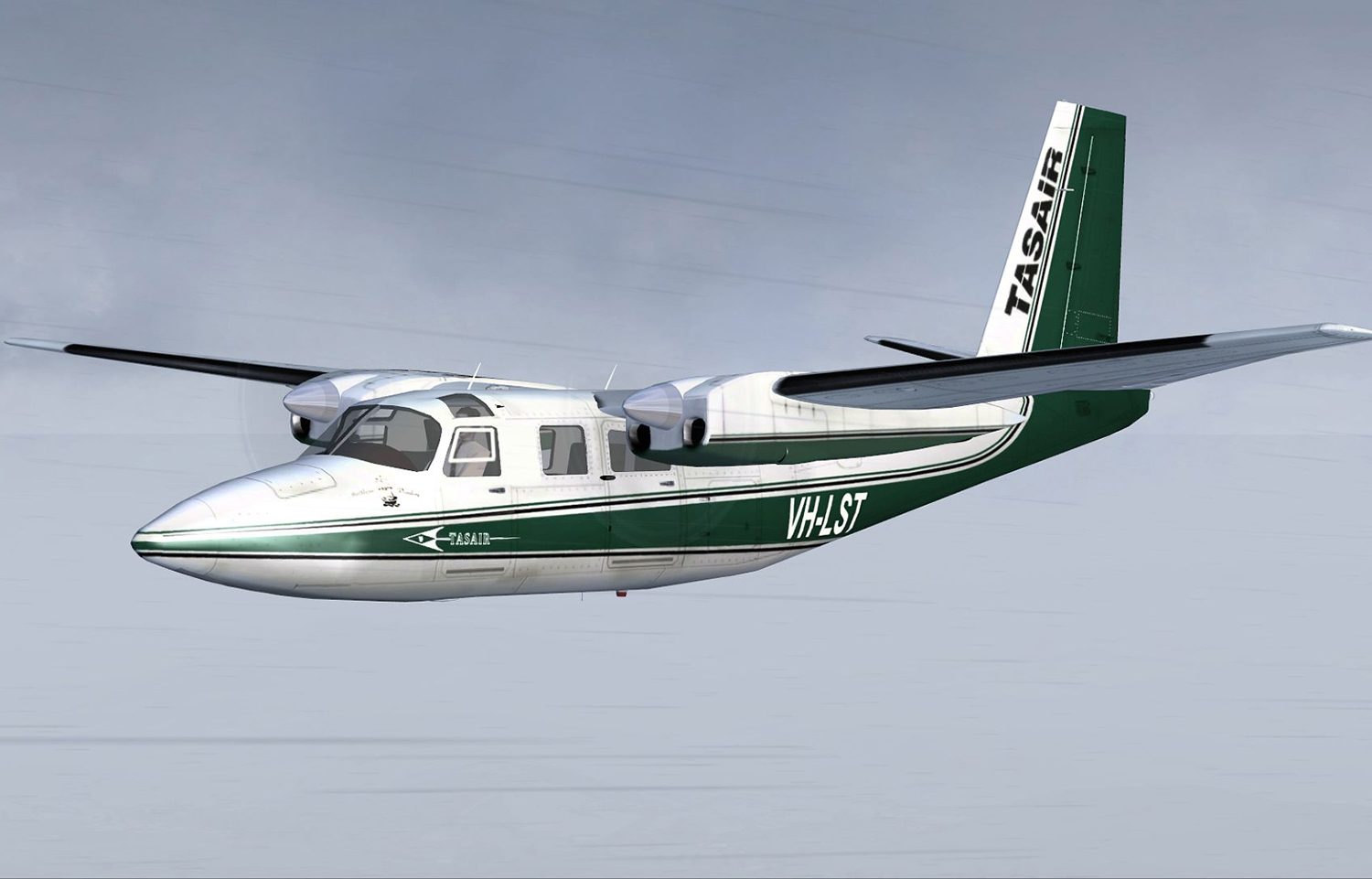
Crash of a Rockwell Shrike Commander 500S near Hobart: 1 killed
Date & Time:
Feb 19, 2004 at 1643 LT
Registration:
VH-LST
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Hobart – Devonport
MSN:
500-3111
YOM:
1971
Crew on board:
1
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
1
Captain / Total hours on type:
40.00
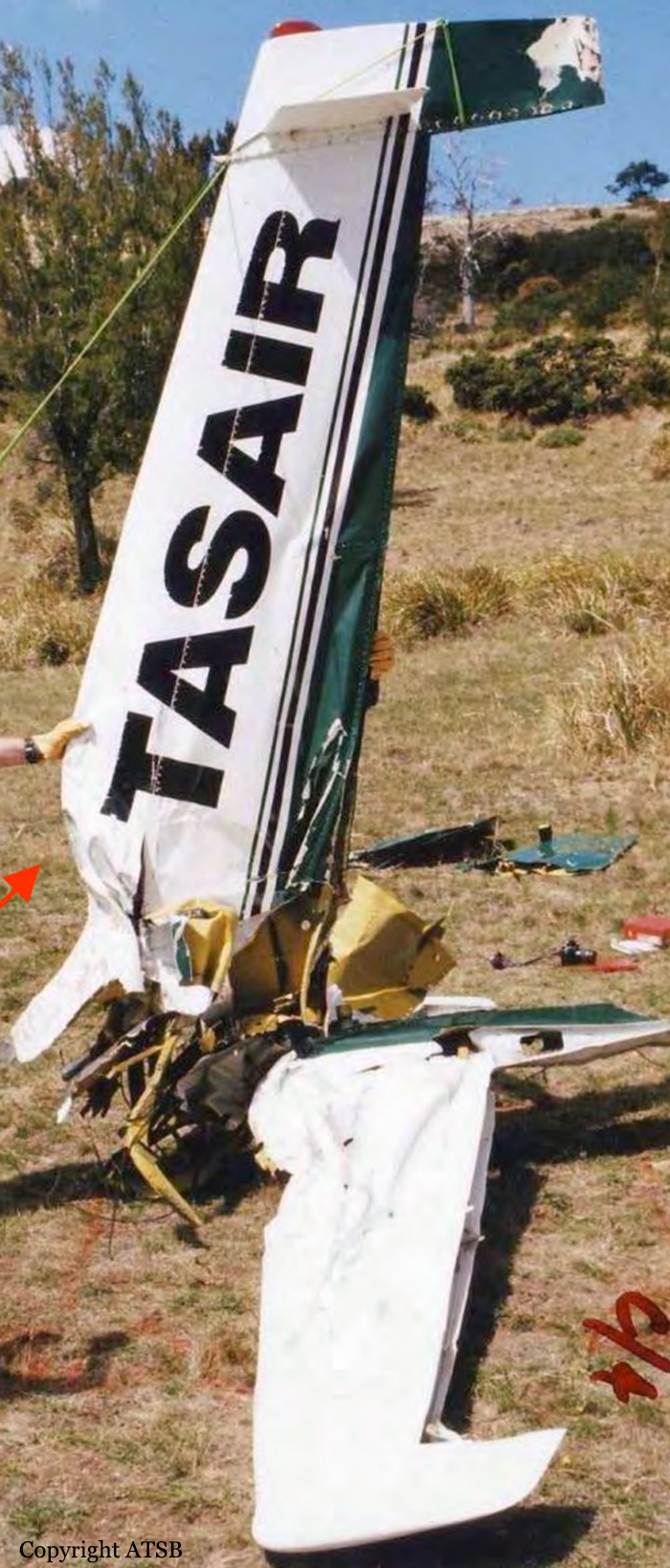
Circumstances:
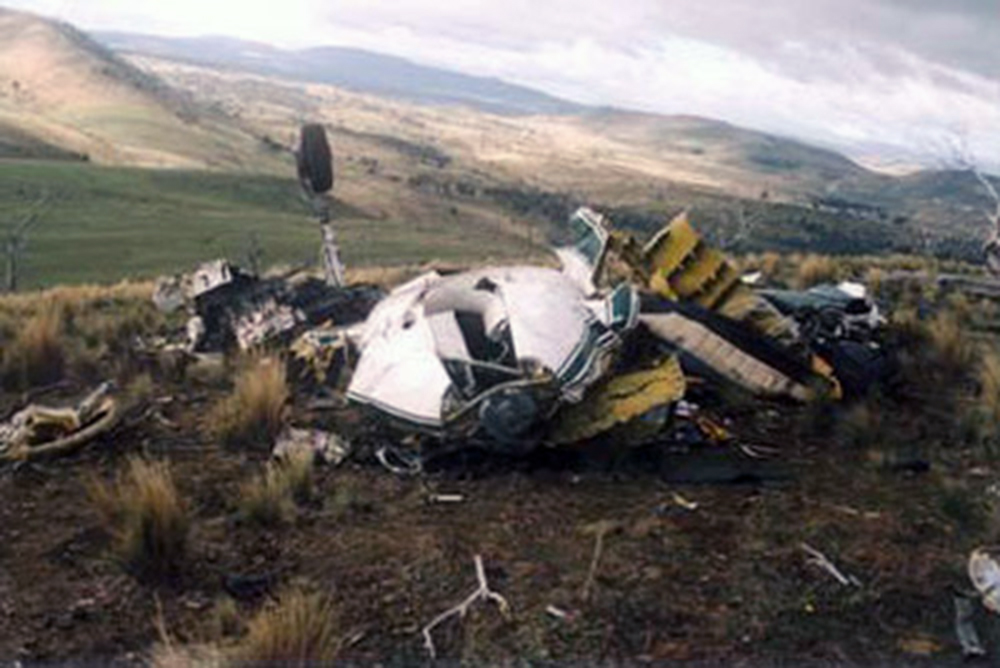
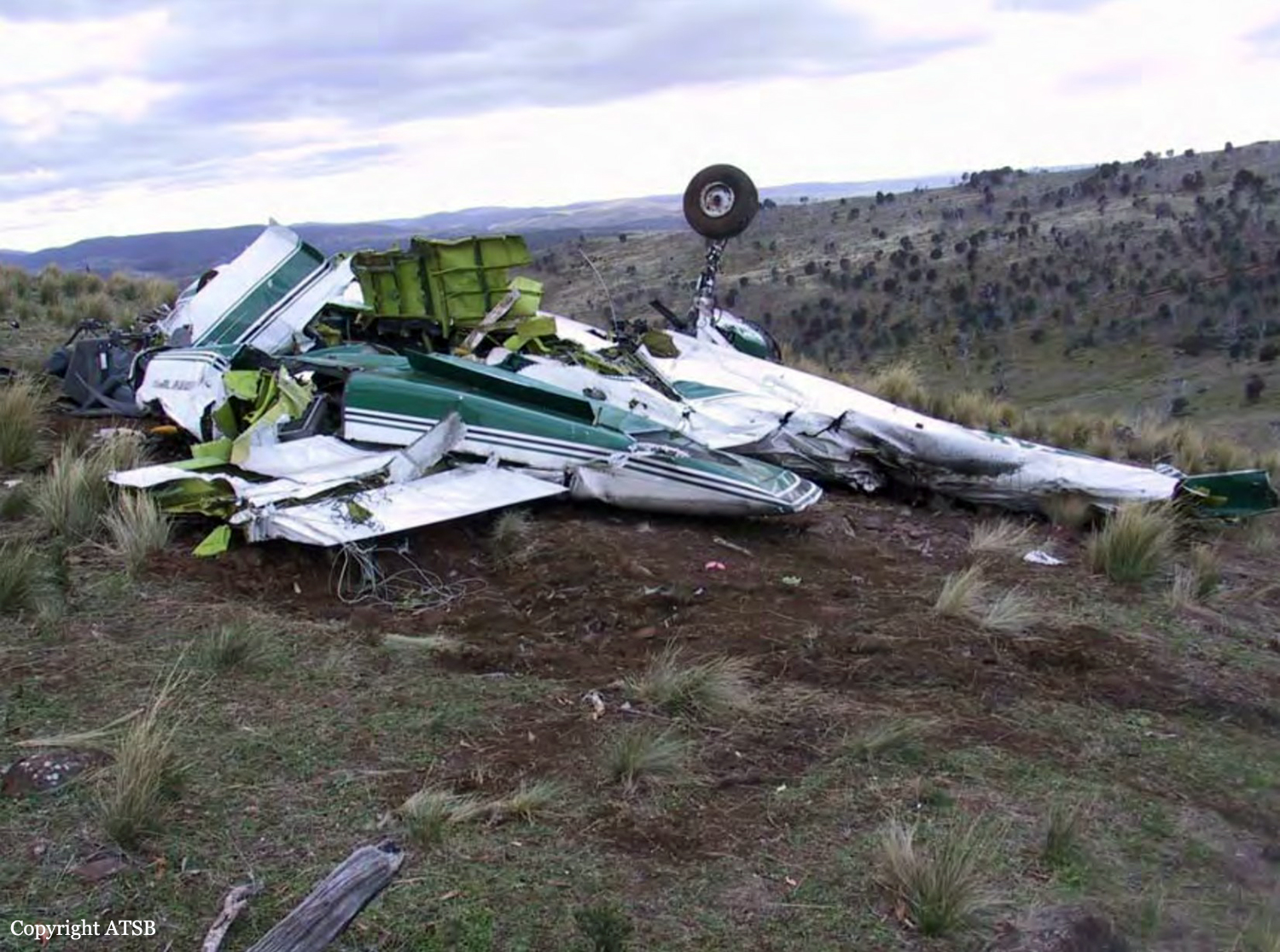
The aircraft commenced taxying at Hobart for a Visual Flight Rules (VFR) ferry flight to Devonport. The pilot, who was the sole occupant, reported a departure time of 1643 to air traffic control, with an intention to climb to 8,500 ft and to fly a track of 319 degrees magnetic. Due to following traffic, the pilot was required to report leaving specific altitudes. At 1646, the pilot reported leaving 4,500 ft, and was advised that air traffic services were terminated. The acknowledgement of that call was the last communication heard from the pilot. At about 1800, the operator’s staff at Devonport advised the Hobart base that the aircraft had not arrived. The operator advised AusSAR and the Hobart air traffic control tower, and organised company search aircraft from both Hobart and Devonport. The non-flying occupant of the Hobart search aircraft sighted the wreckage at about 1930. Shortly after, a search and rescue helicopter arrived at the accident site. The pilot of the aircraft was found fatally injured in the wreckage. The wreckage was located 58 km from Hobart airport on a bearing of 320 degrees magnetic. Based on predictions of aircraft performance and the distance of the accident site from Hobart, the estimated time of the accident was 1656. There were no eyewitnesses to the accident. Aircraft flight profile The aircraft was not equipped with a flight data recorder or cockpit voice recorder, nor was it required to be. As such, and given that the aircraft was operating outside of radar coverage, there was no recorded flight profile information available. The pilot was not required to report cruising at 8,500 ft and there was no evidence to confirm that the aircraft had reached that altitude. However, based on the normal climb and cruise performance, forecast winds and the radio broadcasts made by the pilot, the aircraft should have reached an altitude of 8,500 ft approximately 35 km from Hobart at about 1651, which was 5 minutes prior to the estimated time of the accident at 1656.
Probable cause:
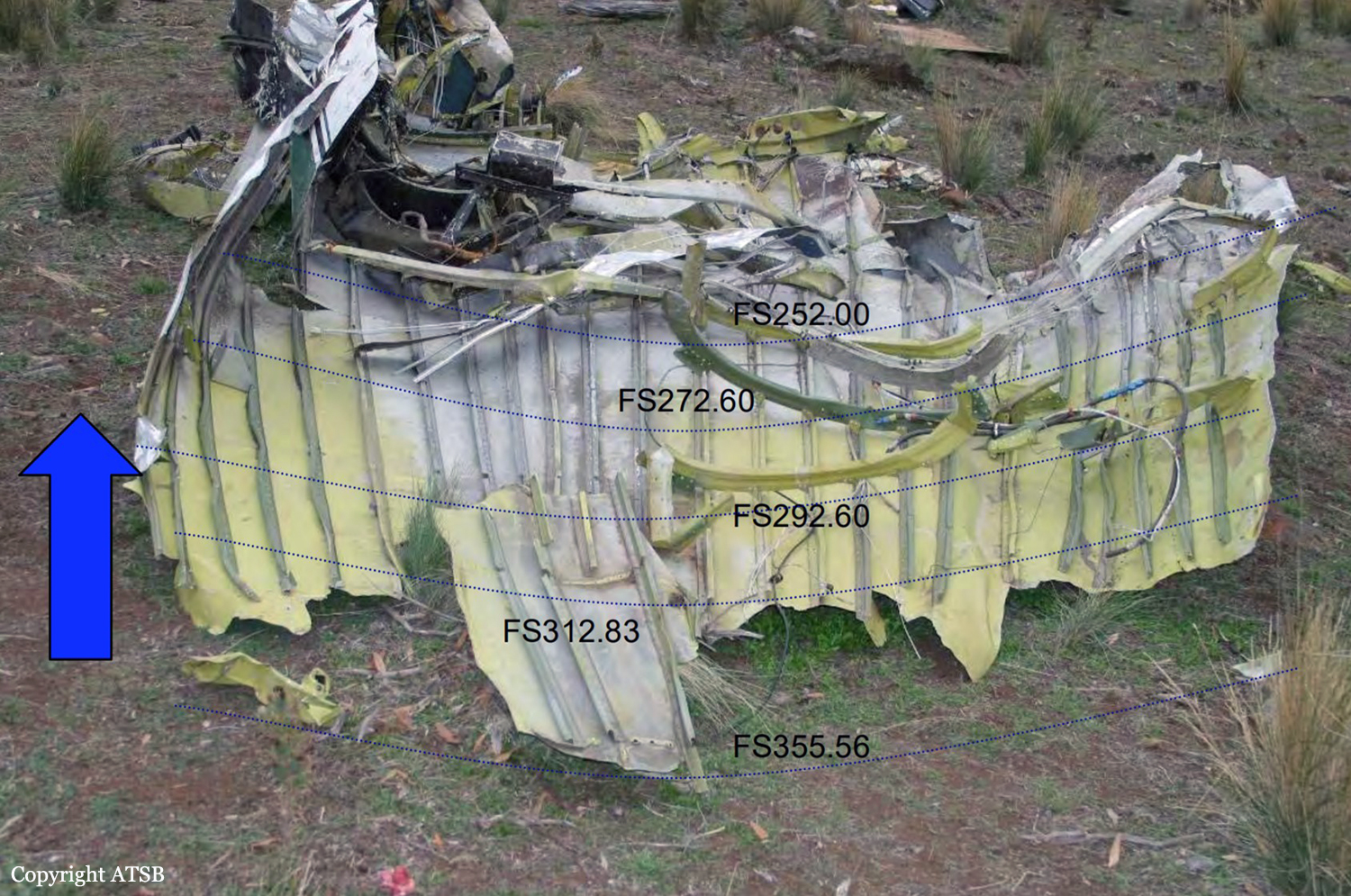
The trajectory analysis provided the ATSB with a high degree of confidence with respect to the aircraft altitude and speed at the time of the in-flight breakup. The aircraft’s speed could have readily accelerated to Vne during a rapid descent from the nominated cruise altitude of 8,500 ft to the break-up altitude of around 3,150 ft. At such a speed, a relatively small control input force or gusts encountered in the longitudinal (pitch) axis of the aircraft could have resulted in the symmetrical downward wing overloading and failure that occurred. There is no compelling evidence to support any one reason for the departure of the aircraft from the cruise altitude into a high speed dive type situation. However, there are a number of factors that provide some weight to the possibility of a flight upset related to operation of the autopilot. These factors include:
• The lack of any reference in the operations manual to the installation of a Bendix FCS-810 autopilot in LST and the lack of information in the operations manual on the operation of the FCS-810 autopilot
• The pilot’s relative inexperience in the operation of the particular autopilot system fitted to LST
• The operating characteristics of the autopilot system fitted to LST
• The illegible nature of the Aircraft Flight Manual supplement pertaining to the limitations and operating procedures for the autopilot system fitted to LST
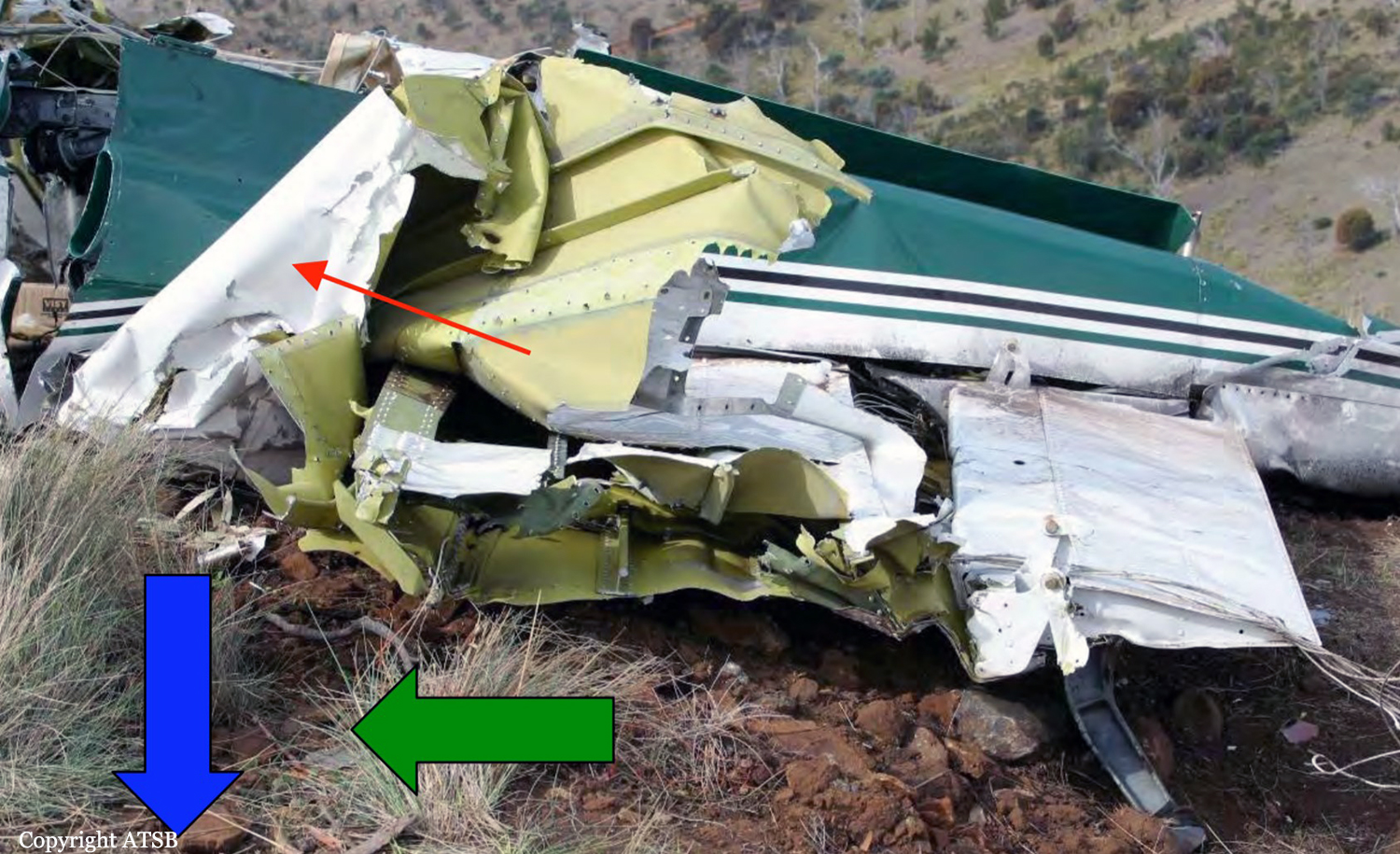
• The autopilot controller pitch command wheel being found at the accident site in the maximum nose-down position
• Both elevator trim tabs being found at the accident site at or close to the maximum nose-down trim position. However, it is not possible to discount other explanations for the departure from cruise flight, including a runaway pitch-trim condition, pilot incapacitation, the effects of mountain waves and/or severe turbulence, or a combination of any of the above. On the evidence available to the investigation, it was not possible to conclusively determine the circumstances that led to the aircraft descending at speed to the altitude at which the in-flight breakup occurred.
• The lack of any reference in the operations manual to the installation of a Bendix FCS-810 autopilot in LST and the lack of information in the operations manual on the operation of the FCS-810 autopilot
• The pilot’s relative inexperience in the operation of the particular autopilot system fitted to LST
• The operating characteristics of the autopilot system fitted to LST
• The illegible nature of the Aircraft Flight Manual supplement pertaining to the limitations and operating procedures for the autopilot system fitted to LST
• The autopilot controller pitch command wheel being found at the accident site in the maximum nose-down position
• Both elevator trim tabs being found at the accident site at or close to the maximum nose-down trim position. However, it is not possible to discount other explanations for the departure from cruise flight, including a runaway pitch-trim condition, pilot incapacitation, the effects of mountain waves and/or severe turbulence, or a combination of any of the above. On the evidence available to the investigation, it was not possible to conclusively determine the circumstances that led to the aircraft descending at speed to the altitude at which the in-flight breakup occurred.
Final Report: