Circumstances:
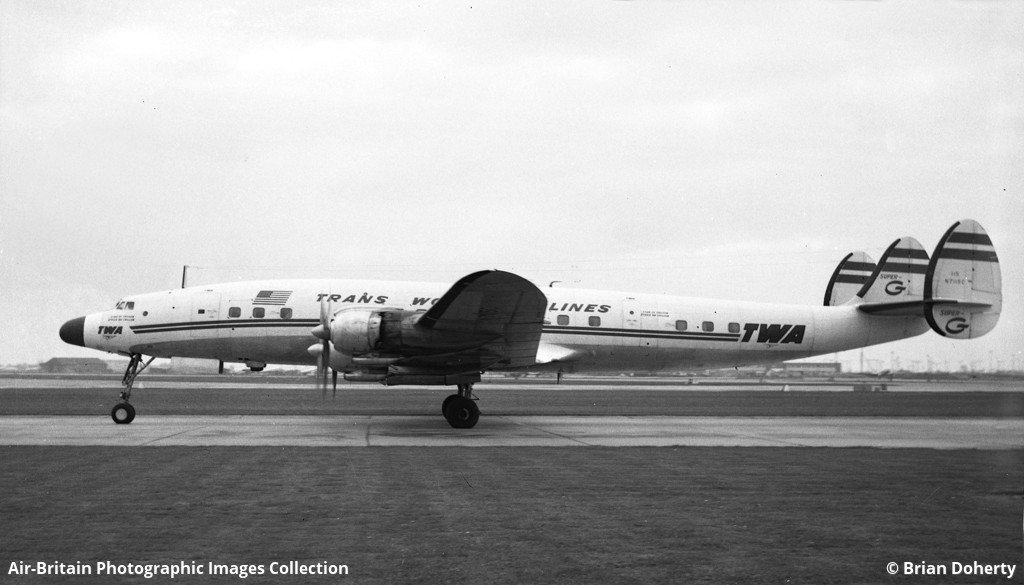
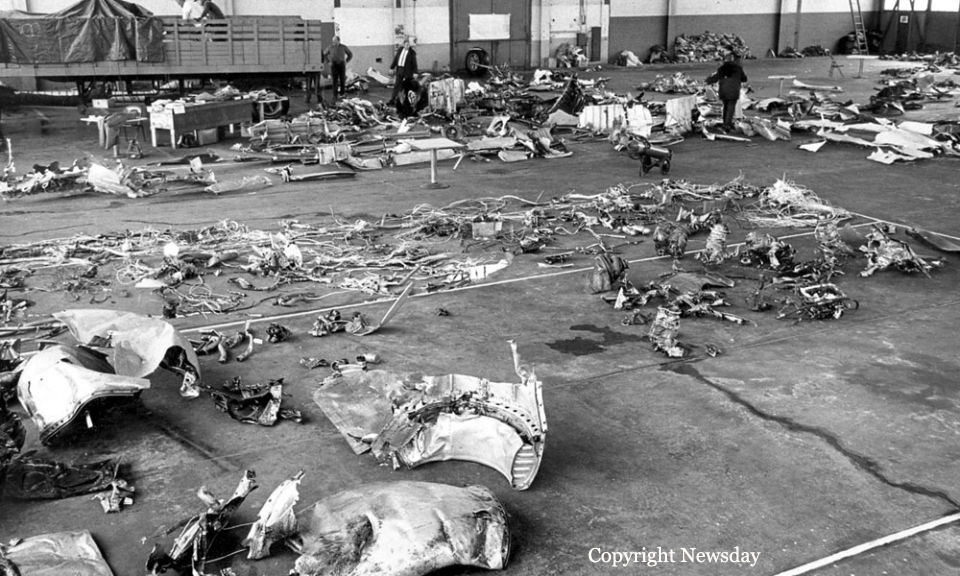
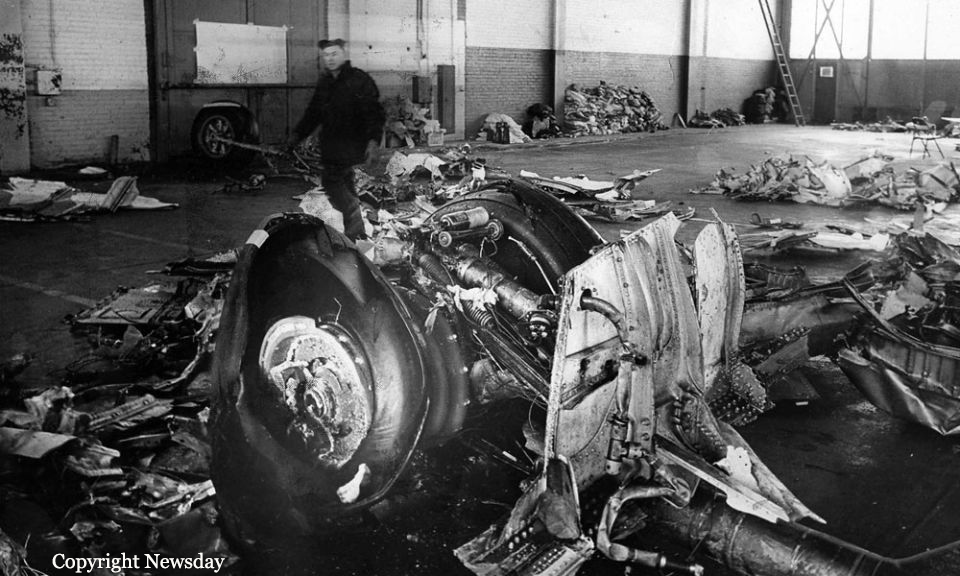
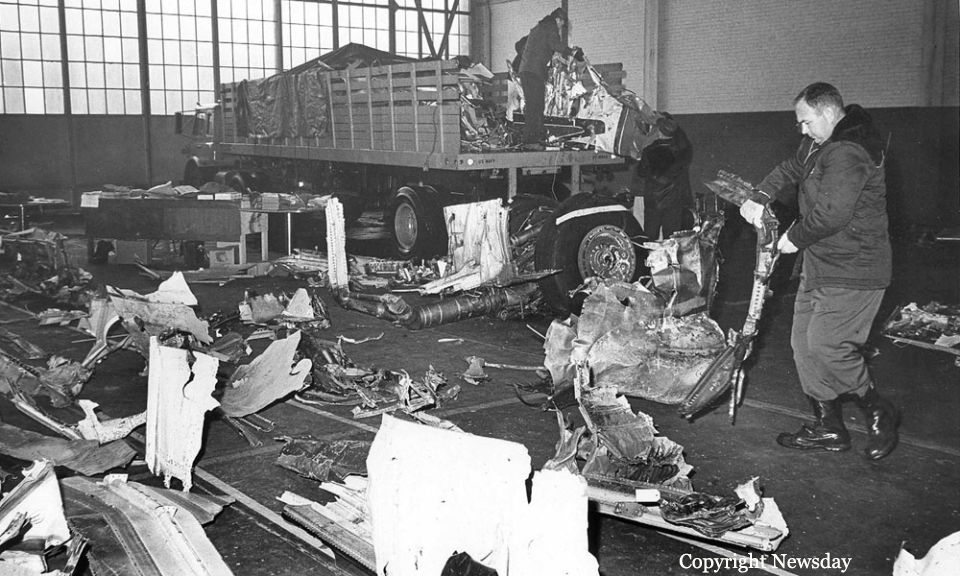
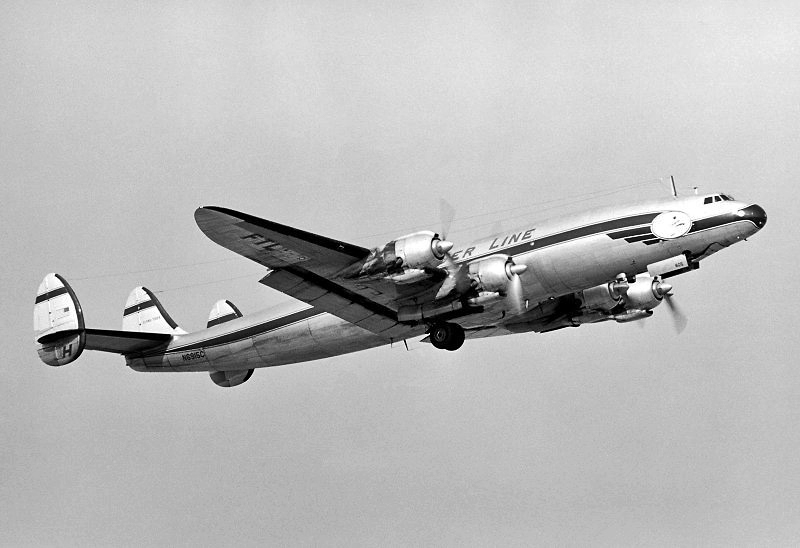
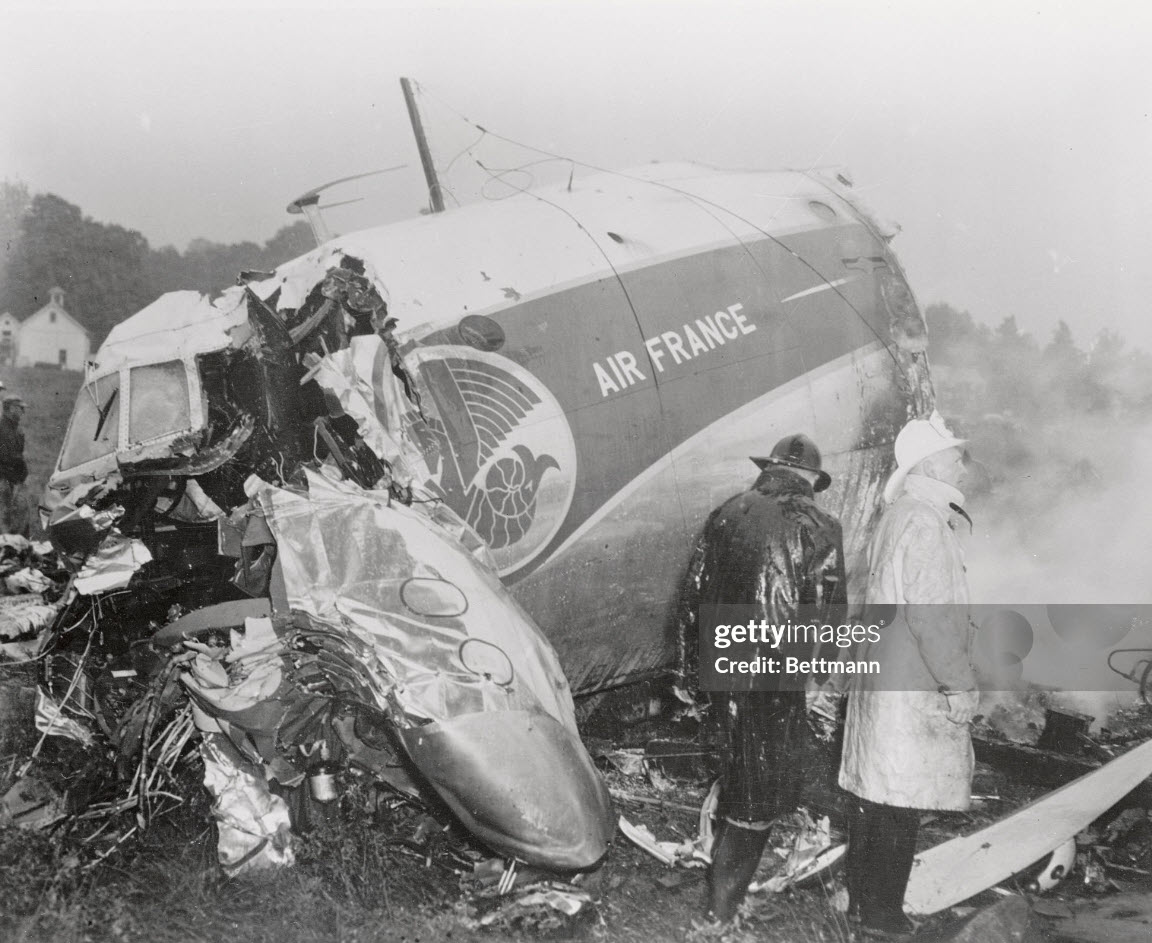
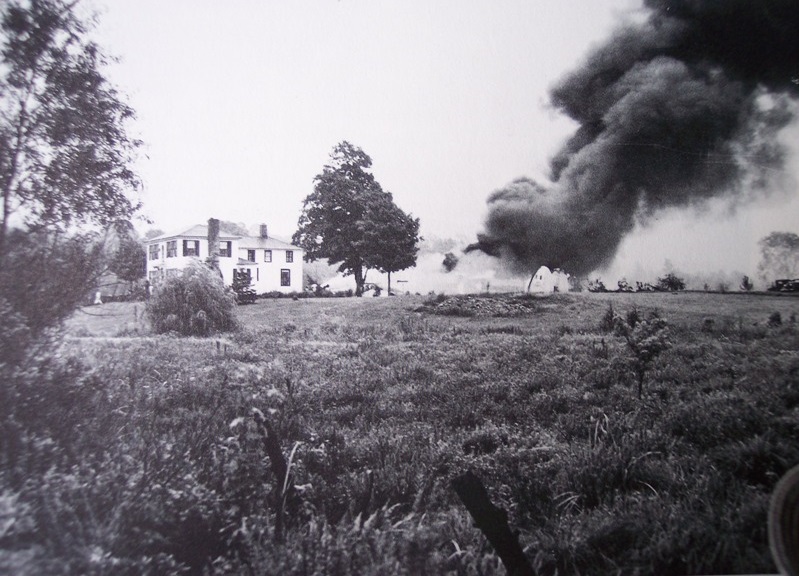
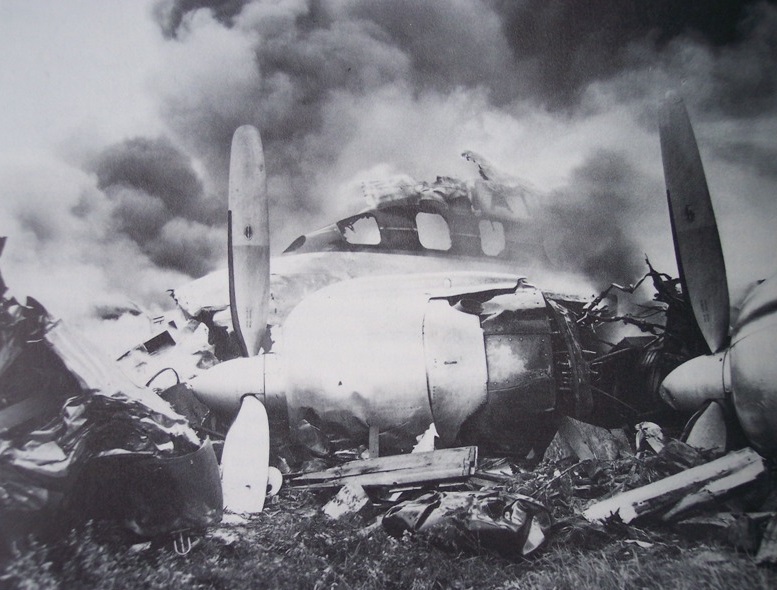
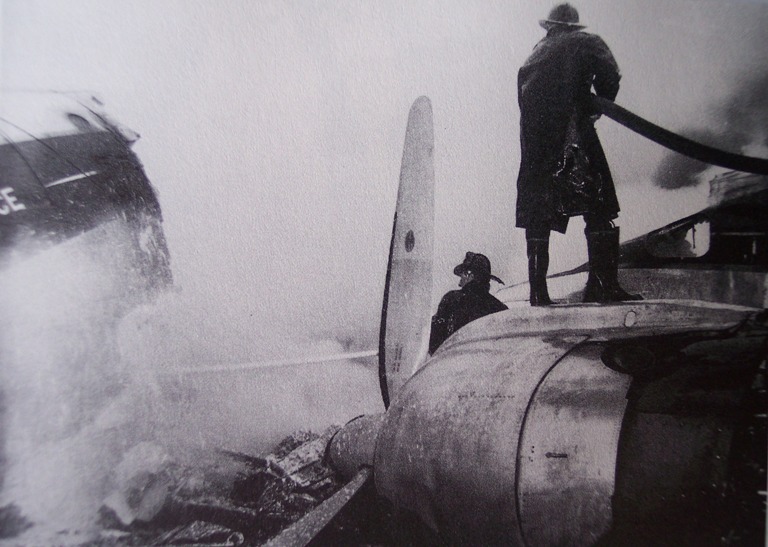
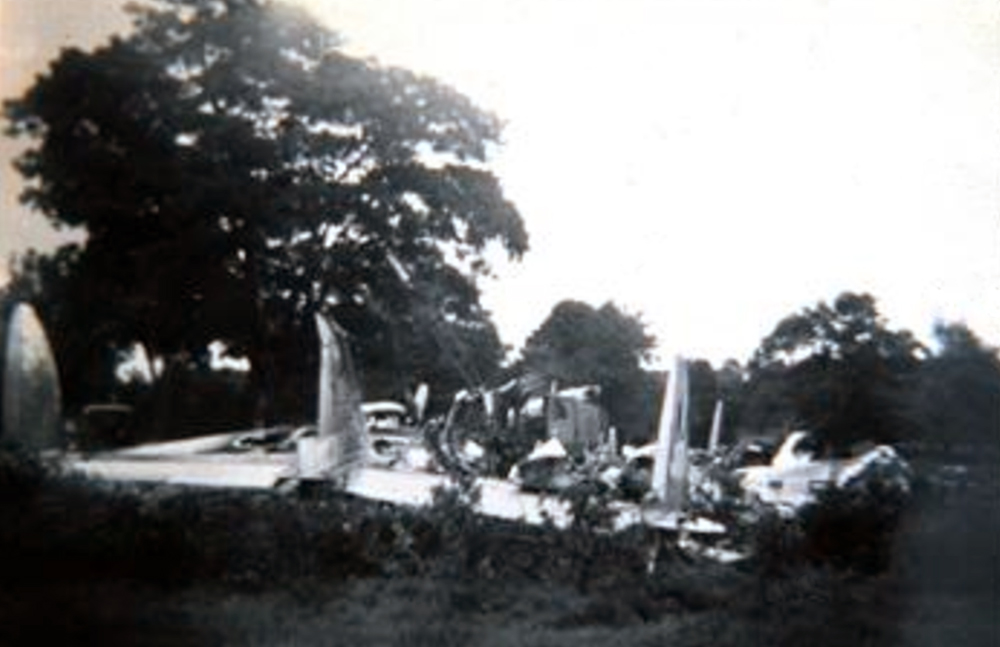
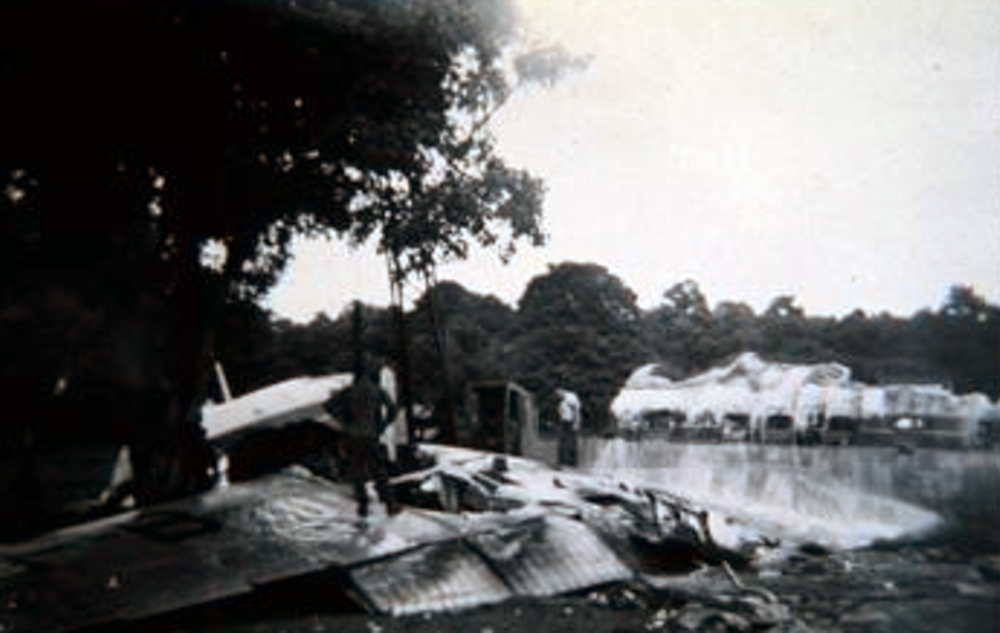
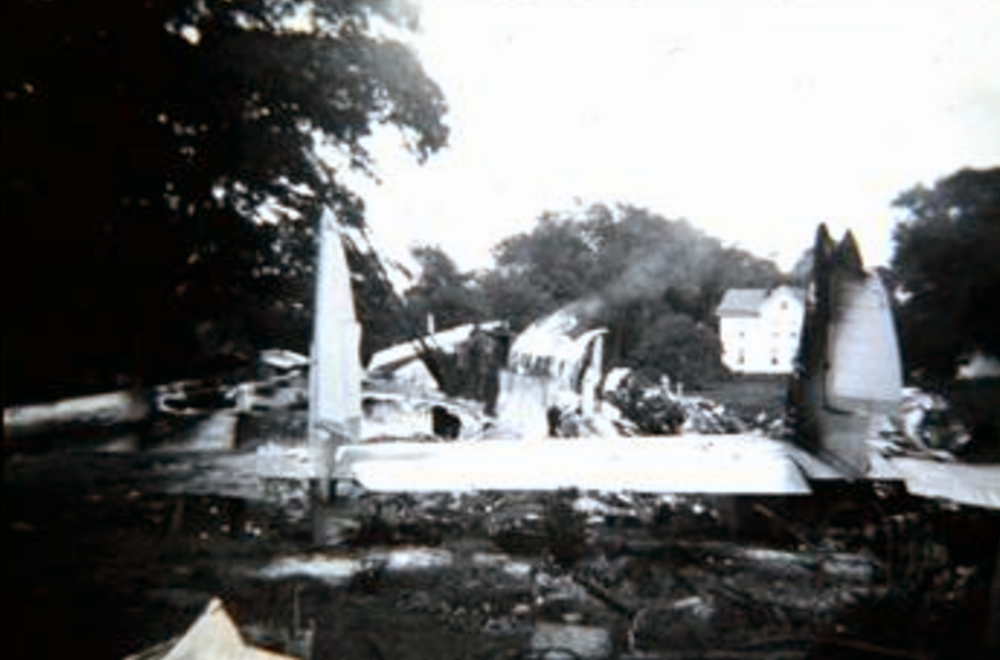
Air France Flight 075 originated at Orly Field, Paris, August 2, 1954, with a crew consisting of Captain Jean Caboche, Copilot Jean Roussean, Navigator Jacques Geffard., First Flight Engineer Albert Grandvaux, Second Flight Engineer Jean-Baptiste *** Stewardess Francine Dono, First Steward Michael Gallet, and Second Steward Jean Capron. The dispatch office had prepared two flight plans - one for a stop at Gander, Newfoundland, the other with a stop at Shannon, Ireland. Owing to marginal weather at Gander with the forecast indicating no improvement, the captain chose the latter plan. The flight departed Paris at 2024 and arrived Shannon at 2247. Fuel tanks were filled and the pilots ware briefed on weather for the nonstop flight to New York. Flight 075 departed Shannon at 0003 the next morning (August 3), estimating 11 hours 49 minutes an route, with fuel for nearly 14 hours. The gross weight at takeoff, 126,100 pounds, was less than the maximum allowable 133,000, and the load was correctly distributed relative to the canter of gravity of the aircraft. The Atlantic crossing was uneventful. Routine position reports were made en route and the flight periodically received weather reports for points along the route and at the destination. Stronger headwinds than had been anticipated were encountered near the North American continent, resulting in lower ground speed and somewhat higher fuel consumption per mile. The flight had approximately 600 gallons of fuel left at 1230 when it reported over Scotland Intersection (15 statute miles southwest of New York International Airport) and received clearance for an ILS approach. It was then 38 minutes behind its original flight plan estimate made at Shannon and had approximately 100 gallons less fuel than anticipated. During the approach, which was being monitored by New York International Airport radar, the flight encountered unexpected heavy turbulence, heavy rain, and a low ceiling, and the captain discontinued the approach at 1237 (0737 e. s. t.) when near his minimum prescribed altitude of 200 feet. The heavy turbulence made control of the aircraft difficult and when the missed approach was made, the captain found himself left of the localizer and below of glide path. The tower, which was immediately advised of the missed approach, told the flight to turn right to 130 degrees (the missed approach course), proceed to Scotland Intersection, and climb to 2,500 feet. Approximately three minutes after the missed approach and while on the 130-degrees course, the flight requested clearance to Boston. Such clearance was issued nine minutes later, as soon as possible consistent with other traffic. Meanwhile, the flight had reported being low on fuel but when asked if an emergency as being declared replied, "Negative, negative, not yet." At the approximate time clearance to Boston was received the flight engineer advised the captain that they had fuel of one more hour of flight. Thirty-three minutes after being cleared to Boston, the flight, at that time in the vicinity of Providence, Rhode Island, called Providence Tower, declared an emergency, and requested weather information. Providence weather, which was marginal, was furnished and the flight was cleared for an approach. However, the pilots found that their navigation kit did not contain an approach plate for Providence Airport and they advised they were not landing there. The captain then descended through a break in the overcast, circled two or three times, and landed with the gear retracted in a field at Preston City, Connecticut. It came to rest in flames in a garden and was destroyed by a post crash fire. All 37 occupants were evacuated safely. Nevertheless, 12 occupants were injured, among them both pilots.
Probable cause:
The Board determines that the probable cause of this accident was inadequate in-flight planning, in that the captain did not make a firm selection of a suitable airport within range of the fuel remaining at the time of the missed approach, necessitating an off-airport landing. The following findings were reported:
- All fuel tanks were filled to capacity during the scheduled stop at Shannon,
- Owing to headwinds the flight had approximately 100 gallons less fuel than anticipated when it arrived over Scotland Intersection, southwest of New York International Airport,
- In the ILS approach to New York International Airport during instrument weather conditions, the flight encountered an unexpected severe local storm with greater turbulence, heavier rain, and a lower ceiling than weather reports had led them to anticipate, and the captain discontinued the approach at 1237,
- The captain decided not to attempt another approach to New York International Airport and instead requested clearance to Boston at 1240 while climbing on the missed approach course,
- The flight was asked by New York International Airport Approach Control if an emergency was being declared, but the copilot replied in the negative,
- An IFR clearance to Boston was issued by New York ARTC at approximately 1249, the flight in the interim having been routed toward Boston via Mitchel range station,
- When the flight reported over Mitchel range station at 1250, the flight engineer advised the captain, upon the latter's request, that there was fuel for one more hour of flight,
- Difficulties with communications after being cleared from ARTC frequency prevented the flight from receiving the dispatcher's suggestion to proceed to Bridgeport or Hartford,
- Testimony of the pilots indicated that the captain intended to land at an intermediate airport between New York and Boston if he could find one with sufficiently good weather conditions,
- There were no language difficulties in conversations with the flight,
- There was sufficient fuel available to fly to Boston or any intermediate airport, but the fuel remaining over Boston, had the flight continued to that point, would have allowed only about 17 minutes of flight thereafter,
- Flight 075 declared an emergency at 1322 (0822 e. a. t.) in its first contact with Providence Tower/INSAC, indicated intention to land at Providence, was cleared for an approach, and then at 1329, advised that they were not landing there,
- The flight descended through a break in the overcast and made an emergency landing at about 1340 (0840 e. s. t. ) in a field and without loss of life.