Crash of a Xian Yunsunji Y-7H-500 in Néma: 39 killed
Date & Time:
May 12, 1998 at 1930 LT
Registration:
5T-MAG
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Néma - Nouakchott
MSN:
00 7H 03
YOM:
1996
Crew on board:
7
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
35
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
39
Circumstances:
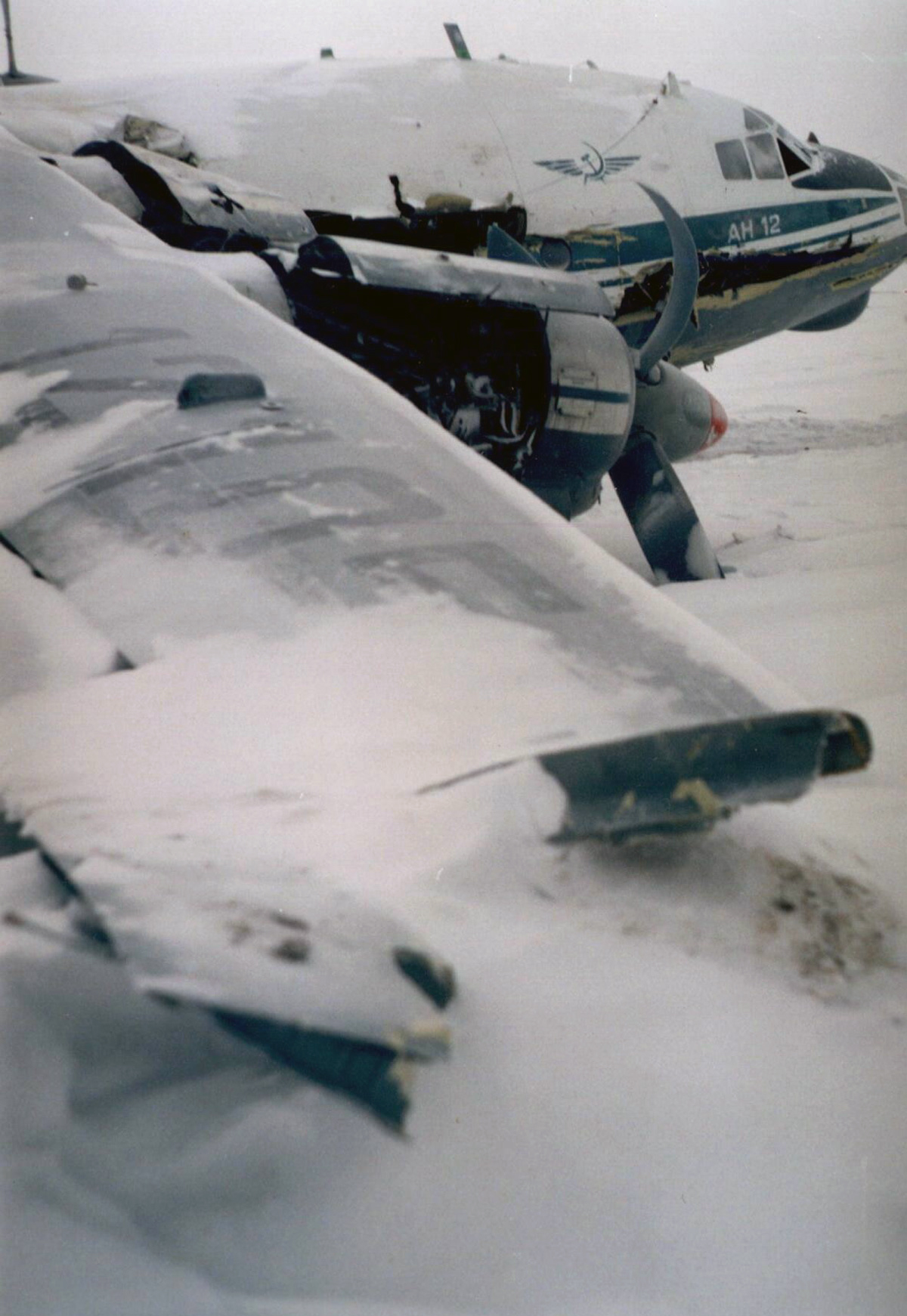
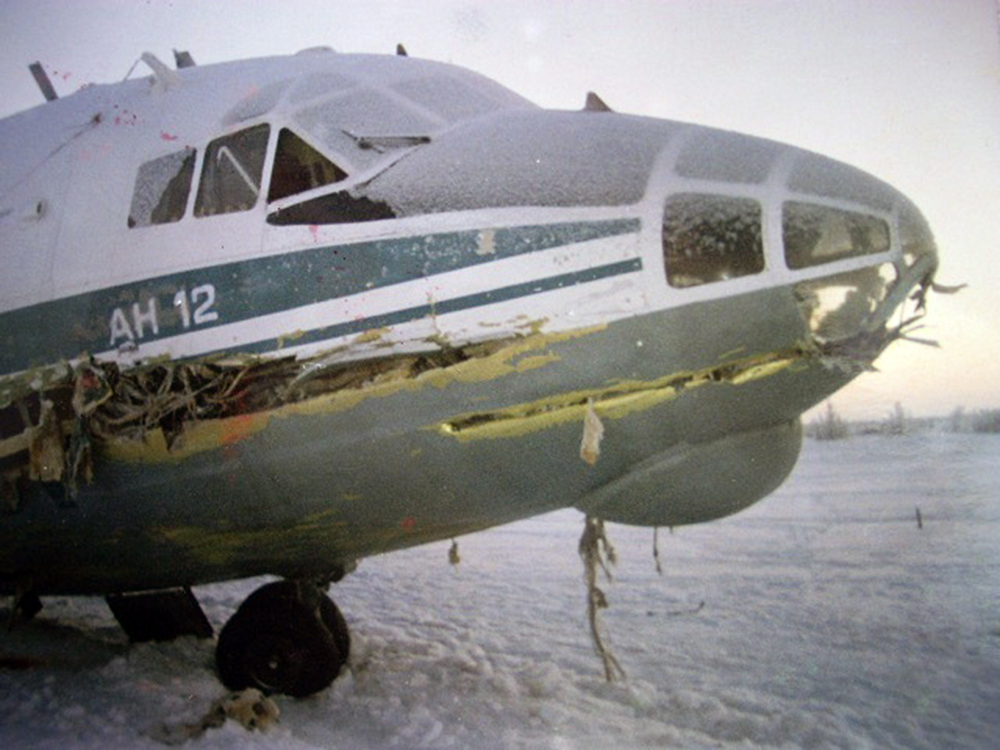
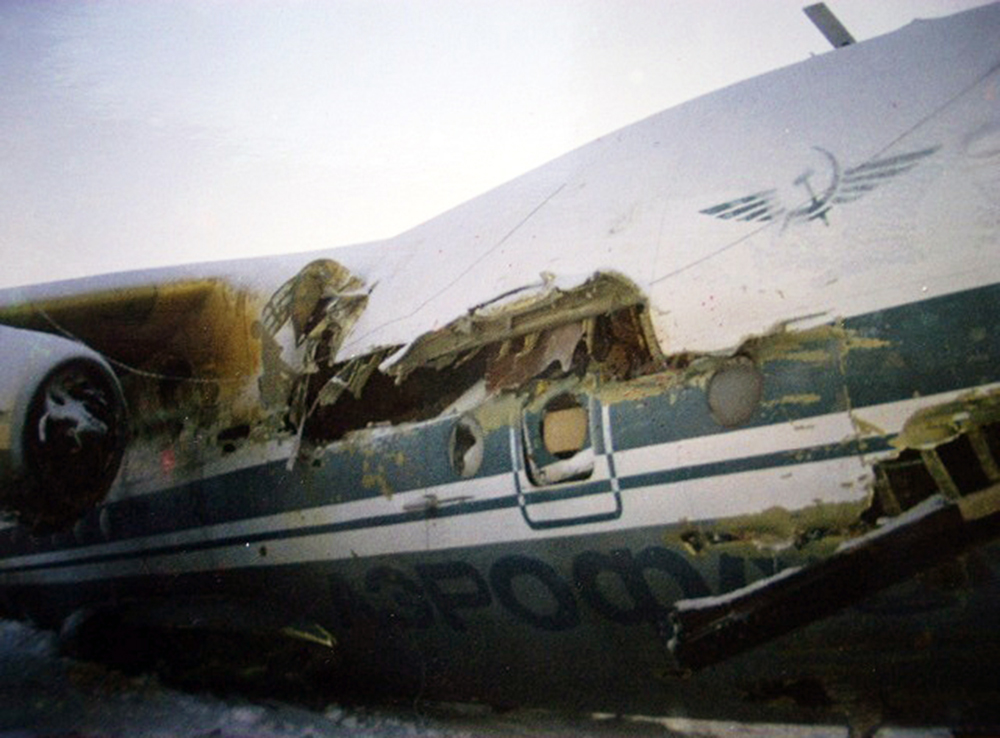
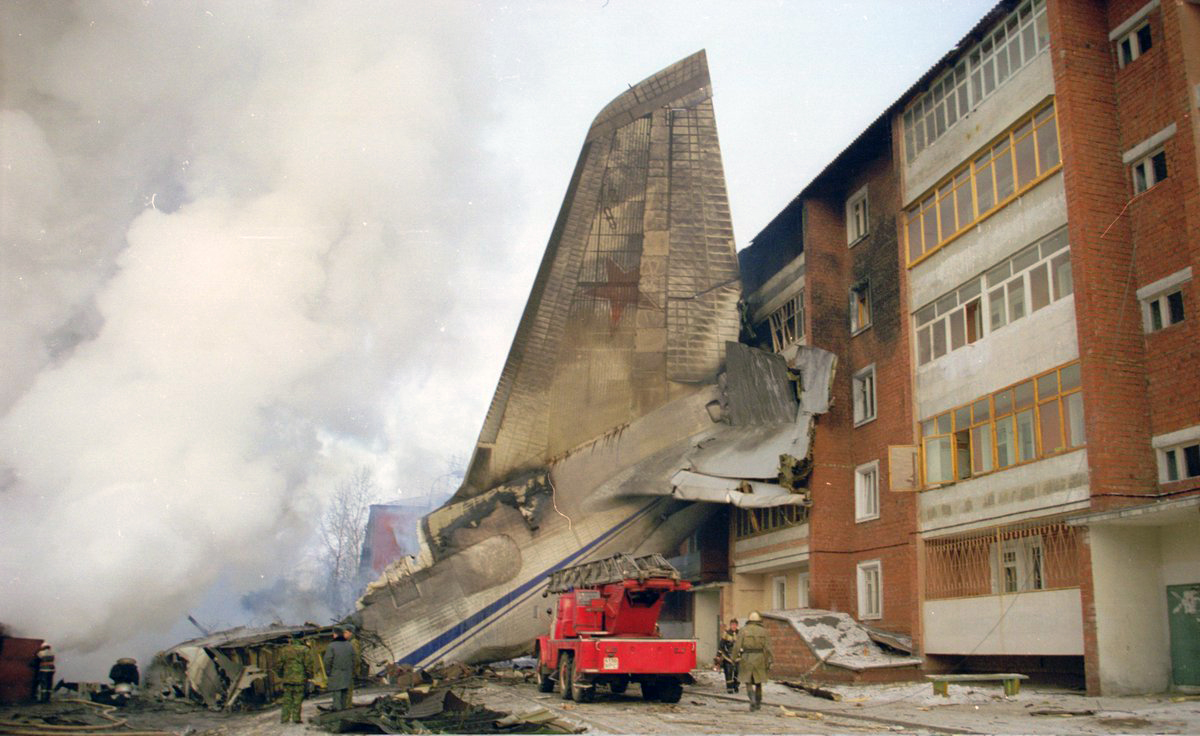
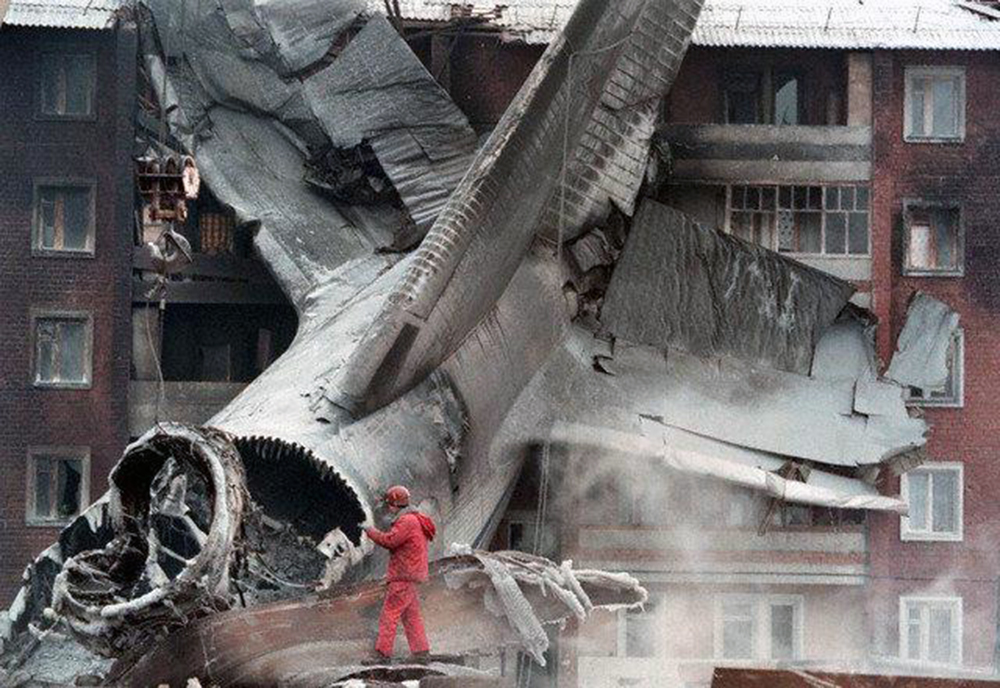
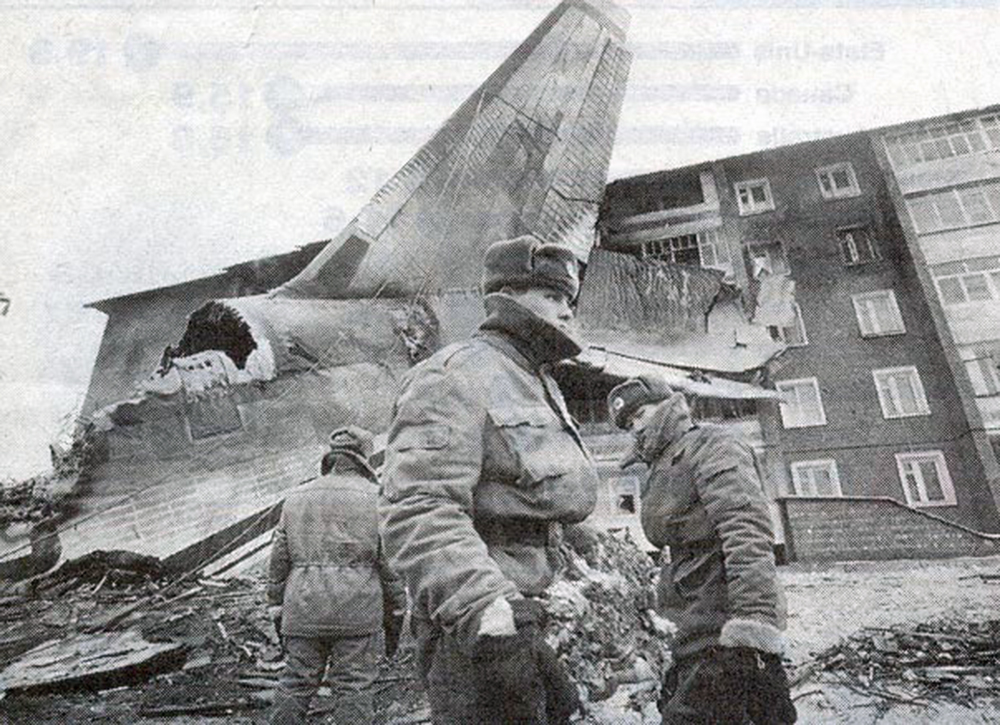
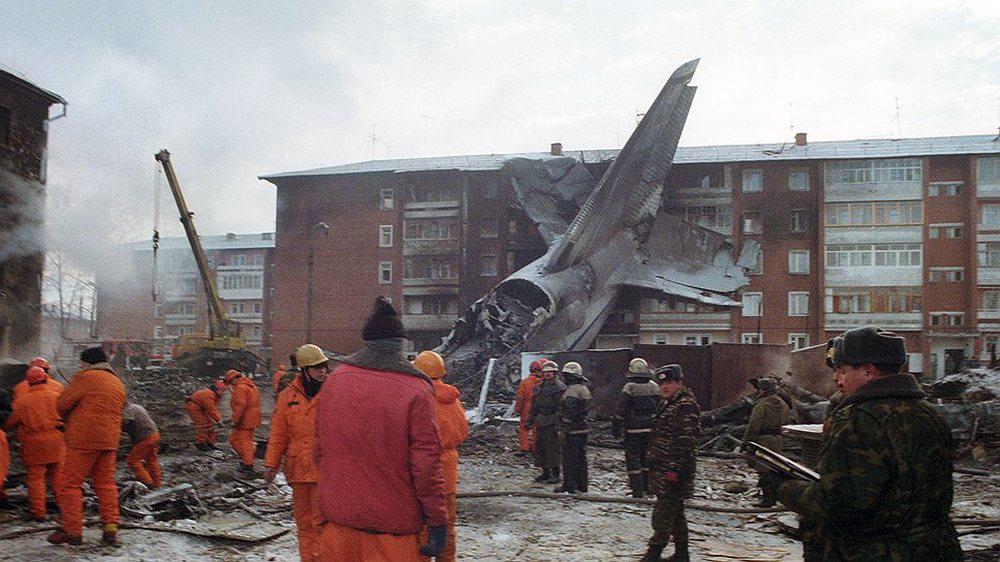
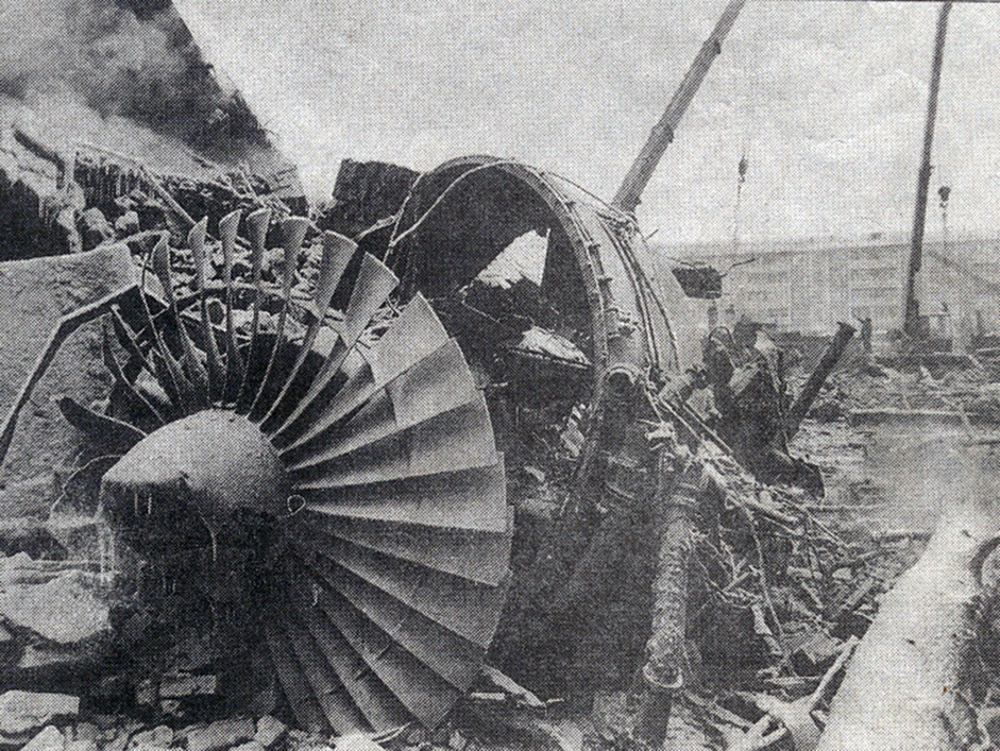
The aircraft was returning to Nouakchott with 35 passengers and seven crew members who accompanied the President of the Republic of Mauritania on an official visit of the Hodh Ech Chargui Region. All passengers were members of the Mauritanian Army fanfare. Shortly after a night takeoff, while in initial climb, the aircraft stalled and crashed in a huge explosion near the runway end. Three passengers were seriously injured while 39 other occupants were killed. The aircraft was totally destroyed by impact forces and a post crash fire.
Probable cause:
Loss of control during initial climb after one of the engine failed for unknown reasons.