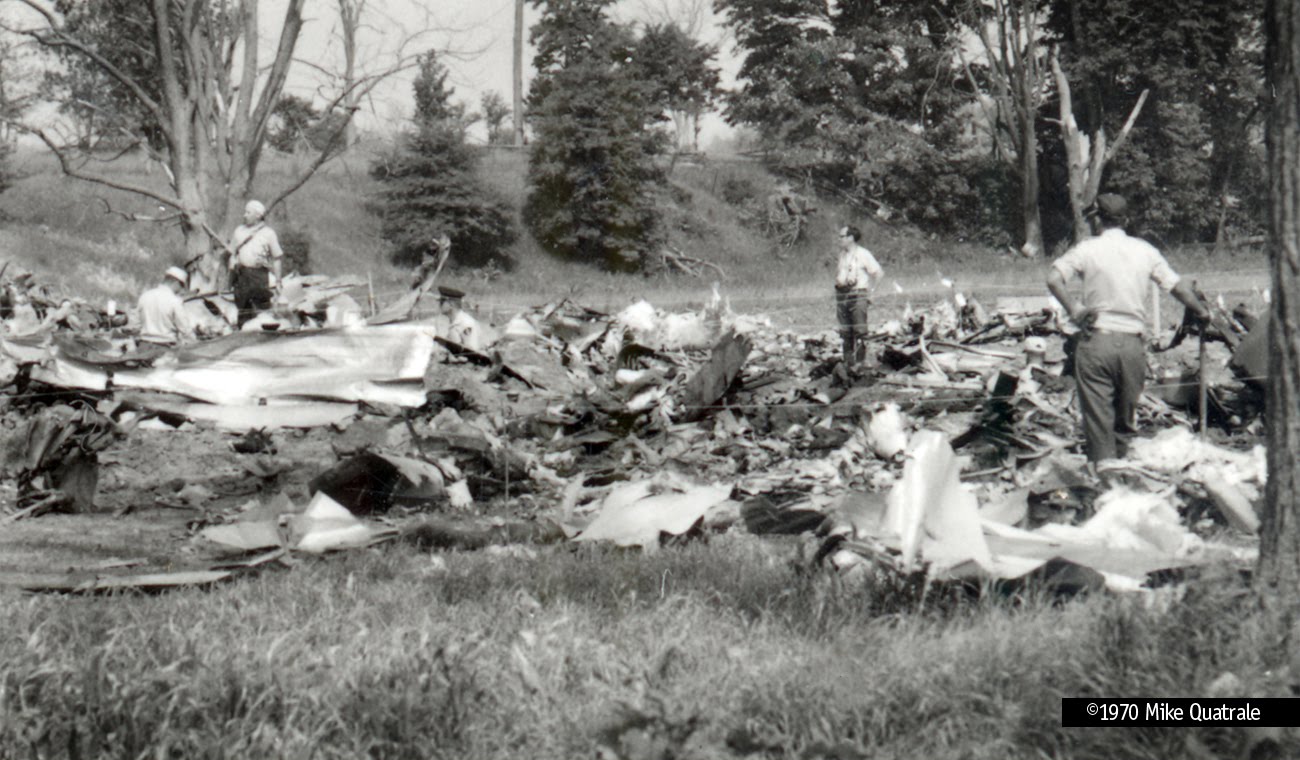
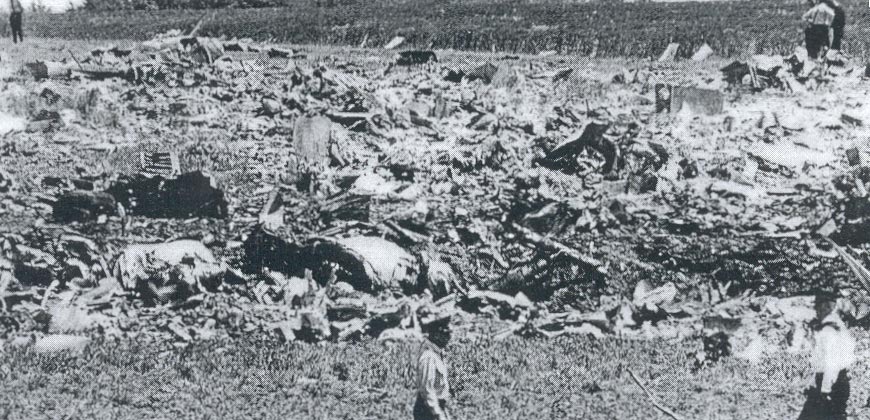
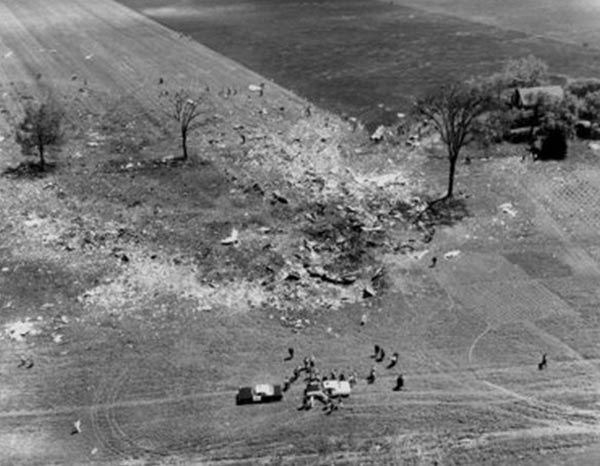
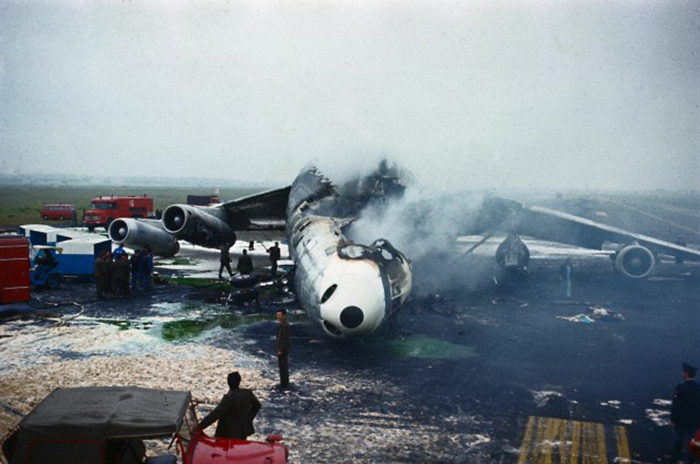
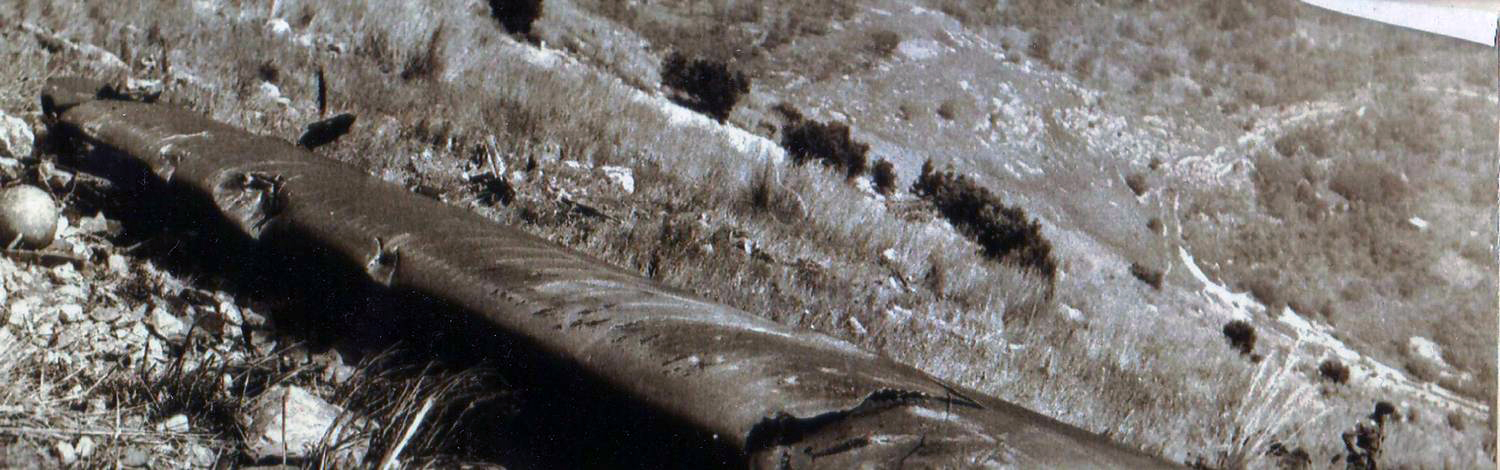
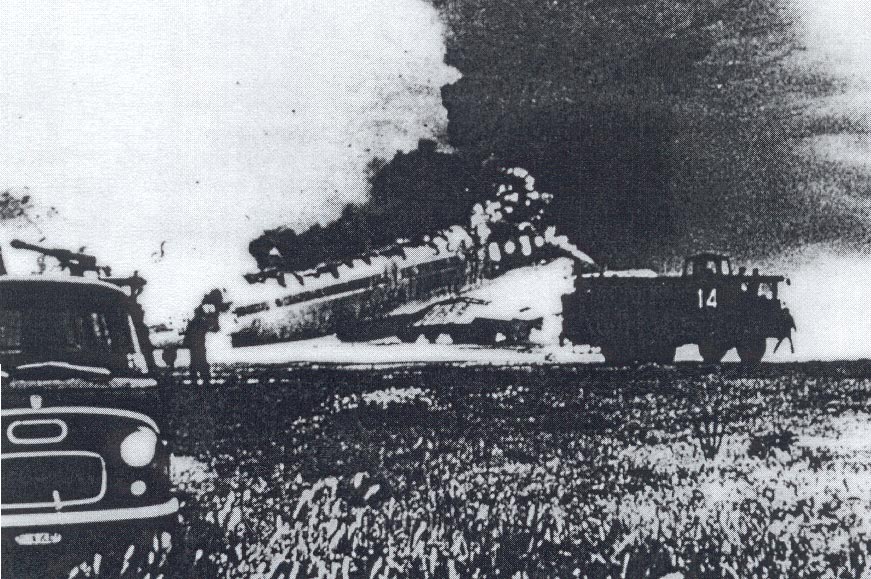
Flight number 621 of Air Canada DC-8-63 CF-TIW with 100 passengers, six cabin air crew and three flight crew aboard on July 5, 1970 from departure at Montreal International Airport until its final crash at Toronto International Airport lasted slightly more than 52 minutes. This aircraft took off at Montreal at 07 hours and 17 minutes EDT, initially touched down on runway 32 at Toronto International Airport at 08 hours 06 minutes and 36 seconds EDT and finally crashed at 08 hours 09 minutes 34 seconds EDT. The flight from Montreal to Toronto was routine. The flight during this interval was also routine. The "In-Range Check" was made when the aircraft was about 10 miles from Toronto International Airport on a southerly heading. The "Before-Landing Check" was made when the aircraft was about 8 miles from this Airport, and just commencing its turn onto final approach. On this Before-Landing cockpit check, which includes the lowering of the undercarriage, the item "spoilers armed" was intentionally omitted. During this period there occurred a conversation between the Captain and the First Officer as to whether the ground spoilers would be armed 'on the flare' or 'on the ground' and an agreement between them as to this was reached. The agreement was that the First Officer would arm them 'on the flare', that is, immediately before the aircraft touched down on the runway. Power was reduced then on the aircraft for the purpose of the flare and the Captain gave the order to the First Officer by saying 'OK'; and immediately thereafter the ground spoilers were deployed. The spoilers were deployed when the aircraft was about 60 feet above the runway. As a result, the aircraft sank rapidly. Practically immediately thereafter the Captain, with an exclamation, applied full throttle to all four engines and pulled back the control panel causing the nose of the aircraft to rotate upwards. During this sequence the First Officer apologized to the Captain for what he had done. Notwithstanding the action taken by the Captain, he did not succeed in preventing the aircraft from touching down on the runway. Instead, the aircraft struck the runway very heavily. It remained on the runway only about half a second and then rose back into the air at which time the ground spoilers commenced to retract and then did retract. When the aircraft struck the runway, number 4 engine and pylon separated from the aircraft and fell on the runway along with a piece of the lower wing plating (which allowed fuel to escape and subsequently ignite). Damage was also done at this time to the attachments relating to number 3 engine, but that engine after touchdown continued to function. After this touchdown, the aircraft climbed to an altitude of 3,100 feet above the ground. During this climb, there were conversations between the First Officer and the aircraft airport control tower from which it is patent, that the air crew considered that they would be able to cause their aircraft to circle for another landing attempt on runway 32. In fact, the air crew did not know, until only about 40 seconds prior to the final crash, that the happening of such final crash was irreversible. During this climb, fire and smoke were seen trailing behind the aircraft intermittently. About 2 and one half minutes after the initial touch down of this aircraft on the runway, the first explosion occurred in the right wing outboard of number 4 engine location causing parts of the outer wing structure to fall free to the ground. Six seconds later, a second explosion occurred in the vicinity of number 3 engine and the engine with its pylon ripped free of the wing and fell to the ground in flames, trailing heavy black smoke. Six and one half seconds later, a third explosion occurred which caused the loss of a large section of the right wing, including the wing tip. The aircraft then went into a violent manoeuvre, and with the right wing still ablaze, lost height rapidly and at the same time more wing plating tore free following which the aircraft struck the ground at a high velocity, about 220 knots in the attitude with the left wing high and the nose low. At final crash, all persons aboard this aircraft were killed.
Probable cause:
Within the meaning of the word "circumstances" ("of any accident") in section 5A of the Aeronautics Act, Revised Statutes of Canada 1952, chapter 2 as amended, there were several contributing circumstances to this accident. Without attempting to weight each or to list them in order of priority, they are set out hereunder:
- The failure of the Captain to follow the procedures laid down in the 'Before-Landing Check' in the Air Canada operating manual, in respect to arming the ground spoilers in this aircraft on this day,
- The action taken by the First Officer, contrary to the order of the Captain on this day, in pulling the ground spoiler actuating lever aft manually to the "Extend", position when the aircraft was about 60 feet above runway 32 at Toronto International Airport,
- The failure of the manufacturer of this aircraft to provide a gate or equivalent means to guard against such inappropriate manual operation of the ground spoiler lever in flight,
- The acceptance and approval by the Ministry of Transport, of the design of the ground spoiler system in this aircraft,
- The acceptance and use by Air Canada of this aircraft with this defective design feature in its ground spoiler system,
- The failure of the manufacturer and Air Canada in their respective manuals unequivocally to inform that the ground spoilers of this aircraft could be deployed when it was in flight by doing what the First Officer did in this case; and, also, to warn of the hazard of extending the ground spoilers when the aircraft is in flight and especially when it is close to the ground,
- The failure of Air Canada to cause its Ground Training School personnel to instruct student pilots that the ground spoilers of this aircraft could be deployed in the way the First Officer did in this case or to warn that the ground spoilers could be deployed when this type of aircraft is in flight and especially when it is close to the ground,
- The failure of the Ministry of Transport to detect the deficiencies and misinformation in the manufacturer's aircraft flight manual as to the operation of the ground spoiler systems on this type of aircraft; and the failure to require the manufacturer in such manual to warn of the danger of inappropriate deployment of the ground spoilers on this type of aircraft when in flight and especially when it is close to the ground,
- The failure of the Ministry of Transport:
1) to have noted the differences in the manuals of Air Canada and other Canadian aircraft operators in relation to the hazards of operating this ground spoiler in this aircraft,
2) to have alerted Air Canada of this, and
3) to have taken appropriate remedial action so that Air Canada's manual in respect thereto was not deficient in respect thereto,
- Under the subject overload conditions, the failure of the manufacturer to design attachments of the engine pod to wing structure to provide for safe sequential separation, or failing which to otherwise ensure the integrity of the fuel and the electrical systems.