Circumstances:
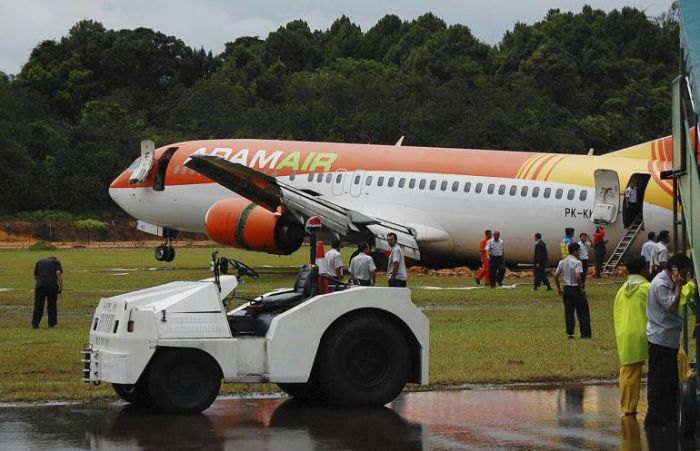
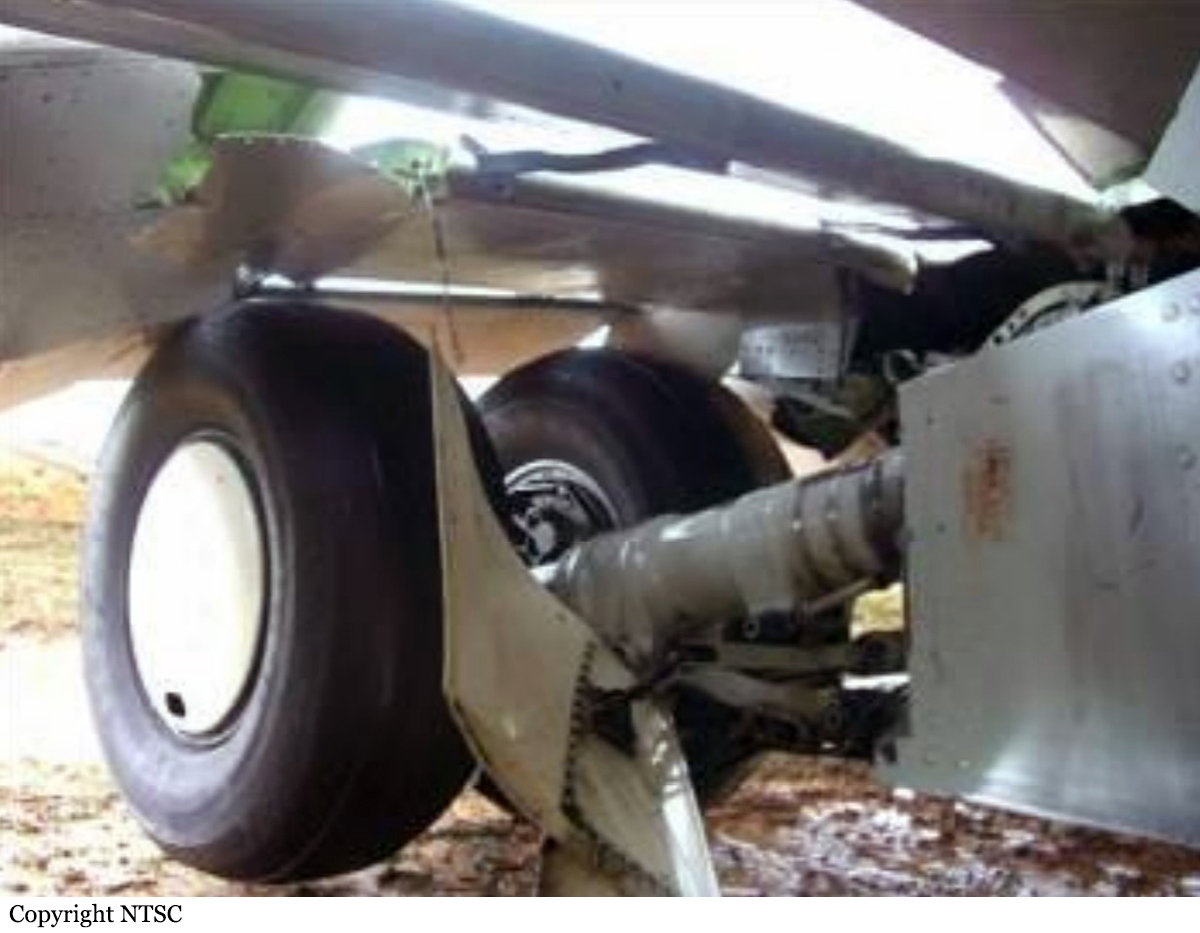
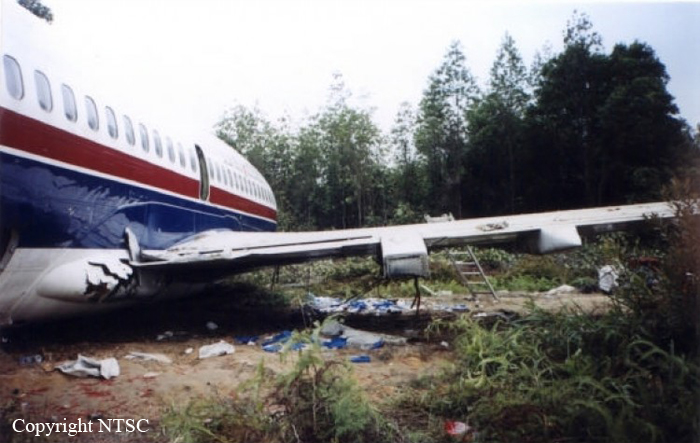
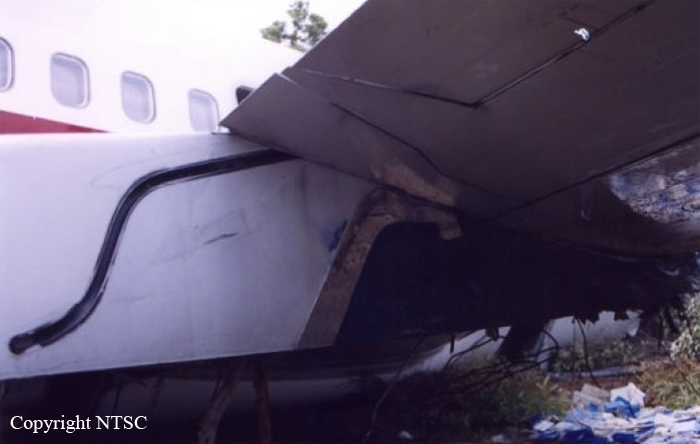
On 10 March 2008, a Boeing Company 737-400 aircraft, registered PK-KKT, was being operated by Adam SkyConnection Airlines (Adam Air) as scheduled passenger flight with flight number DHI292. The flight departed Soekarno – Hatta Airport, Jakarta at 01:30 UTC with destination Hang Nadim Airport, Batam and the estimated time of arrival was 03:05 UTC. On board in this flight were 177 people consisted of two pilots, four flight attendants, and 171 passengers. The Pilot in Command (PIC) acted as pilot flying (PF) and the Second in Command (SIC) acted as pilot monitoring (PM). The flight until commencing descend was uneventful. Prior to descend, the flight crew received weather information indicating that the weather was fine. At 0302 UTC the flight crew contacted Hang Nadim tower controller and informed them that the visibility was 1,000 meters and they were sequence number three for landing runway 04. The flight crew of the aircraft on sequence number two informed to Hang Nadim tower controller that the runway was insight at an altitude of about 500 feet. The Hang Nadim tower controller forwarded the information to the flight crew of DHI 292, and followed this by issuing landing clearance, and additional information that the wind velocity was 360 degrees at 8 knots and heavy rain. The DHI 292 flight crew acknowledged the information. The landing configuration used flaps 40 degrees with landing speed of 136 knots. The flight crew were able to see the runway prior to the Decision Altitude (DA), however the PIC was convinced that continuing the approach to landing was unsafe and elected to go around. The Hang Nadim tower controller instructed the flight crew to climb to 3000 feet, maintain runway heading, and contact Singapore Approach. At 0319 UTC, DHI 292 was established on the localizer runway 04, and the Hang Nadim tower controller informed them that the visibility improved to 2,000 meters. While on final approach, the flight crew DHI 292 reported that the runway was in sight and the Hang Nadim tower controller issued a landing clearance. On touchdown, the crew felt that the main wheels barely touch the runway first. During the landing roll, as the ground speed decreased below 30 knots, the aircraft yawed to the right. The flight crew attempted to steer the aircraft back to centerline by applying full left rudder. The aircraft continued yaw to the right and came to stop on the runway shoulder at approximately 40 meters from the right side of the runway edge, and 2,760 meters from the runway 04 threshold. No one was injured in this accident. The aircraft was seriously damaged with the right main landing gear assembly detached and collapsing backward and damaging the right wing and flaps. The right engine was displaced from its attachment point.
Probable cause:
The Flight Data Recorder (FDR) and the Cockpit Voice Recorder (CVR) data were downloaded. The CVR data showed that the aircraft was flying below the correct glide path indicated by a glide slope aural warning, and the crew had difficulty in recovering the condition. The CVR also recorded landing gear warning after touchdown which indicated the landing gear had collapsed. The FDR data showed that the vertical acceleration during landing was 2.97 g, however this amount of vertical acceleration should not damage the landing gear. The FDR data showed that just after touchdown, the right main landing gear collapsed. The FDR also recorded that the aircraft experienced hard landing and had bounced on a previous flight, and the value of the vertical acceleration recorded was 1.78 g. It was most likely that the hard landing and bounce had affected the strength of the landing gear. The examination of the failed landing gear also found corrosion on the fracture surface of the right main landing gear strut.