Crash of a Hindustan Aeronautics HAL-748-219-2 in Dubagunta: 22 killed
Date & Time:
Dec 24, 1996 at 1540 LT
Registration:
H1032
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Tambaram – Hyderabad
MSN:
528
YOM:
1971
Crew on board:
5
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
17
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
22
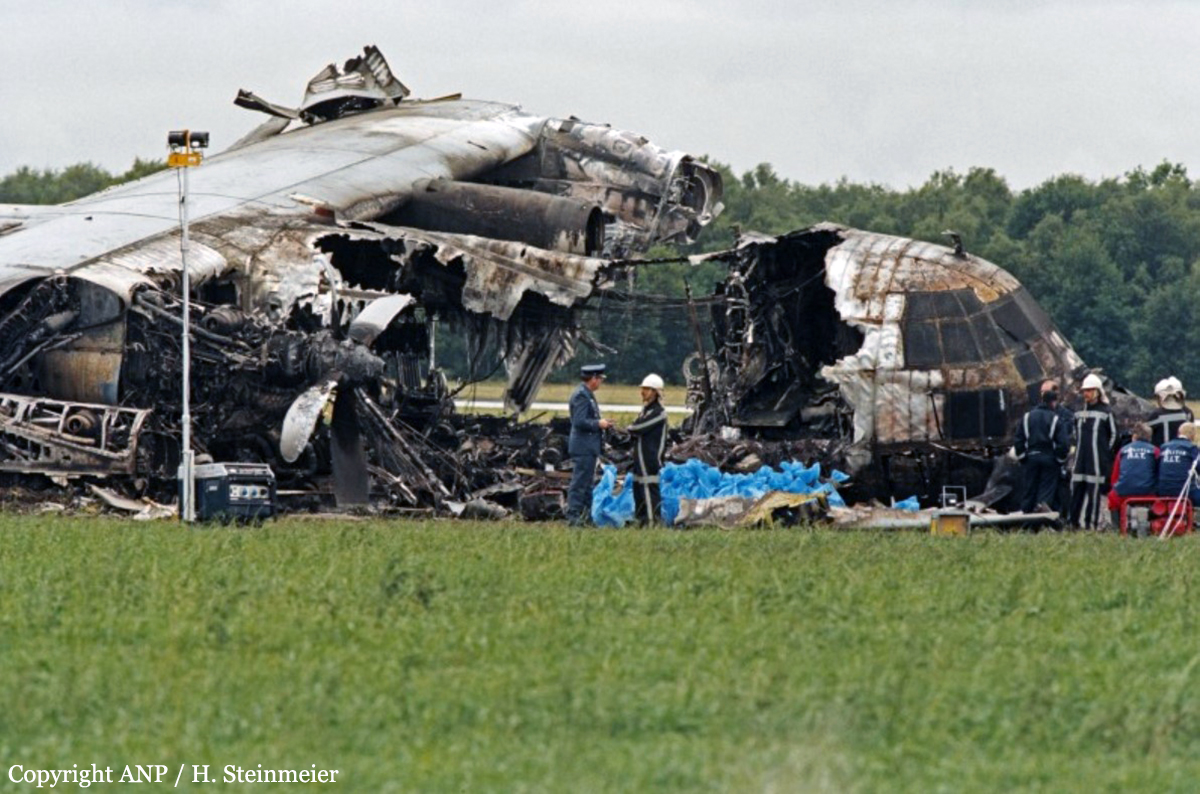
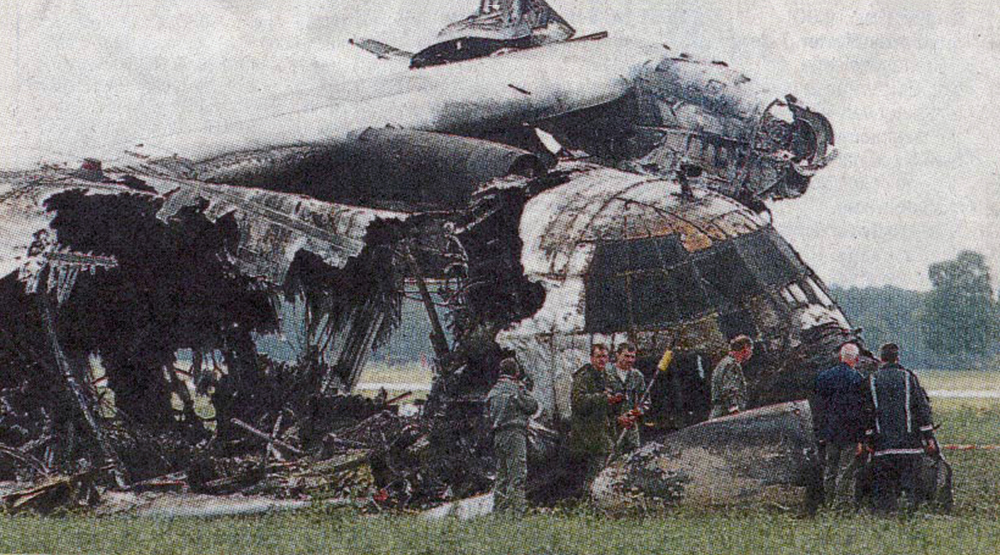
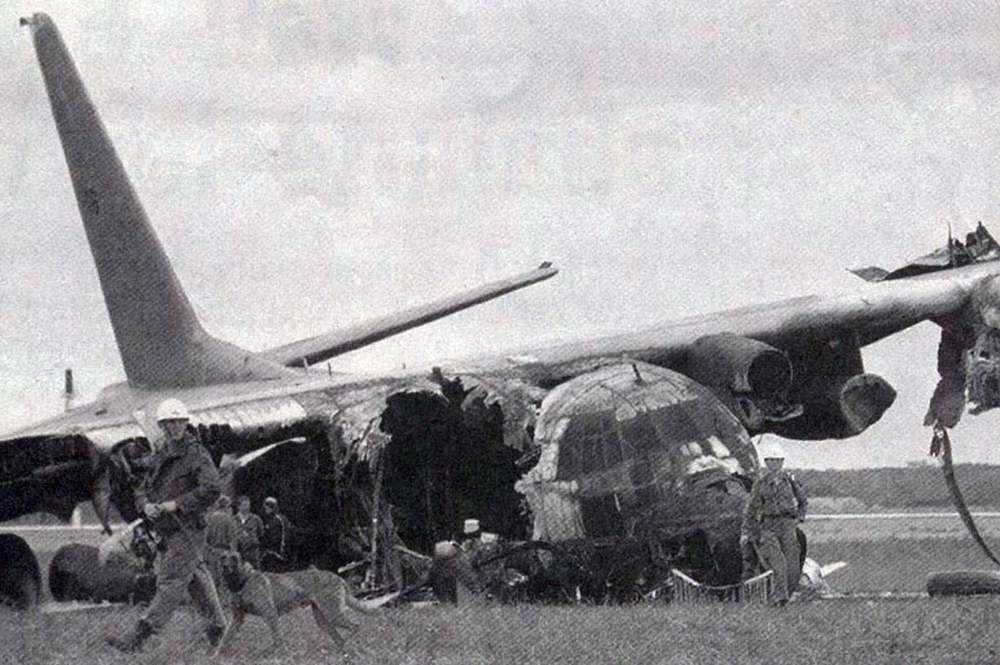
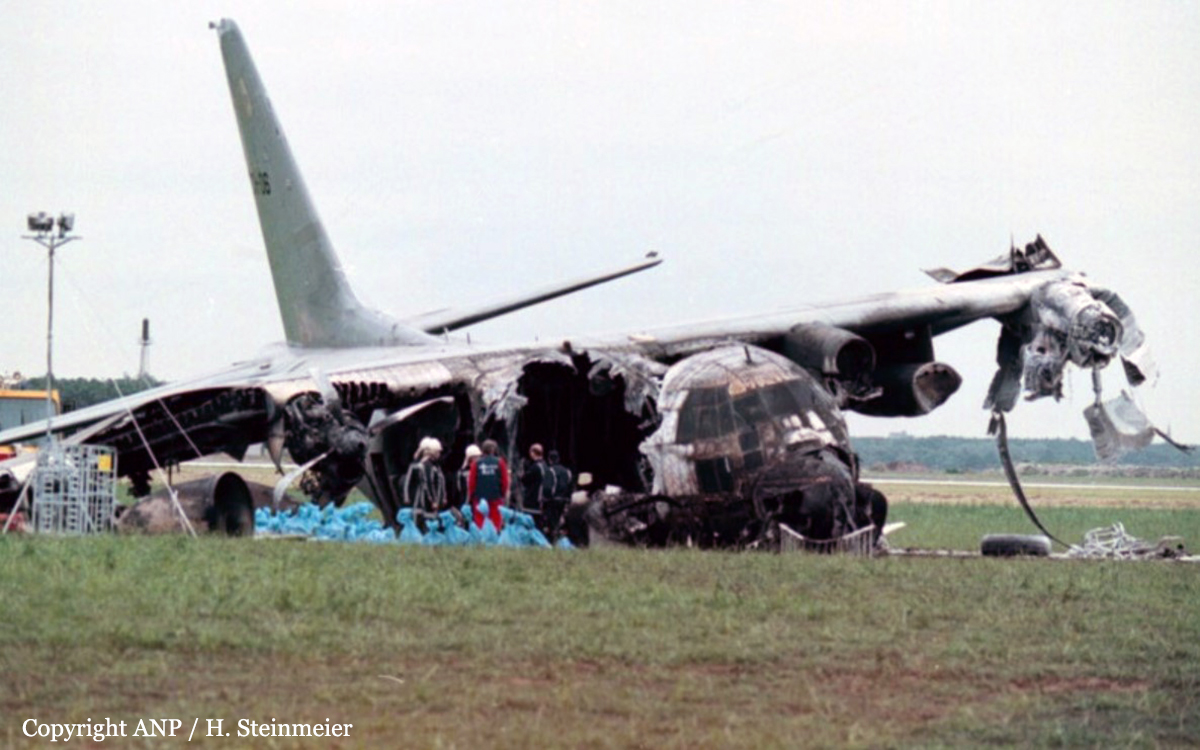
Circumstances:
En route from Tambaram to Hyderabad, while in cruising altitude, the captain declared an emergency and informed ATC about the failure of an engine. Shortly later, the aircraft entered an uncontrolled descent and crashed near Dubagunta, killing all 22 occupants.
Probable cause:
It was determined that an engine failed in flight and later detached, causing the separation of a wing. The failure of the high compressor disk was the consequence of fatigue cracks that were not detected during the last maintenance inspection.