Crash of a Piper PA-42-720 Cheyenne IIIA in Zurich
Date & Time:
Oct 28, 2003 at 0742 LT
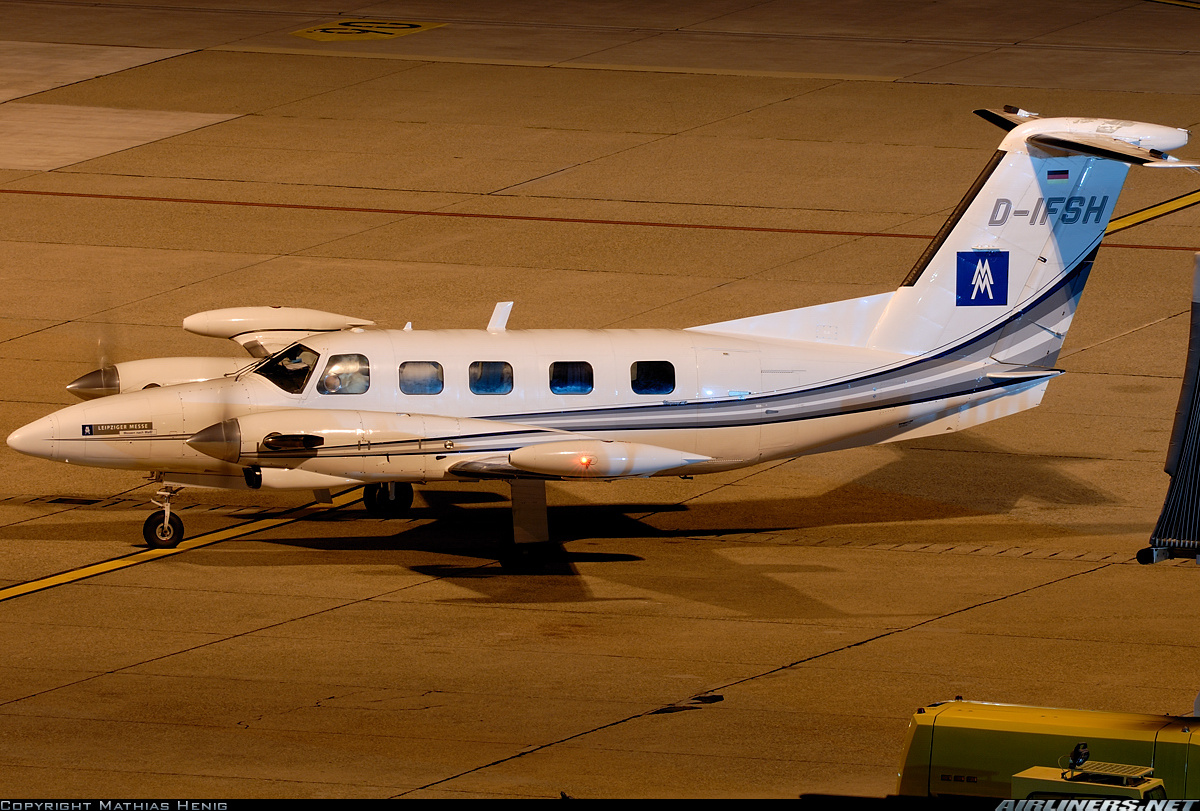
Registration:
D-IFSH
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Leipzig – Zurich
MSN:
42-8001101
YOM:
1982
Flight number:
RUS1050
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Captain / Total hours on type:
900.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
34
Aircraft flight hours:
5276
Aircraft flight cycles:
4370
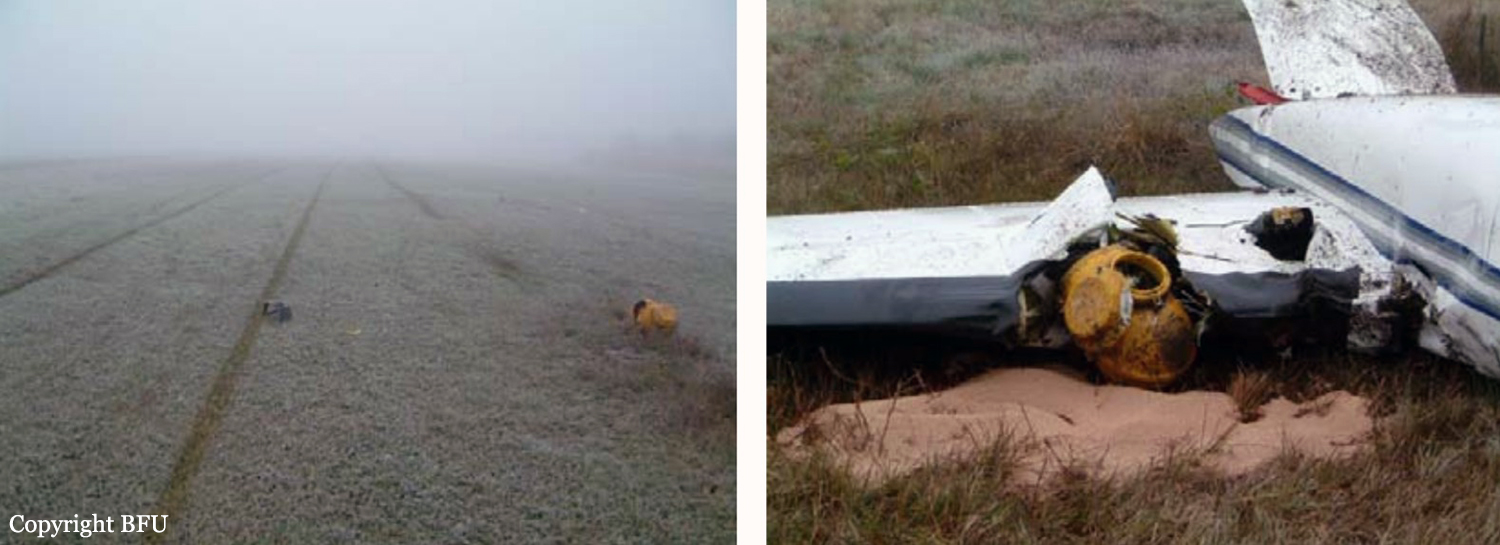
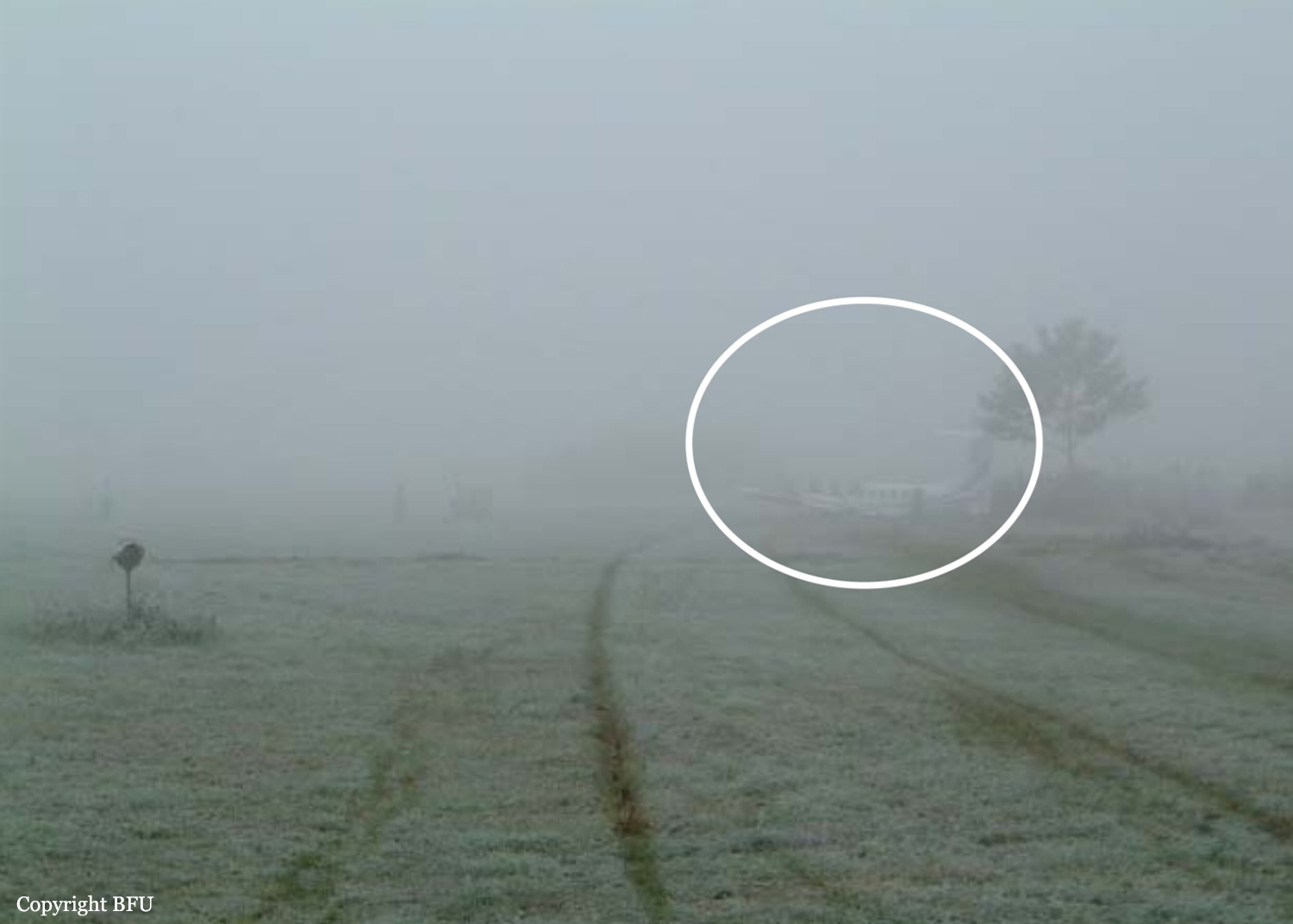
Circumstances:
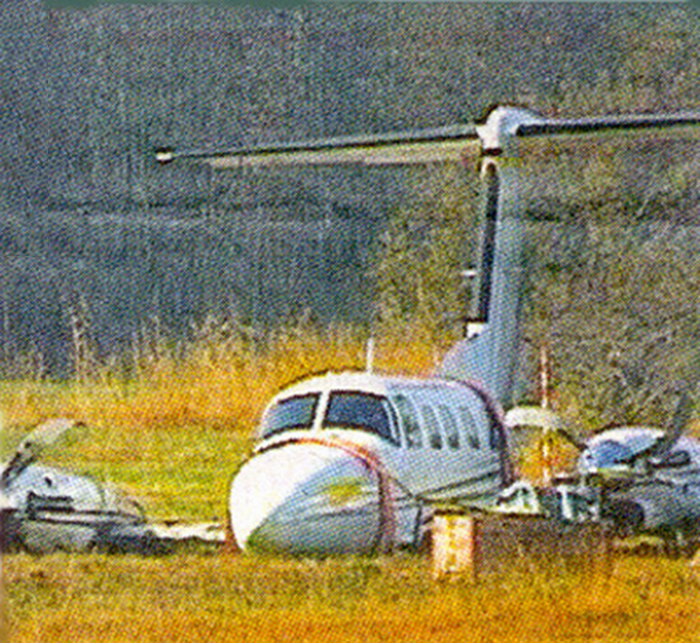
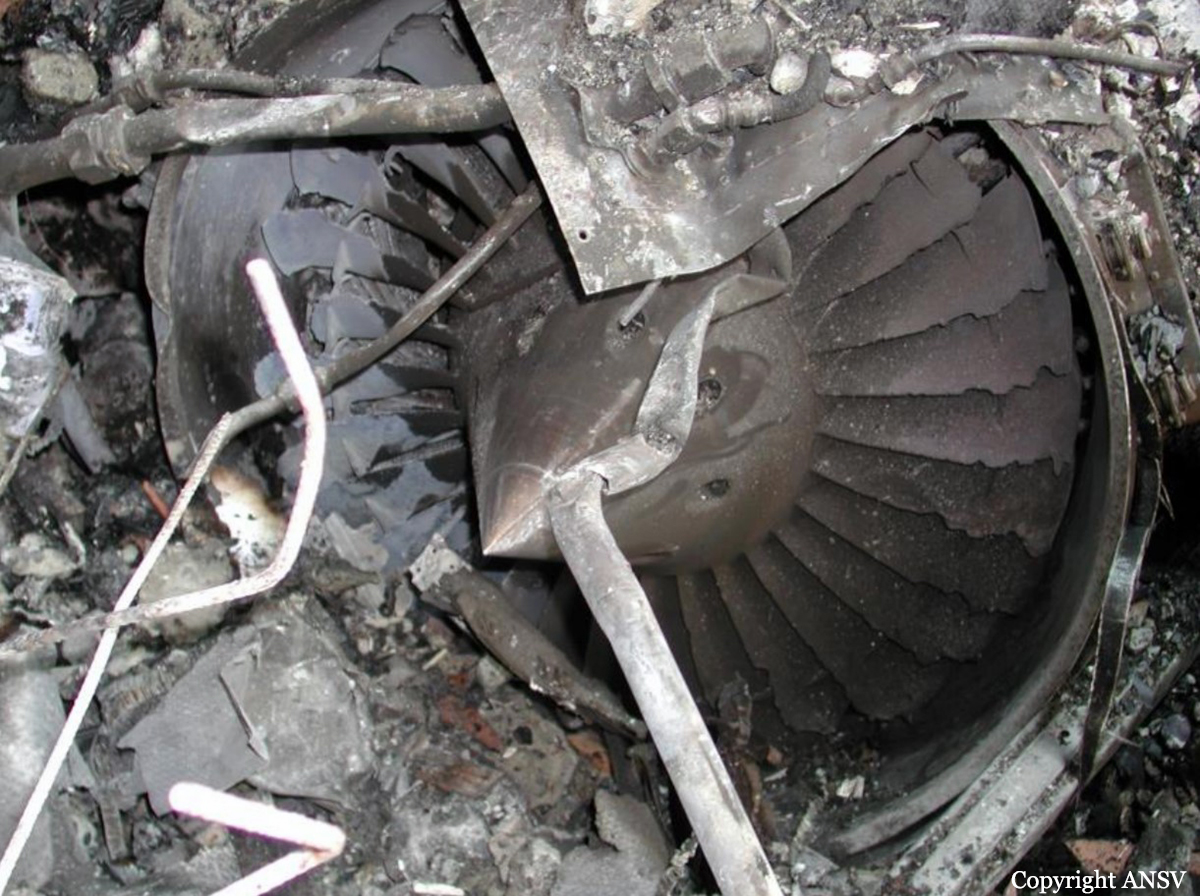
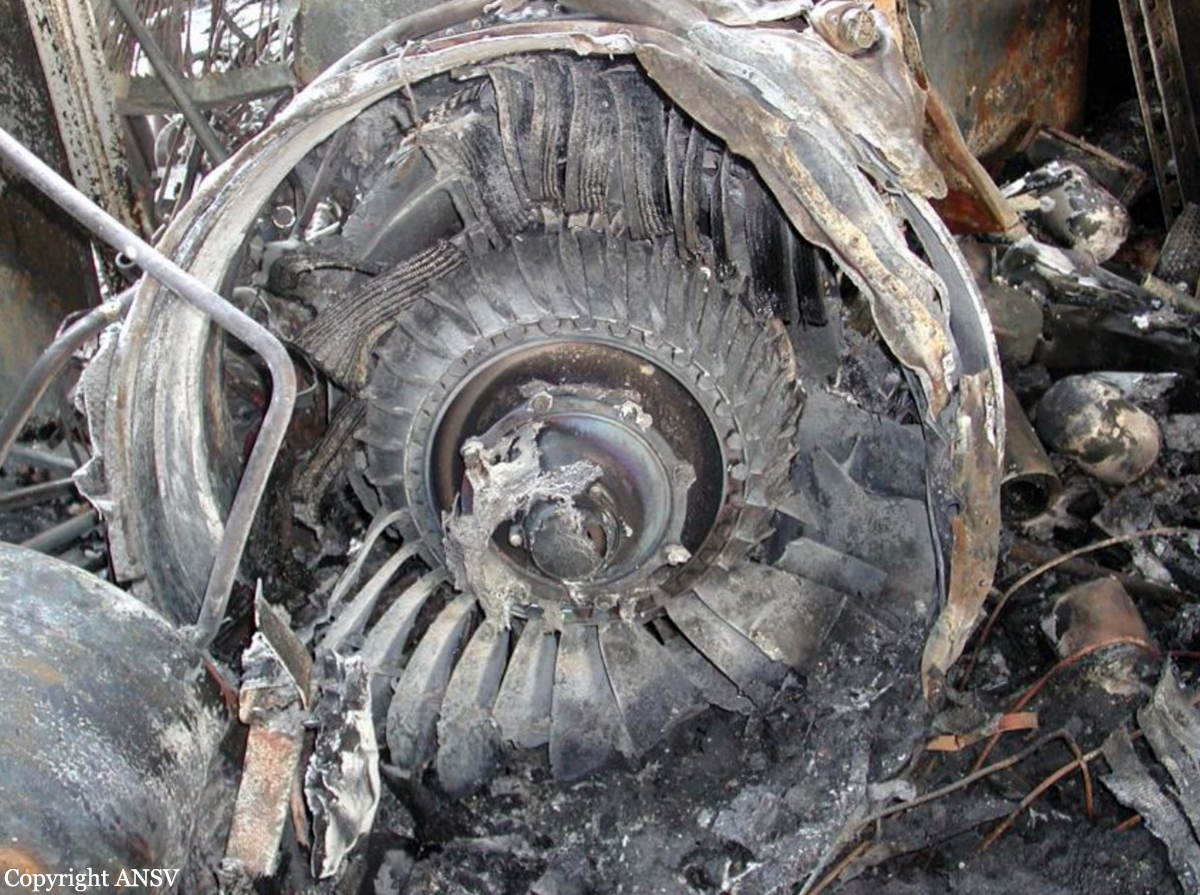
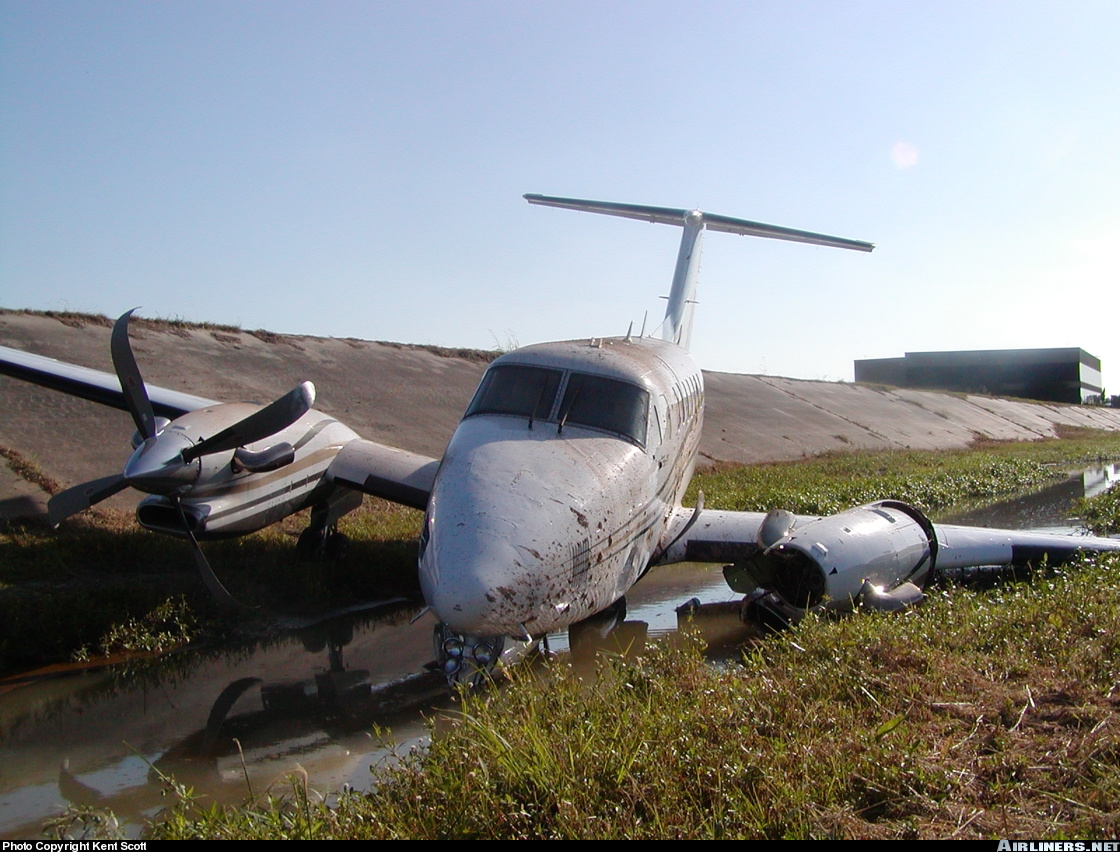
The crew was completing a positioning flight (RUS1050) from Leipzig to Zurich on behalf of FSH Luftfahrtunternehmen but under contract of Cirrus Aviation. On final approach to Zurich-Kloten Airport, the crew encountered poor visibility due to foggy conditions. Despite the RVR for runway 14 was estimated to be 275 metres (below minimums of 400 metres for a CAT II approach if aircraft and crew are qualified), the crew decided to continue the approach, descended below the MDA until the aircraft struck the ground between both runways 14 and 16. The aircraft rolled for few dozen metres then lost its undercarriage and came to rest in a frosty field. Both pilots escaped with minor injuries and the aircraft was damaged beyond repair. At the time of the accident, the vertical visibility was 300 feet, the horizontal visibility was 200 metres with freezing fog, an OAT of -3° C and a dew point of -4° C.
Probable cause:
The accident is due to the fact that the crew continued the approach below the decision height during an ILS approach to runway 14 without sufficient visual references. As a result, the plane struck the ground and crashed. The following factors contributed to the development of the accident:
- The aircraft was neither equipped nor approved for approaches under the prevailing weather conditions.
- The crew was not trained for approaches in such weather conditions.
- The crew failed to comply with SOP's and did not assigned tasks.
- The crew was not familiar with the procedural requirements.
- The crew knowledge was insufficiently checked by the operator.
- The aircraft was neither equipped nor approved for approaches under the prevailing weather conditions.
- The crew was not trained for approaches in such weather conditions.
- The crew failed to comply with SOP's and did not assigned tasks.
- The crew was not familiar with the procedural requirements.
- The crew knowledge was insufficiently checked by the operator.
Final Report: