Date & Time:
Mar 5, 1967 at 0256 LT
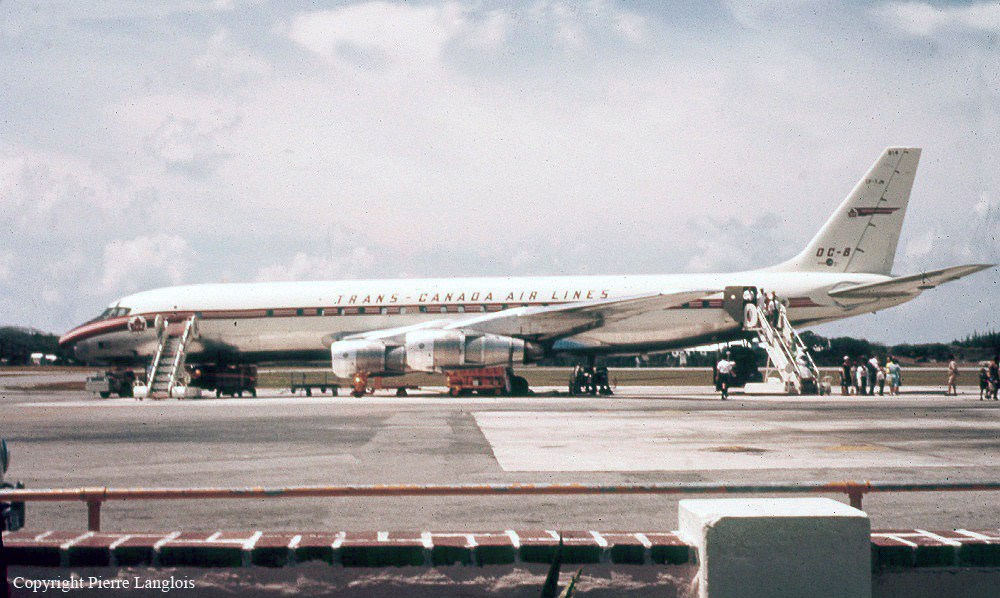
Operator:

Schedule:
Beirut – Rome – Monrovia – Rio de Janeiro
Crew fatalities:
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Captain / Total flying hours:
17718
Captain / Total hours on type:
1787.00
Copilot / Total flying hours:
15911
Copilot / Total hours on type:
408
Aircraft flight hours:
16775
Circumstances:
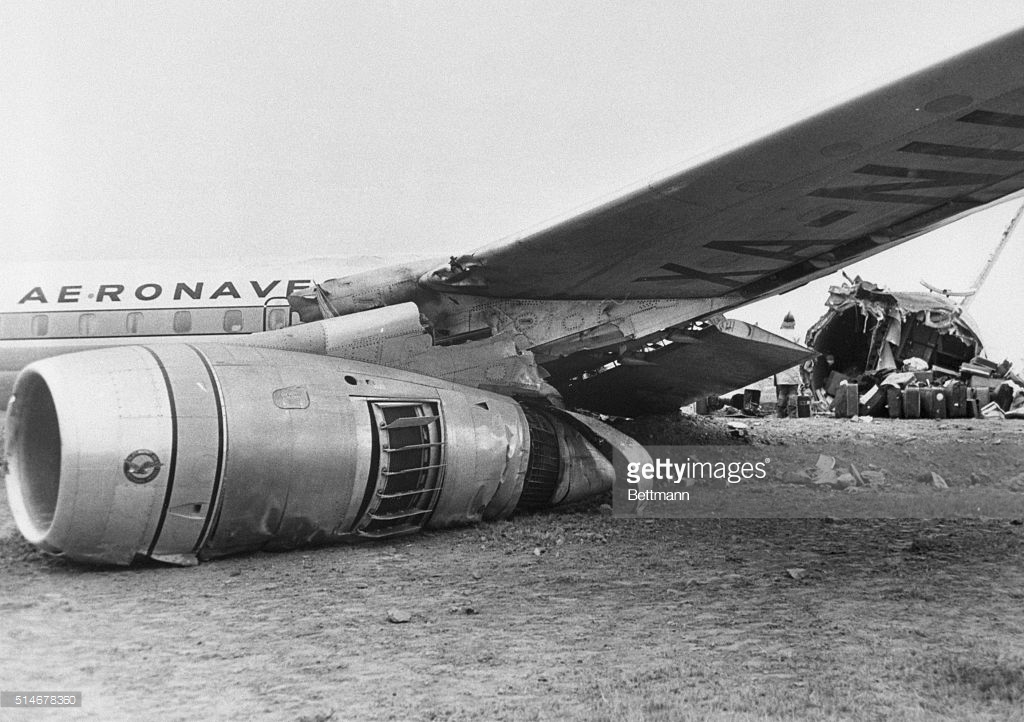
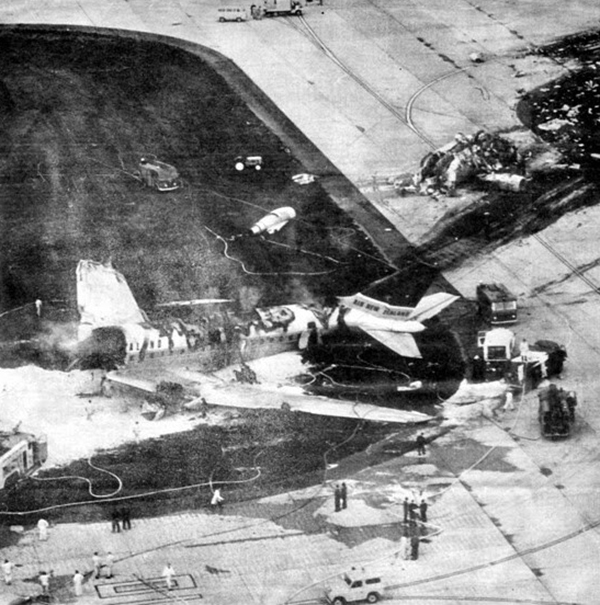
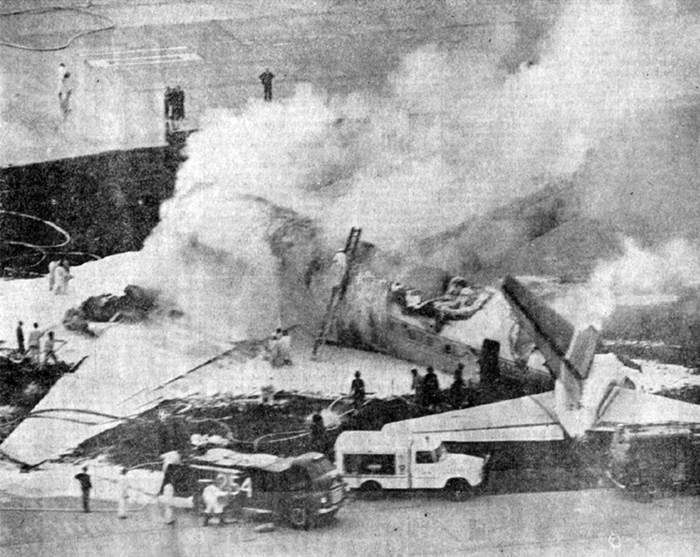
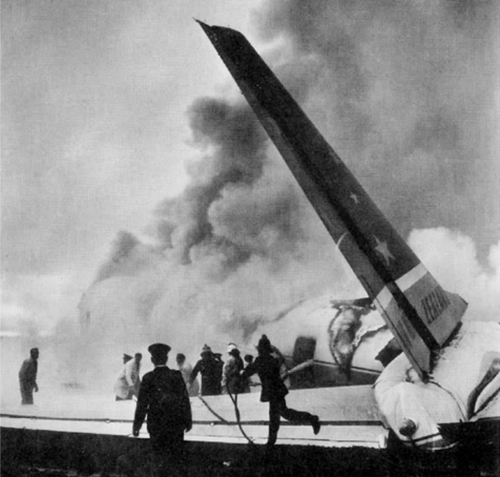
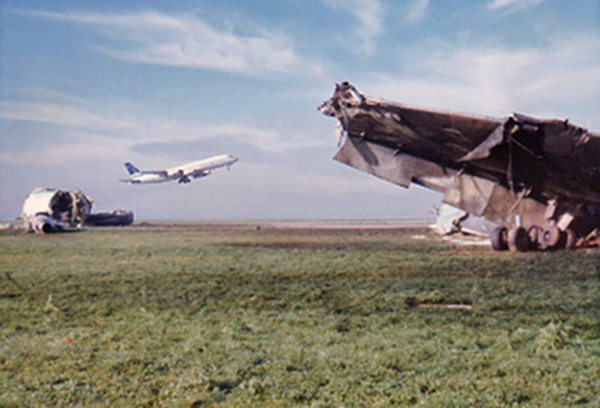
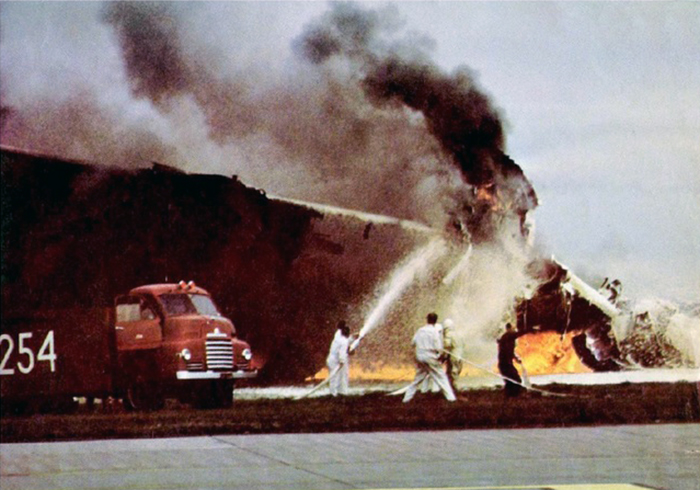
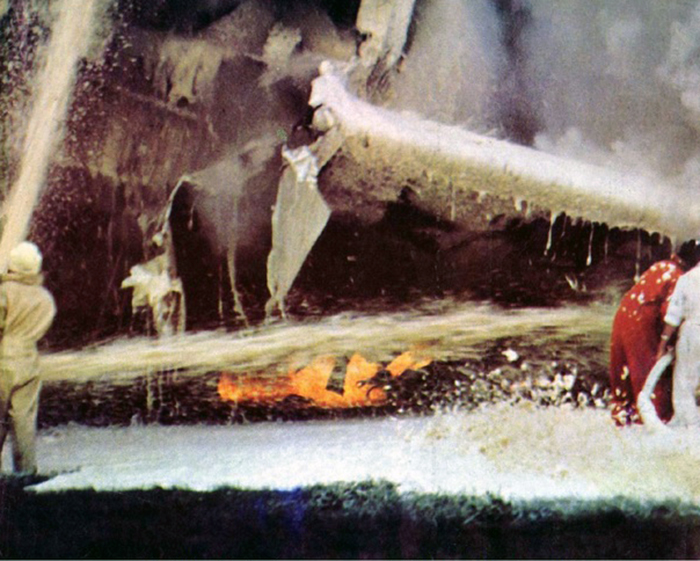
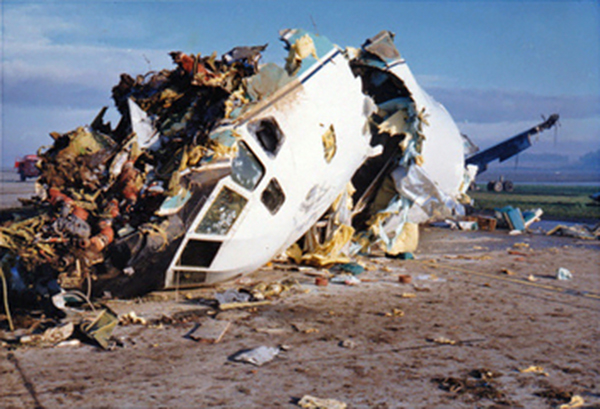
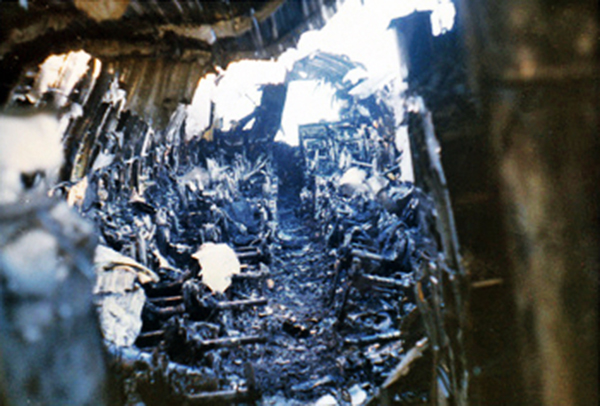
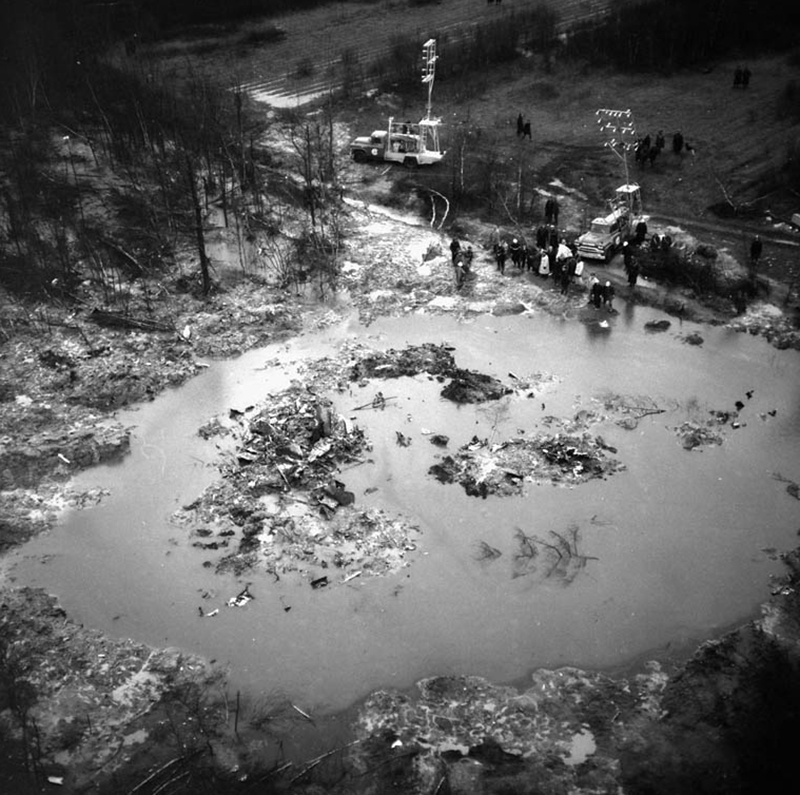
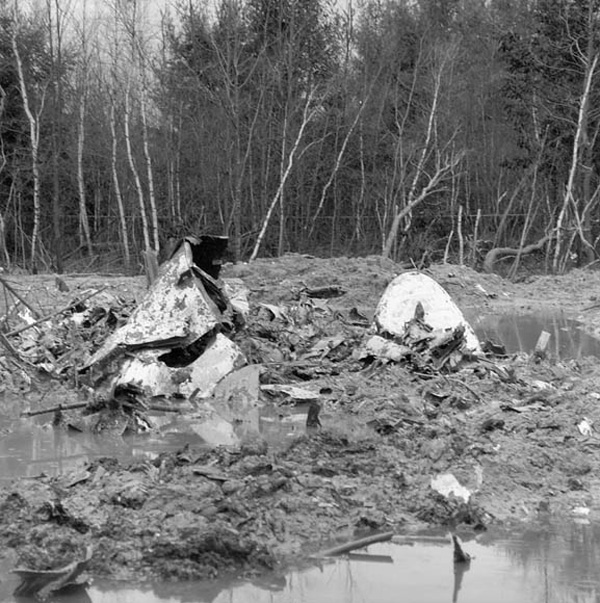
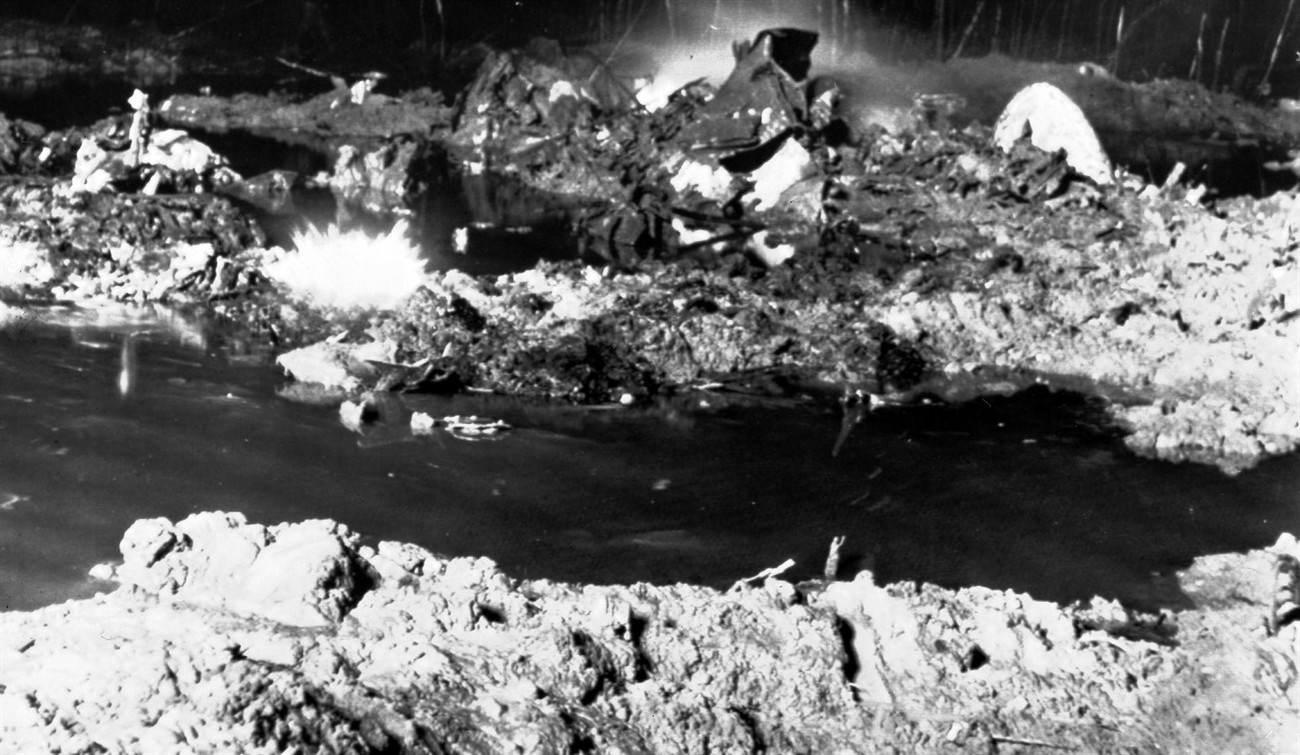
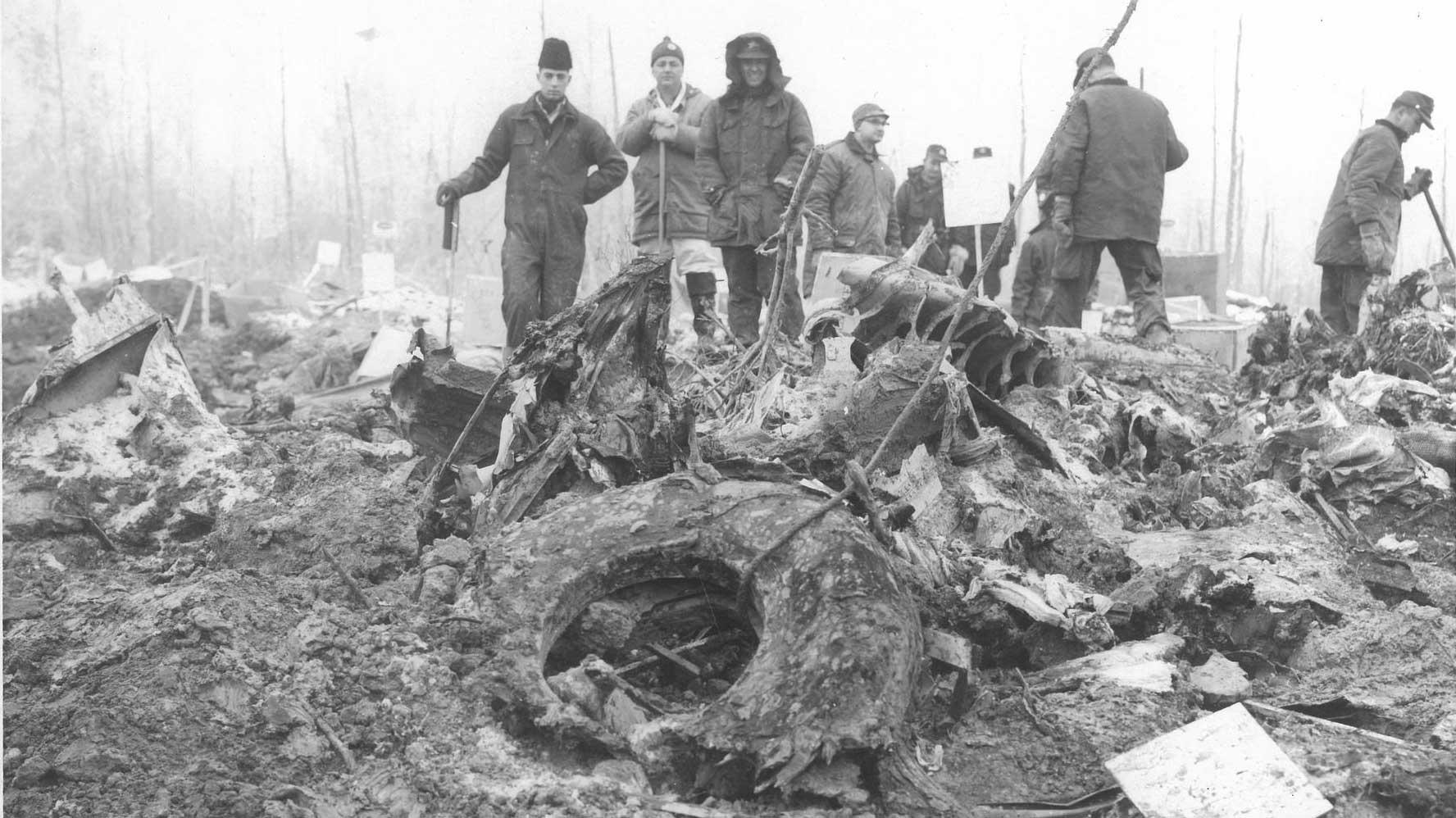
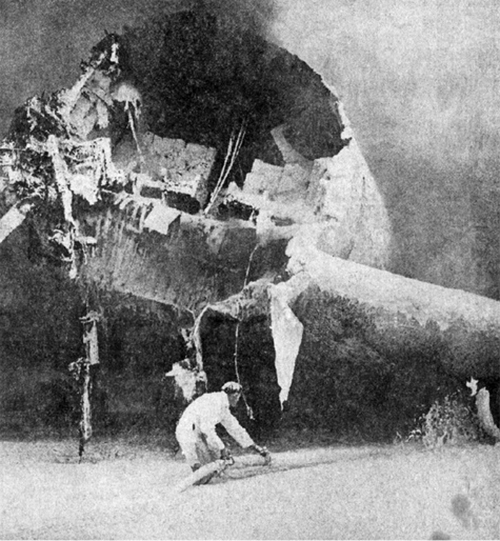
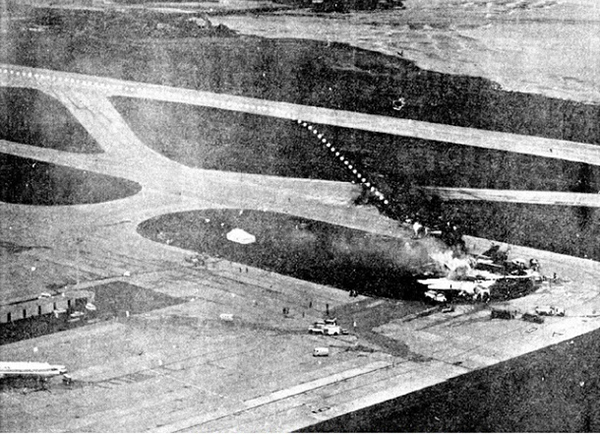
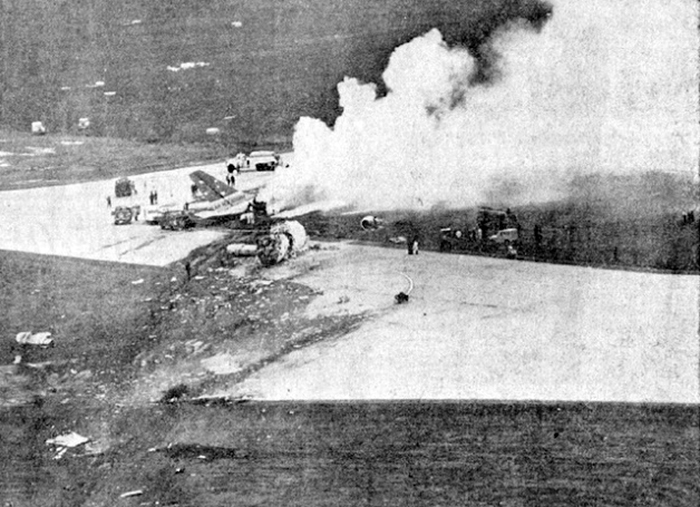
VARIG Flight RG837 departed Rome-Fiumicino Airport, Italy, at 21:08 hours GMT on a flight to Monrovia, Liberia. The flight was uneventful until the crew reported at FL45, five miles from the Roberts VOR. ATC then cleared the flight to descend further down to 3000 feet on the VOR and reported a QNH of 1009 mb. The QNH was read back correctly, but the crew did not mention the descent clearance. The pilot-in-command continued to the VOR at FL45 (4500 feet). After sighting the aerodrome runway lights from vertically overhead, the pilot informed the co-pilot that despite the fact that he had the runway completely in sight he would make an IFR/VOR procedure. A VOR/Locator instrument let-down was commenced from 4500 feet over the VOR at an indicated airspeed of 210 slowing to 170 kt, descending at a rate of between 500 to 700 feet per minute until the aircraft arrived at a point inbound over the coastline at 1800 feet on a heading of 047- degrees with the gear down and 35-deg flaps for landing on runway 04. At this point the co-pilot reported: "Runway in sight a little to the left". During the approach from the coast to the airport, the pilot did not make any use of the DME. After the procedure turn, the aircraft was on the correct VOR radial and a smooth approach was carried out during which the aircraft was flown manually. After the procedure turn, the co-pilot called each 100 feet of altitude and the speed and he checked the indication of the vertical speed indicators. At an altitude of about 1000 feet, flaps were put in the full down position and shortly thereafter, at an altitude of 700-800 feet, the aircraft entered some stratus and, further down, fog patches. When entering the stratus layer, the captain told the co-pilot that it was no longer necessary to report altitude and speed and was instructed to look outside and to report as soon as he could see the runway. Over the FR locator beacon, the altitude was about 800 feet, whereas his correct altitude should have been 520 feet. He then increased his rate of descent to between 1200-1500 ft/min, by reduction of power and by pitching the nose of the aircraft down. About 15 seconds after passing FR the co-pilot reported runway in sight, saying also that the visibility was poor and that they were too low. Descent was continued until the DC-8 impacted the ground 6023 feet from the threshold of runway 04, 180 feet to the right of the runway extended centre line with the aircraft coming to rest after a ground slide of approximately 850 feet. The aircraft caught fire and was totally destroyed. A crew members, 50 passengers and five people on a house were killed.
Probable cause:
The failure of the pilot-in-command to arrest in time the fast descent at a low altitude upon which he had erroneously decided, instead of executing a missed approach when he found himself too high over the locator beacon. The following findings were reported:
- The captain did not make use of the available navigational aids by disregarding the indications of his distance measuring equipment during final approach,
- At an altitude below 1 000 ft, the aircraft entered a stratus layer, which at that time completely obscured the runway,
- At the FR, positioned 1.7 NM before the runway threshold, the pilot-in-command saw that his altitude was 800 ft, whereas the correct altitude should have been 520 ft. Contrary to company instructions, he increased his rate of descent to between 1 200-1 500 ft/min by reducing engine power and pitching the nose of the aircraft down, with the intention to arrest his descent at about 500 ft,
- The attempt to level off was insufficient and/or too late, with the result that the aircraft touched the ground some 6 000 ft before the runway threshold when his glide path angle must have been 4.50 or more,
- During impact and the subsequent ground slide of about 850 it, the aircraft broke,up and caught fire,
- Those crew members who escaped relatively unhurt, once outside, might have directed more effort in further evacuation,
- The fire crew acted promptly, but its limited force and the necessary elapse time to reach the scene of the accident prevented them from saving people who might not yet have died.
Final Report: