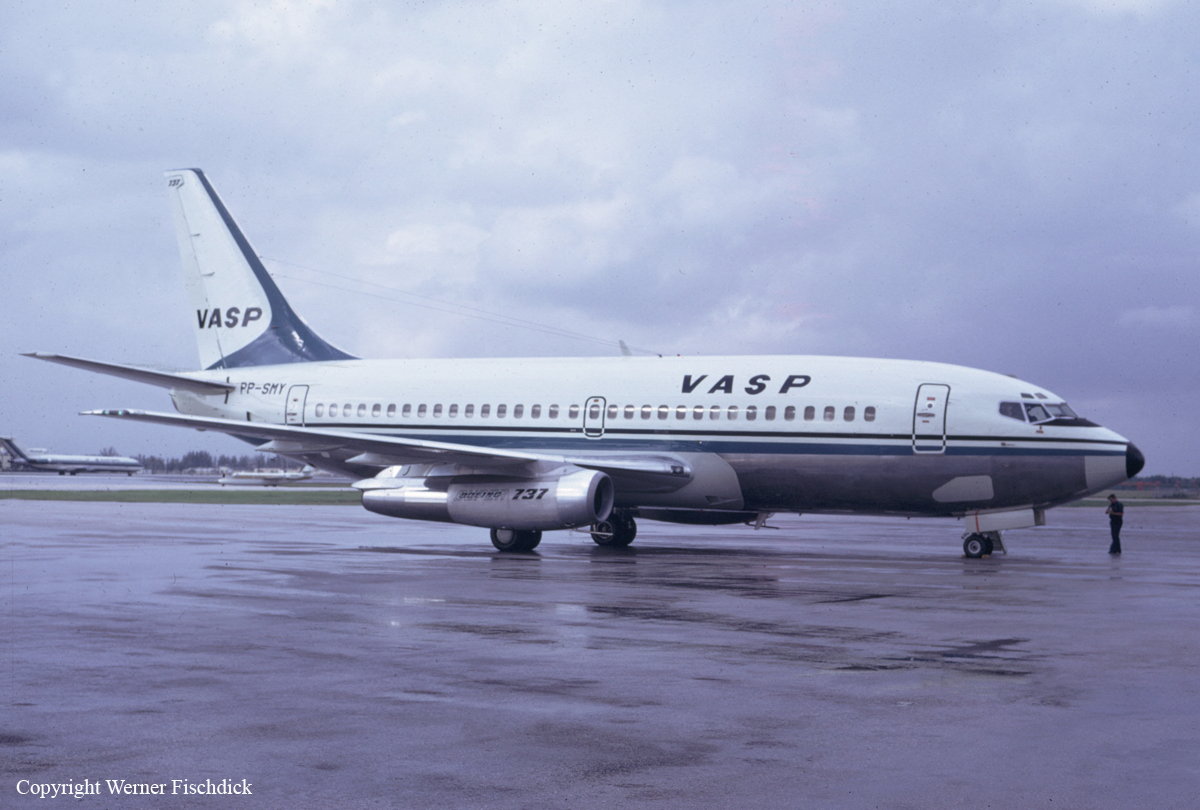Circumstances:
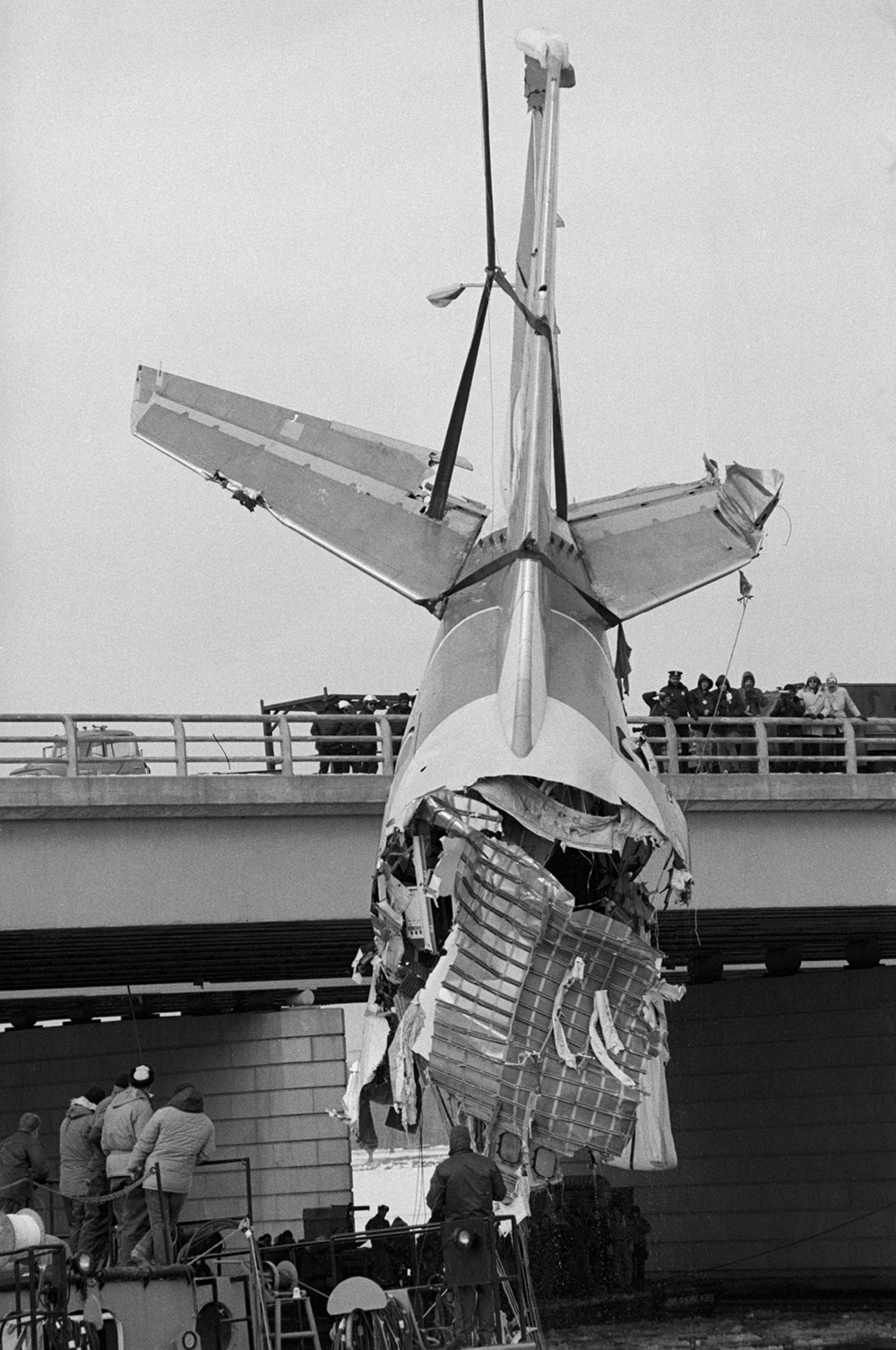
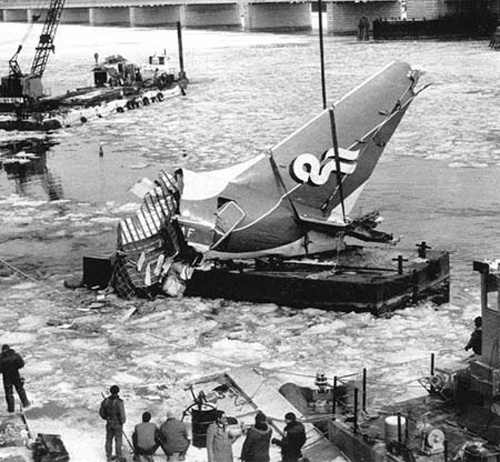
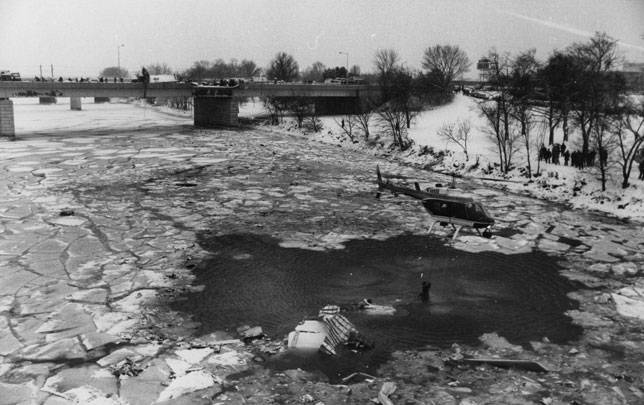
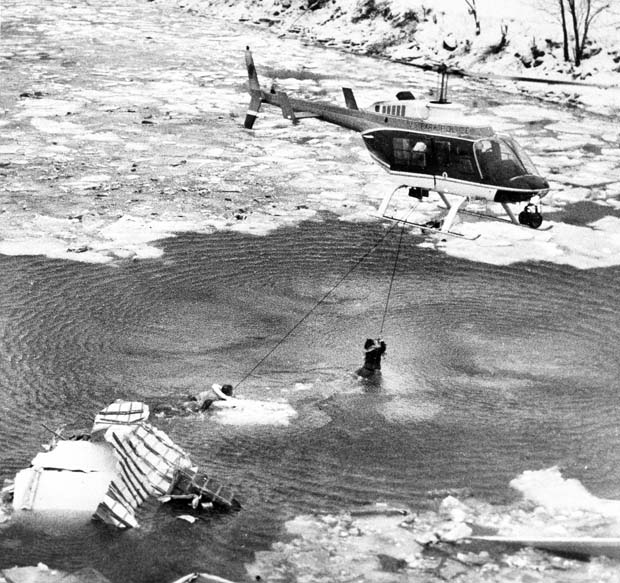
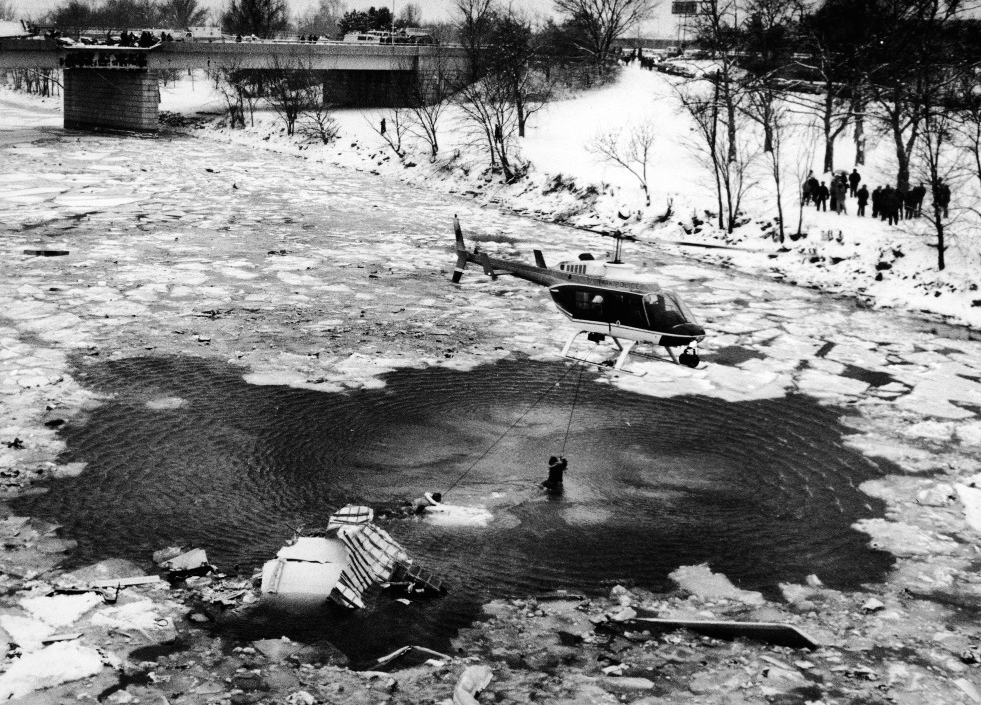
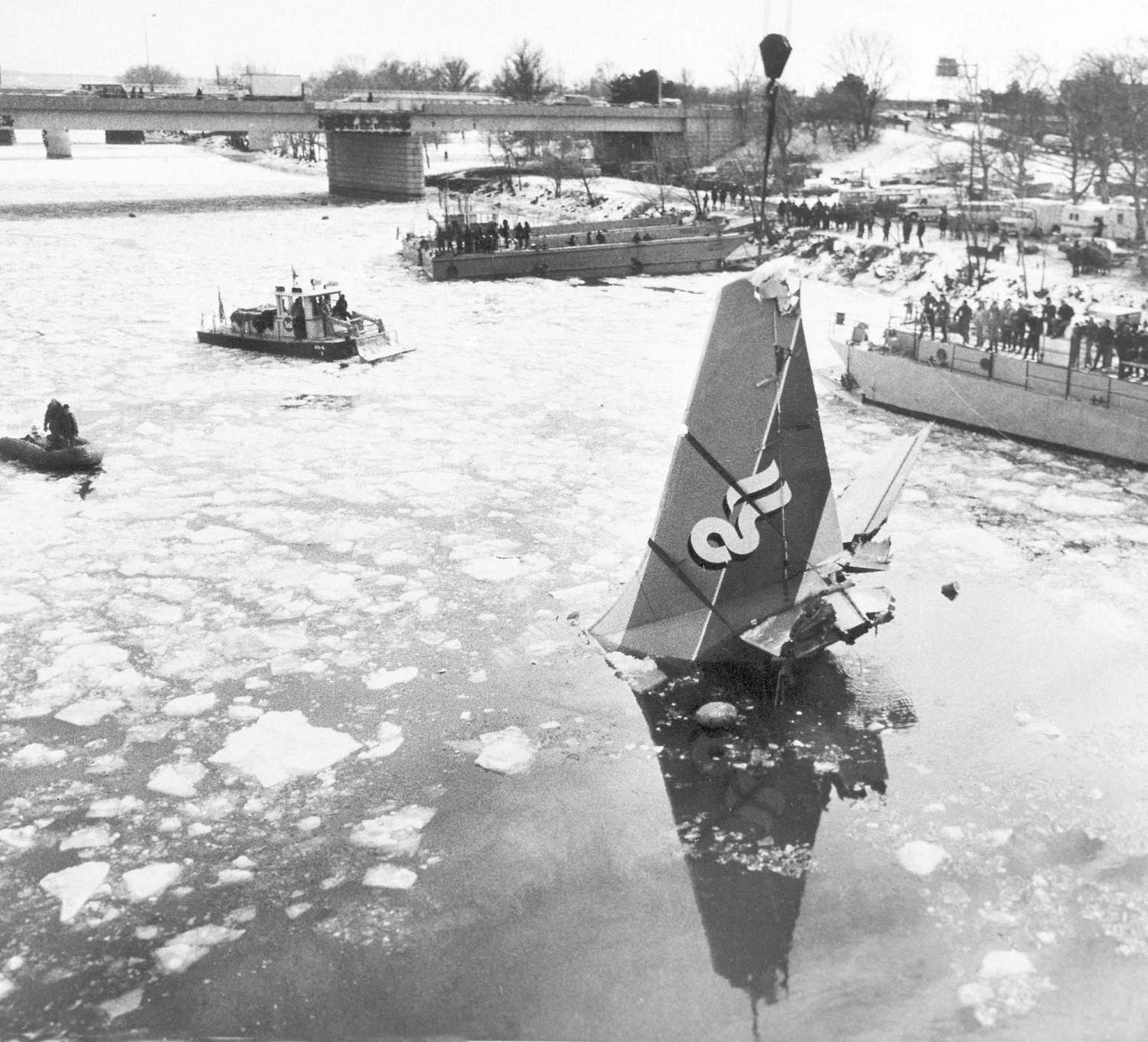
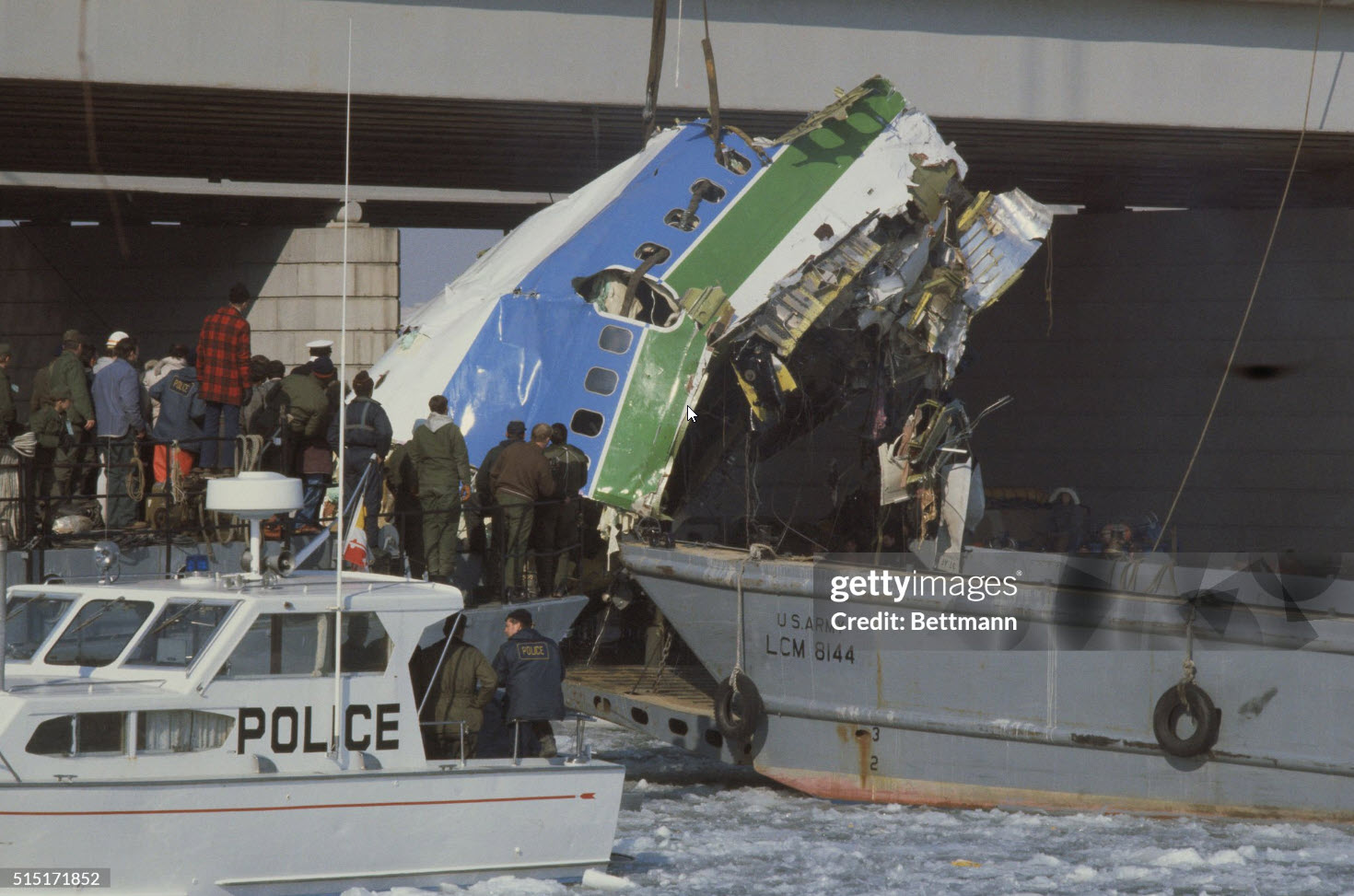
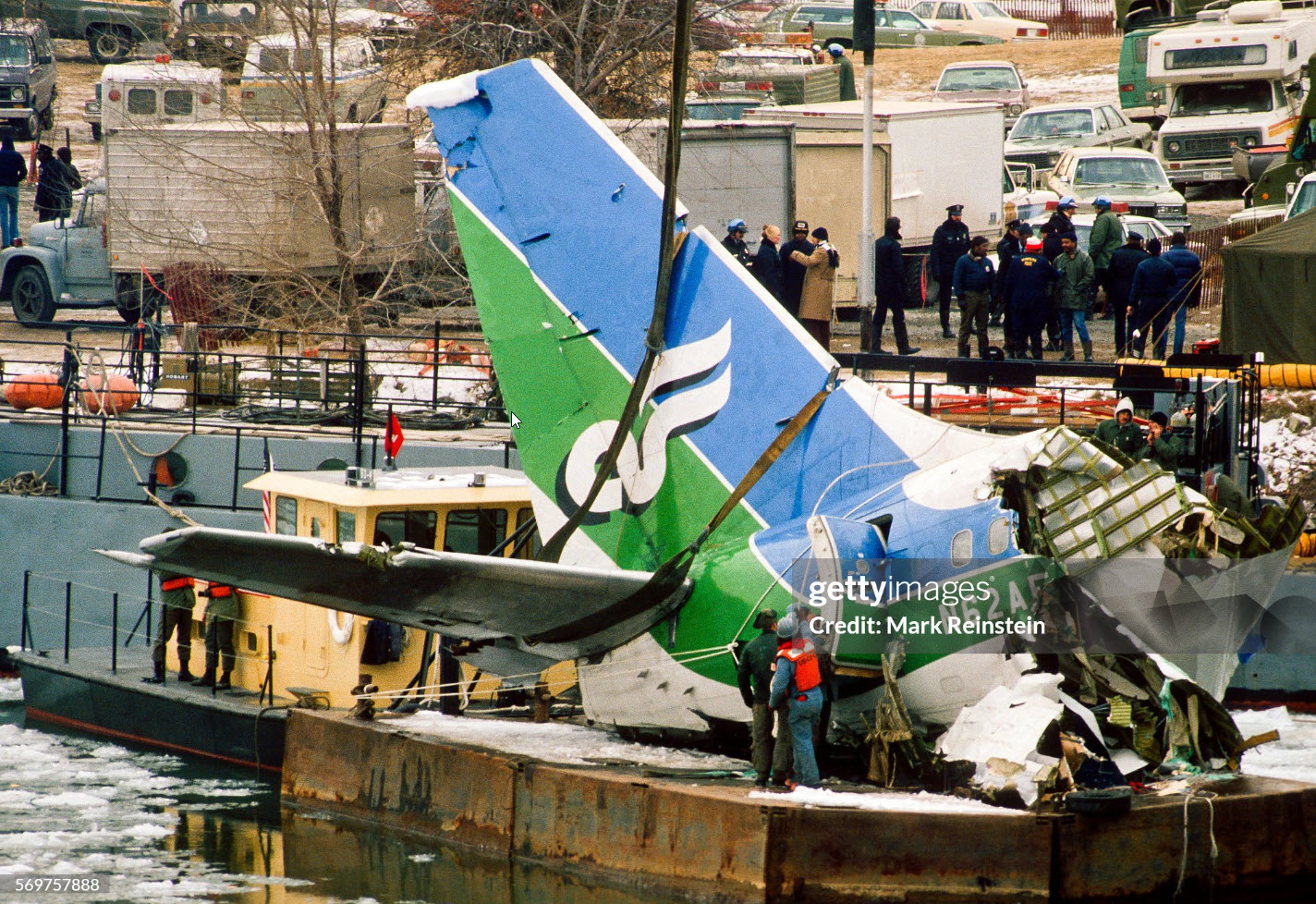
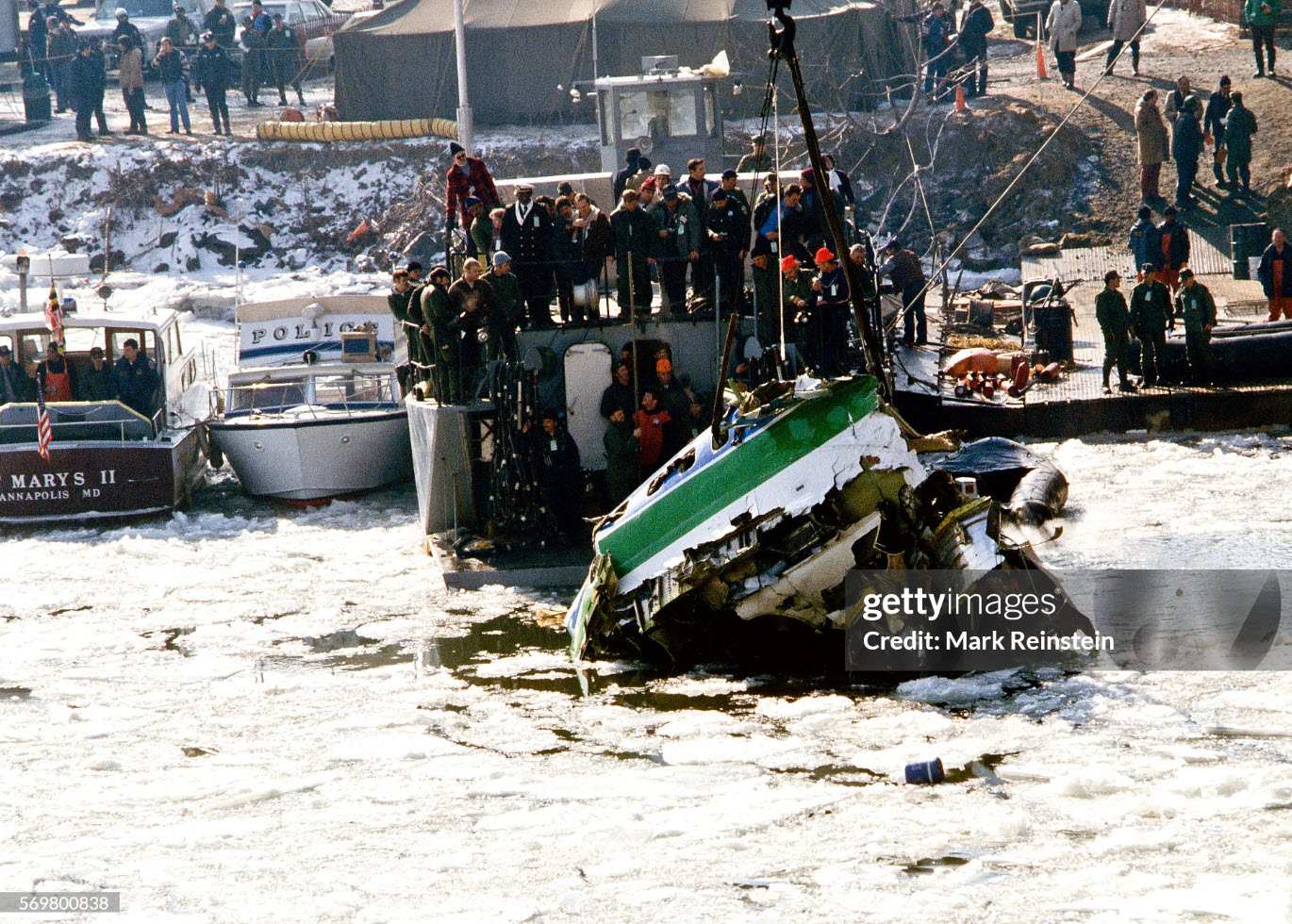
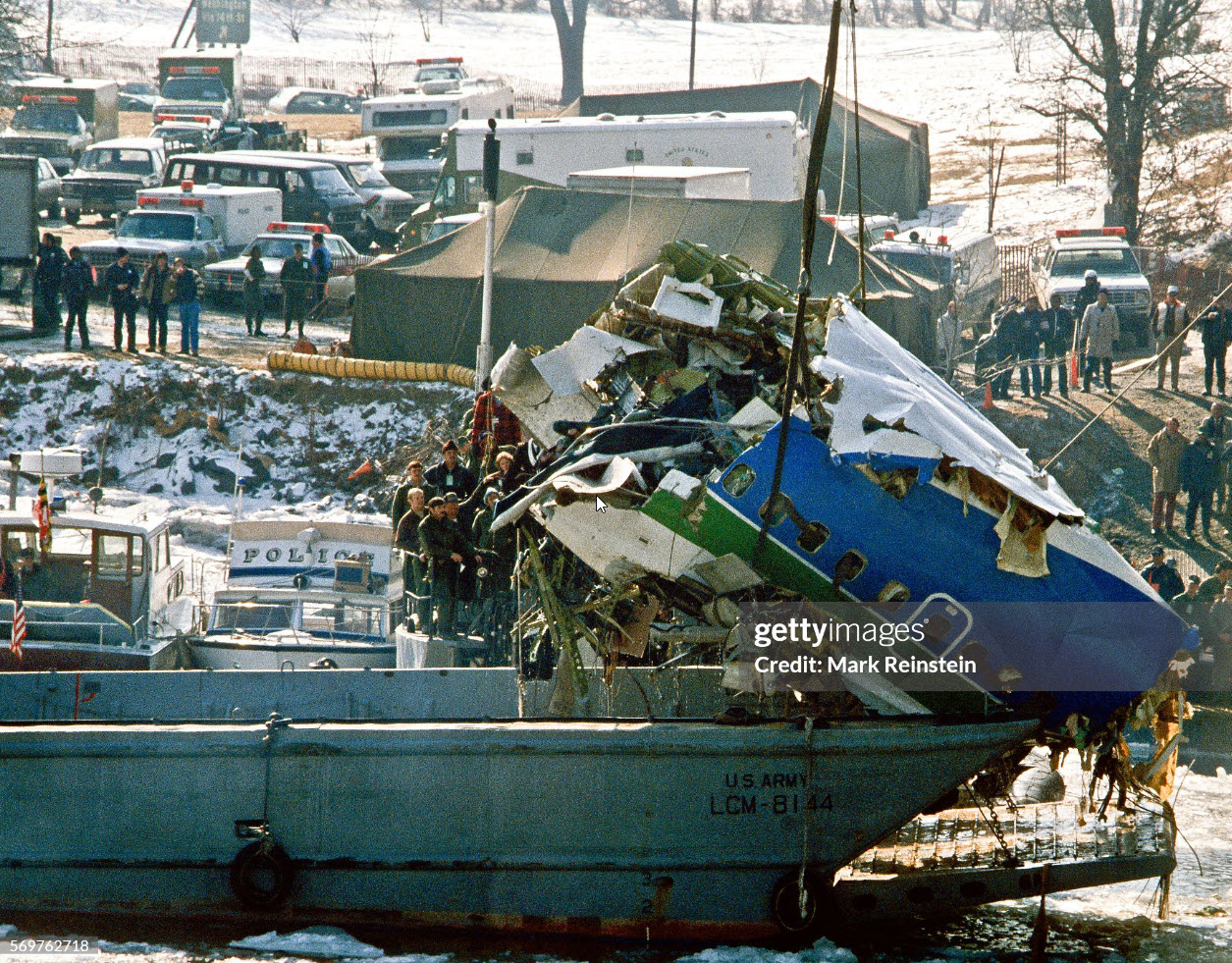
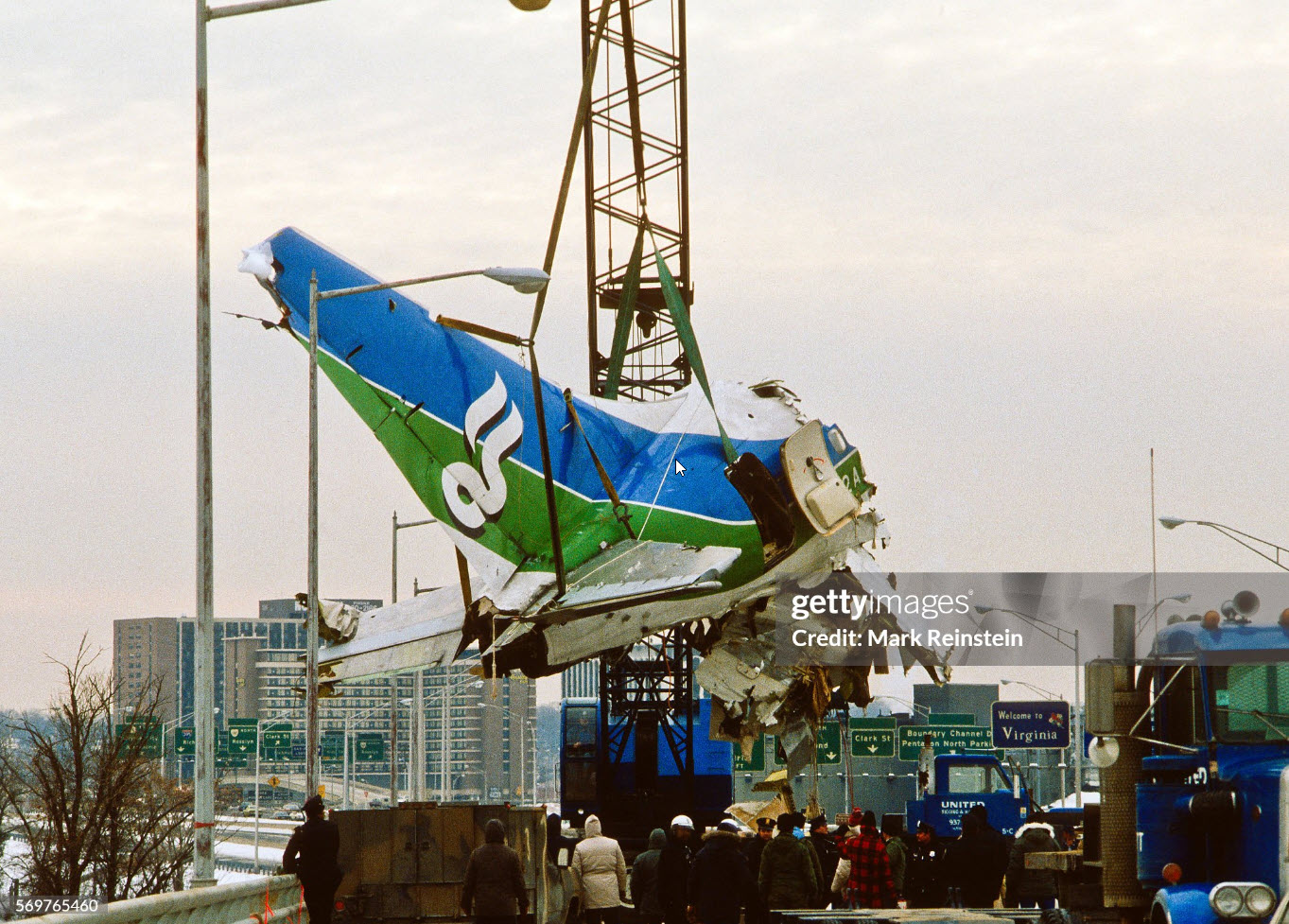
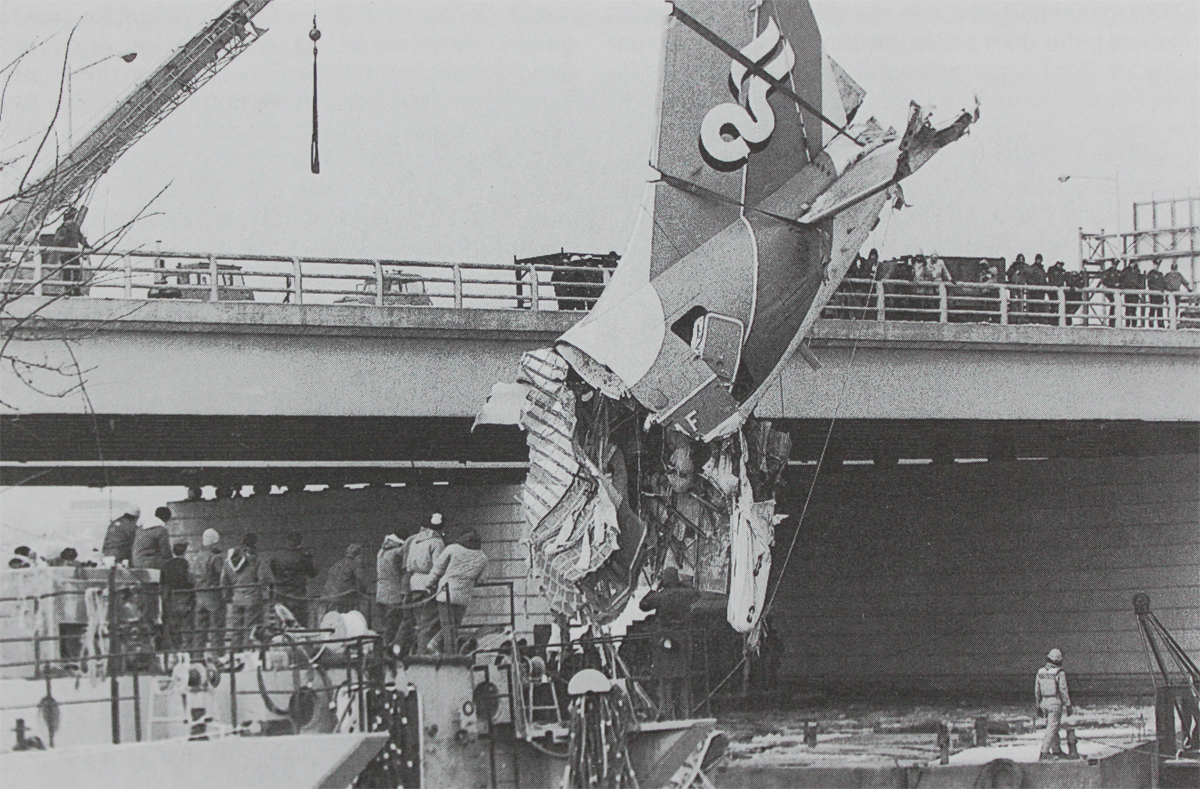
Air Florida Flight 90 was scheduled to leave Washington National Airport at 14:15 EST for a flight to Fort Lauderdale International Airport, FL (FLL), with an intermediate stop at the Tampa, FL (TPA). The aircraft had arrived at gate 12 as Flight 95 from Miami, FL, at 13:29. Because of snowfall, the airport was closed for snow removal from 13:38 to 14:53. At about 14:20 maintenance personnel began deicing the left side of the fuselage with deicing fluid Type II because the captain wanted to start the deicing just before the airport was scheduled to reopen (at 14:30) so that he could get in line for departure. Fluid had been applied to an area of about 10 feet when the captain terminated the operation because the airport was not going to reopen at 14:30. Between 14:45 and 14:50, the captain requested that the deicing operation be resumed. The left side of the aircraft was deiced first. No covers or plugs were installed over the engines or airframe openings during deicing operations. At 15:15, the aircraft was closed up and the jet way was retracted and the crew received push-back clearance at 15:23. A combination of ice, snow, and glycol on the ramp and a slight incline prevented the tug, which was not equipped with chains, from moving the aircraft. Then, contrary to flight manual guidance, the flight crew used reverse thrust in an attempt to move the aircraft from the ramp. This resulted in blowing snow which might have adhered to the aircraft. This didn't help either, so the tug was replaced and pushback was done at 15:35. The aircraft finally taxied to runway 36 at 15:38. Although contrary to flight manual guidance, the crew attempted to deice the aircraft by intentionally positioning the aircraft near the exhaust of the aircraft ahead in line (a New York Air DC-9). This may have contributed to the adherence of ice on the wing leading edges and to the blocking of the engine’s Pt2 probes. At 15:57:42, after the New York Air aircraft was cleared for takeoff, the captain and first officer proceeded to accomplish the pre-takeoff checklist, including verification of the takeoff engine pressure ratio (EPR) setting of 2.04 and indicated airspeed bug settings. Takeoff clearance was received at 15:58. Although the first officer expressed concern that something was 'not right' to the captain four times during the takeoff, the captain took no action to reject the takeoff. The aircraft accelerated at a lower-than-normal rate during takeoff, requiring 45 seconds and nearly 5,400 feet of runway, 15 seconds and nearly 2,000 feet more than normal, to reach lift-off speed. The aircraft initially achieved a climb, but failed to accelerate after lift-off. The aircraft’s stall warning stick shaker activated almost immediately after lift-off and continued until impact. The aircraft encountered stall buffet and descended to impact at a high angle of attack. At about 16.01, the aircraft struck the heavily congested northbound span of the 14th Street Bridge and plunged into the ice-covered Potomac River. It came to rest on the west end of the bridge 0.75 nmi from the departure end of runway 36. When the aircraft struck the bridge, it struck six occupied automobiles and a boom truck before tearing away a 41-foot section of the bridge wall and 97 feet of the bridge railings. Four persons in vehicles on the bridge were killed; four were injured, one seriously.
Probable cause:
The flight crew's failure to use engine anti-ice during ground operation and takeoff, their decision to take off with snow/ice on the airfoil surfaces of the aircraft, and the captain’s failure to reject the takeoff during the early stage when his attention was called to anomalous engine instrument readings. Contributing to the accident were the prolonged ground delay between deicing and the receipt of ATC takeoff clearance during which the airplane was exposed to continual precipitation, the known inherent pitch up characteristics of the B-737 aircraft when the leading edge is contaminated with even small amounts of snow or ice, and the limited experience of the flight crew in jet transport winter operations.