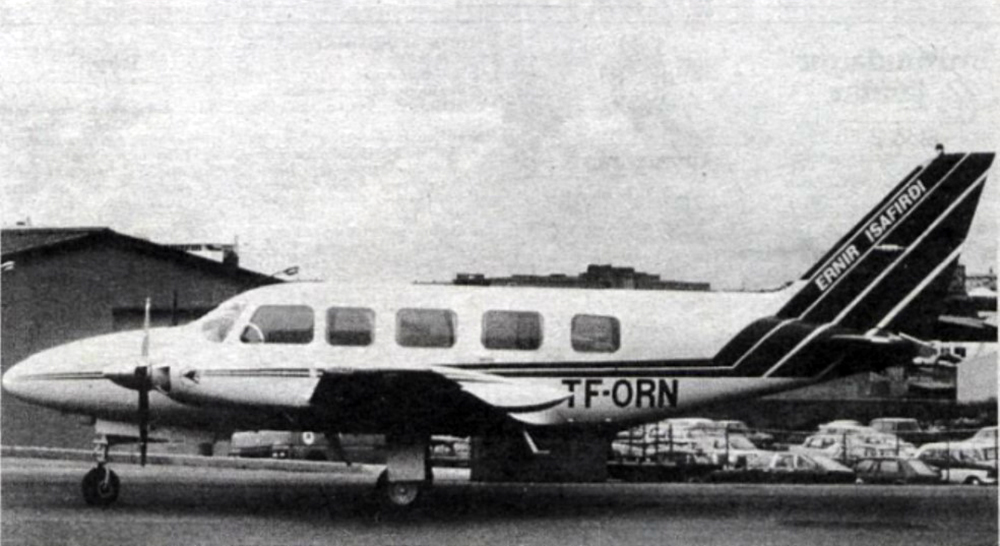
Crash of a Piper PA-31-350 Navajo Chieftain off Isafjördur: 1 killed
Date & Time:
Jan 21, 1987 at 1956 LT
Registration:
TF-ORN
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Akureyri – Isafjörđur
MSN:
31-7952174
YOM:
1979
Crew on board:
1
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
1
Captain / Total hours on type:
156.00
Circumstances:
While approaching Isafjörđur Airport, the pilot encountered poor visibility due to the night and poor weather conditions. While trying to locate the airport, he lost control of the airplane that crashed in the sea about six km offshore. The aircraft sank and was lost and the pilot, sole on board, was killed.
Final Report: