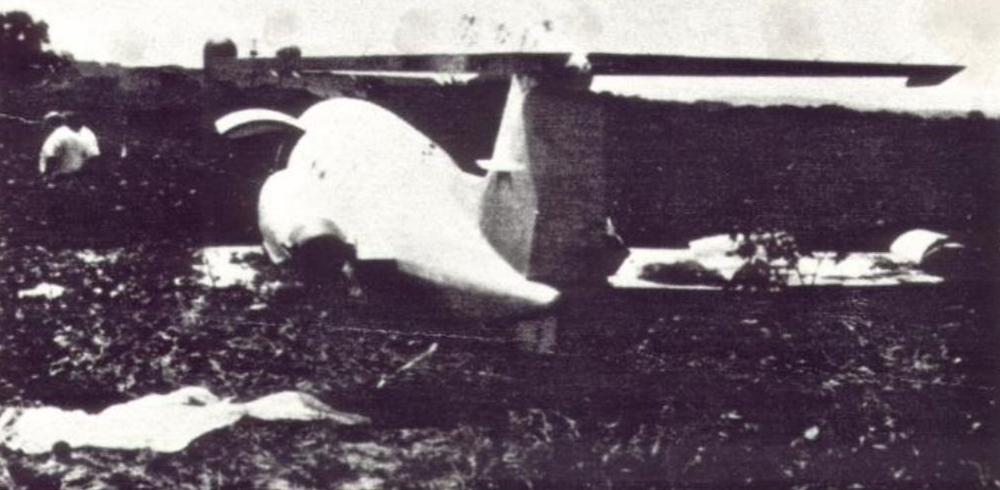
Crash of a Beechcraft C90 King Air in Fort Wayne: 1 killed
Date & Time:
Oct 24, 1983 at 1615 LT
Registration:
N4TS
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Fort Wayne - Tulsa
MSN:
LJ-541
YOM:
1972
Crew on board:
1
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
1
Aircraft flight hours:
3821
Circumstances:
At 1604 est, the aircraft departed Fort Wayne on a ferry flight. IFR conditions prevailed and the pilot had filed an IFR flight plan. While climbing after takeoff, the pilot passed his assigned altitude of 2,500 feet msl and flew to 4,200 feet. Also, he failed to turn to his initial assigned heading of 130°. He had problems contacting departure control as he was not on the assigned frequency. He reported problems with his heading indicator and his 'gyro'. Shortly after his last transmission, the aircraft left 4,200 feet msl and crashed in a steep dive. Before takeoff, the atp pilot reported he had flown all King Air aircraft and was currently flying the Beech 200. A review of his last log book revealed over 2,000 hours in the Beech 200, but showed no time in the Beech C90. A witness that reviewed the aircraft with the pilot before the flight believed he (the pilot) was very familiar with the aircraft systems. During an inspection of the wreckage, no evidence was found to verify a pre-impact malfunction or failure of the aircraft or engines. All instruments were destroyed. The pilot, sole on board, was killed.
Probable cause:
Occurrence #1: loss of control - in flight
Phase of operation: climb
Findings
1. (c) reason for occurrence undetermined
----------
Occurrence #2: in flight collision with terrain/water
Phase of operation: descent - uncontrolled
Phase of operation: climb
Findings
1. (c) reason for occurrence undetermined
----------
Occurrence #2: in flight collision with terrain/water
Phase of operation: descent - uncontrolled
Final Report: