Circumstances:
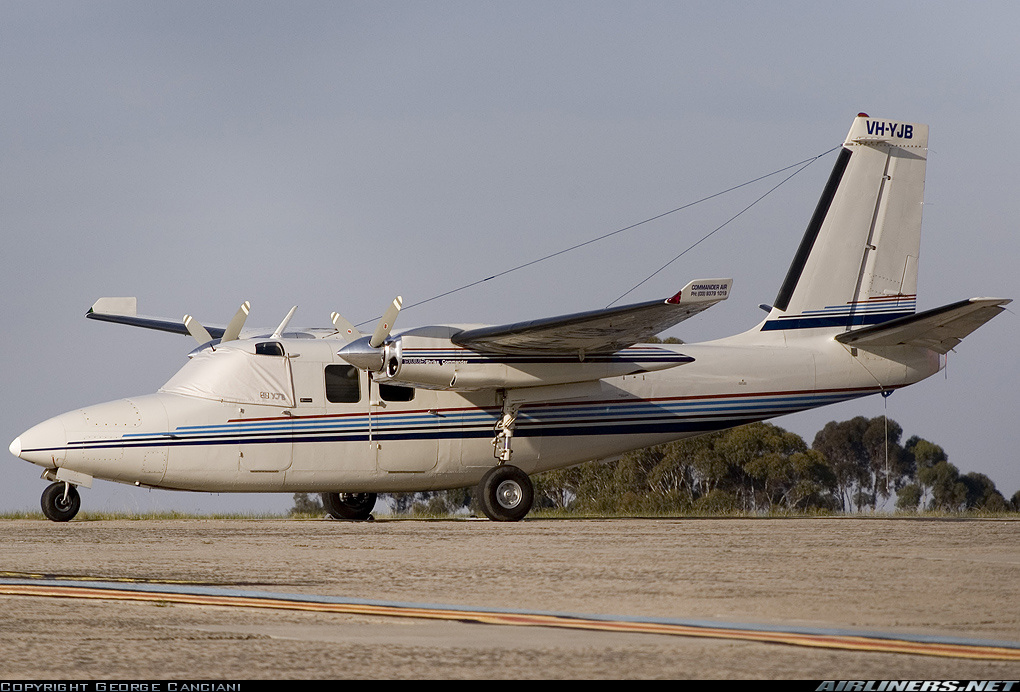
At 1946 Eastern Standard Time on 31 July 2007, a Rockwell International Aero Commander 500S, registered VH-YJB (YJB), departed Essendon Airport, Vic. on a business flight to Shepparton that was conducted at night under the instrument flight rules (IFR). On board were the pilot and one passenger. At 1958, while in the cruise at 7,000 ft above mean sea level (AMSL) in Class C controlled airspace, radar and radio contact with the aircraft was lost simultaneously by air traffic control when it was about 25 NM (46 km) north-north-east of Essendon. The air traffic controller declared a distress phase after a number of unsuccessful attempts to contact the pilot. At 2003, the Operations Director at Melbourne Centre declared the aircraft as probably lost and advised AusSAR. A search was commenced using a helicopter and an aeroplane in addition to ground search parties. No emergency locator transmitter signal was reported. At 2147, aircraft wreckage was located by a searching aircraft in timbered ranges near Clonbinane, approximately 50 km north of Melbourne. At about 2200, a ground search party confirmed that the wreckage was that of YJB and that there were no survivors. The flight was arranged to take the company owner, who was also a licensed aircraft maintenance engineer (LAME), to Shepparton to replace an unserviceable starter motor in another of the operator‟s aircraft. The pilot, who had landed at Essendon at 1915 from a previous flight in another of the operator‟s aircraft, was tasked to fly the owner to Shepparton. The pilot transferred to YJB, which had previously been prepared for flight by another company pilot. At 1938, while taxiing for takeoff, the pilot advised the aerodrome controller of the intention to conduct the IFR flight, adding, „…and request a big favour for a submission of a flight plan, with an urgent departure Essendon [to] Shepparton [and] return‟. The aerodrome controller did not have the facilities for processing flight notifications and sought the assistance of a controller in the Melbourne air traffic control centre. There were no eyewitnesses to the accident. Residents living in the vicinity of the accident site were inside their homes and reported difficulty hearing anything above the noise made by the wind and the foliage being blown about. One of the residents reported hearing a brief, loud engine noise. Another resident thought the noise was that of a noisy vehicle on the road. The noise was described as being constant, „…not spluttering or misfiring‟ and lasted for only a few seconds. Some of those residents near the accident site reported hearing and feeling an impact only moments after the engine noise ceased. The aircraft was seriously damaged by excessive in-flight aerodynamic forces and impact with the terrain. The vegetation in the immediate vicinity of the main aircraft wreckage was slightly damaged as the aircraft descended, nearly vertically, through the trees. The pilot and passenger were fatally injured.
Probable cause:
Structural failure and damage:
From the detailed examination and study of the aircraft wreckage undertaken by ATSB investigation staff, it was evident that all principal structural failures had occurred under gross overstress conditions i.e. stresses significantly in excess of the physical strength of the respective structures. The examination found no evidence of pre-existing cracking, damage or material degradation that could have appreciably reduced the strength of the failed sections, nor was there any indication that the original manufacture, maintenance or repair processes carried out on the aircraft were in any way contributory to the failures sustained.
Breakup sequence:
From the localised deformation associated with the spar failures, it was evident that the aircraft had sustained a large negative (downward) loading on the wing structure. That downward load resulted in the localised bending failure of the wing around the station 145 position (145” outboard of the aircraft centreline). The symmetry of both wing failures and the absence of axial twisting within the fuselage section suggested that the load encountered was sudden and well in excess of the ultimate strength of the wing structure. Based upon the witness marks on both wing under-surfaces and the crushing and paint transfer along the leading edges of the horizontal stabilisers, it was concluded that after separating from the inboard structure, both wings had moved aft in an axial twisting and rotating fashion; simultaneously impacting the leading edges of both horizontal tailplanes. Forces imparted into the empennage structure from that impact subsequently produced the rearward separation of the complete empennage from the fuselage. The loss of the left engine nacelle fairing was likely brought about through an impact with a section of wing leading edge as it rotated under and to the rear. The damage sustained by all of the aircraft‟s control surfaces was consistent with failure and separation from their respective primary structure under overstress conditions associated with the breakup of the aircraft. There was no evidence of cyclic or oscillatory movement of the surfaces before separation that might have suggested the contribution of an aerodynamic flutter effects.
Findings
The following statements are a summary of the verified findings made during the progress of the aircraft wreckage structural examination and analysis:
- All principal failures within the aircraft wings, tailplanes and empennage had occurred as a result of exposure to gross overstress conditions.
- The damage sustained by the aircraft wreckage was consistent with the aircraft having sustained multiple in-flight structural failures.
- The damage sustained by the aircraft wreckage was consistent with the structural failure sequence being initiated by the symmetric, downward bending failure of both wing sections, outboard of the engine nacelles.
- Breakup and separation of the empennage was consistent with having been initiated by impact of the separated outboard wings with the leading edges of the horizontal stabilisers.
- There was no evidence of material or manufacturing abnormalities within the aircraft structure that could be implicated in the failures and breakup sustained.
- There was no evidence of service-related degradation mechanisms (such as corrosion, fatigue cracking or environmental cracking) having affected the aircraft structure in the areas of failure.