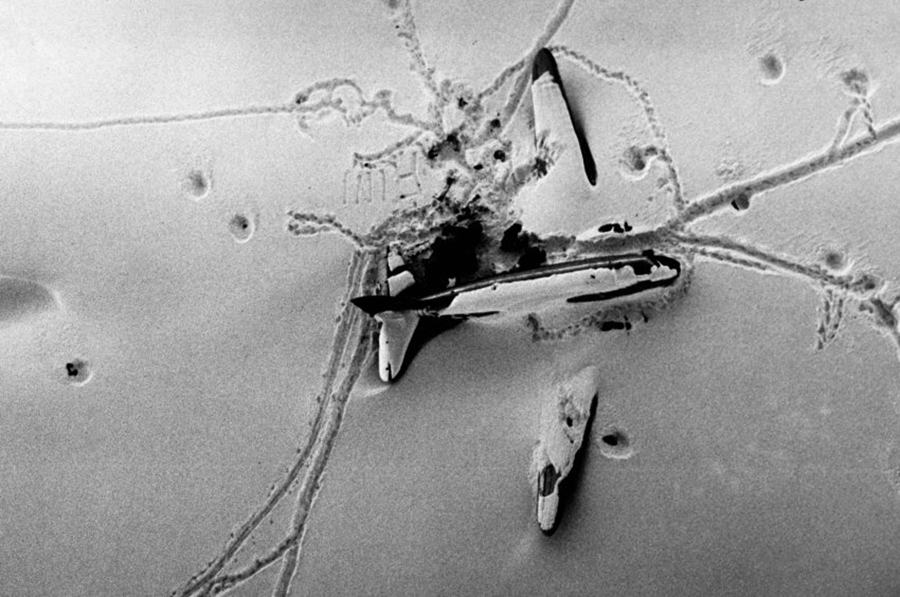
Crash of a Cessna 425 Conquest I in Bern: 8 killed
Date & Time:
Mar 3, 1986 at 0822 LT
Registration:
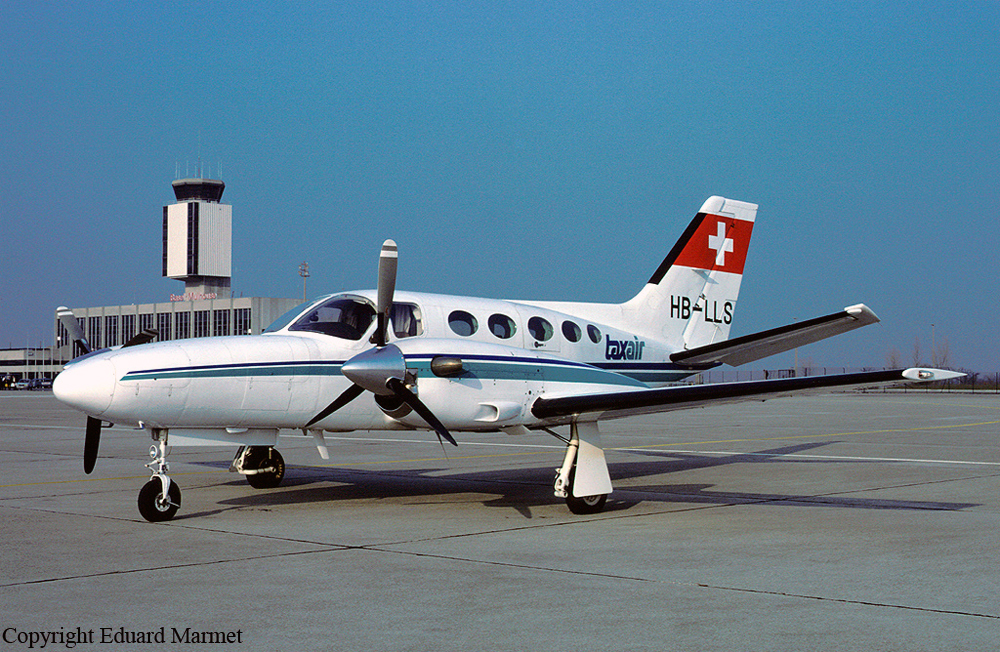
HB-LLS
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Bern - Düsseldorf
MSN:
425-0040
YOM:
1981
Crew on board:
1
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
7
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
8
Captain / Total hours on type:
514.00
Aircraft flight hours:
1074
Circumstances:
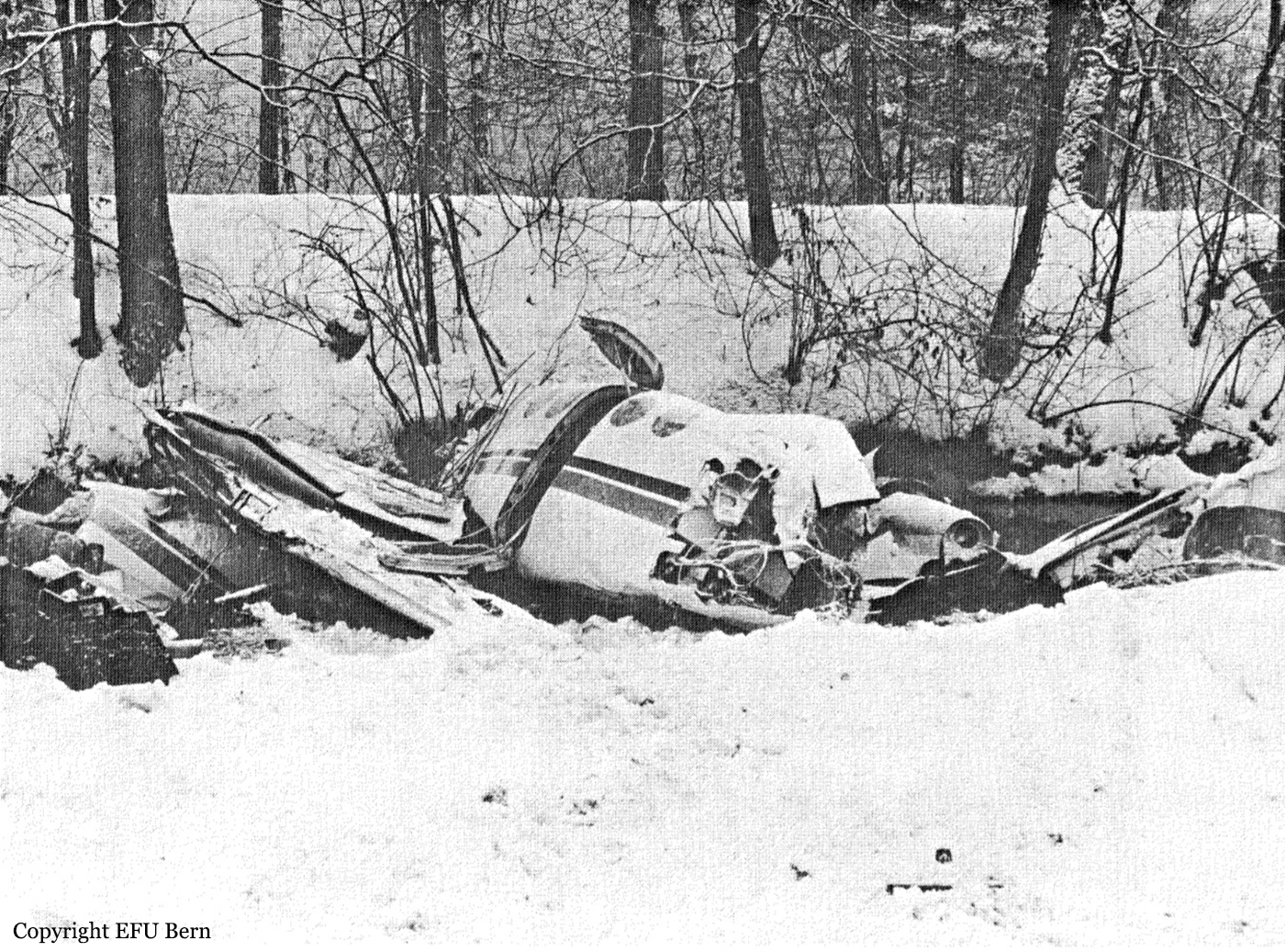
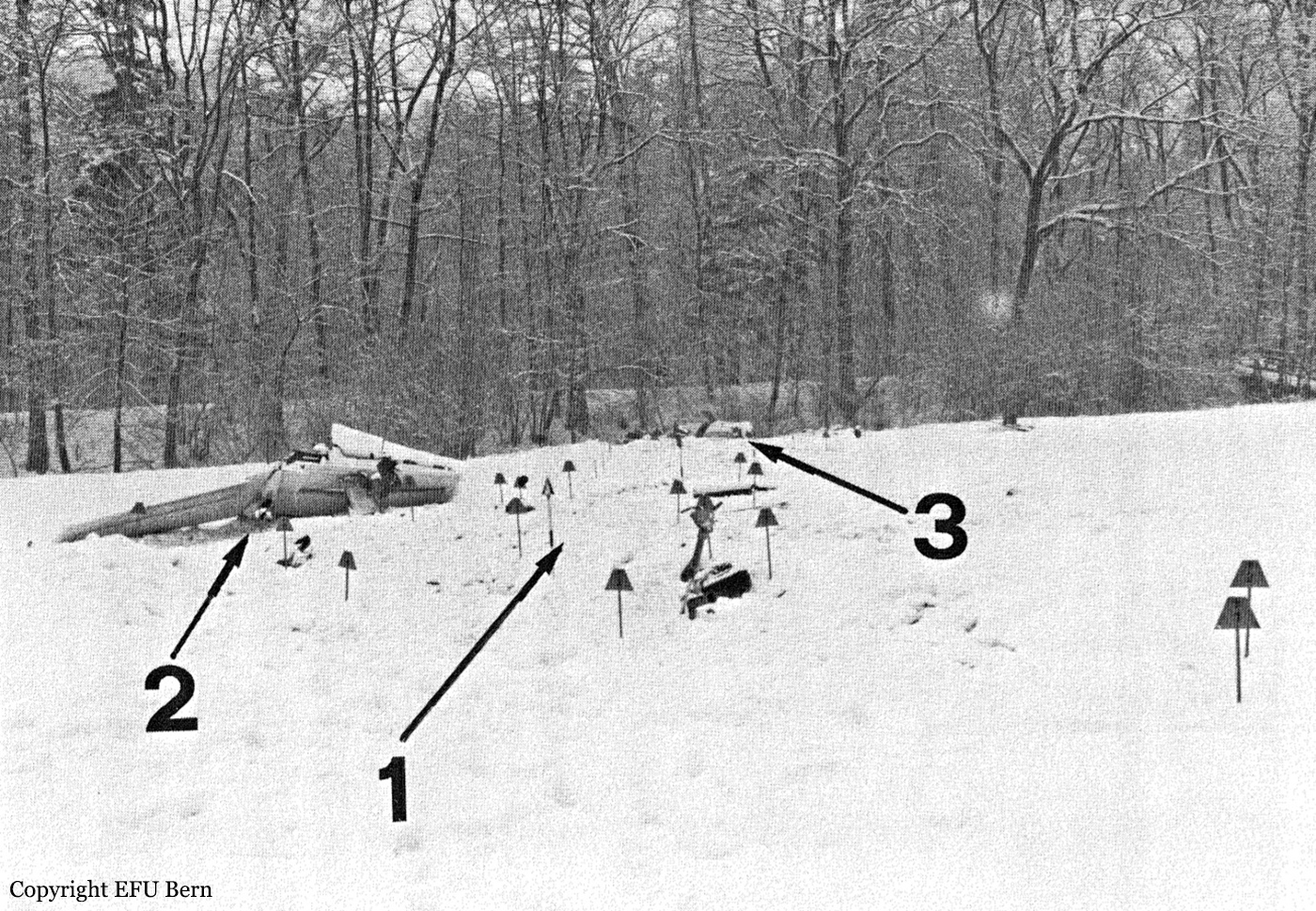
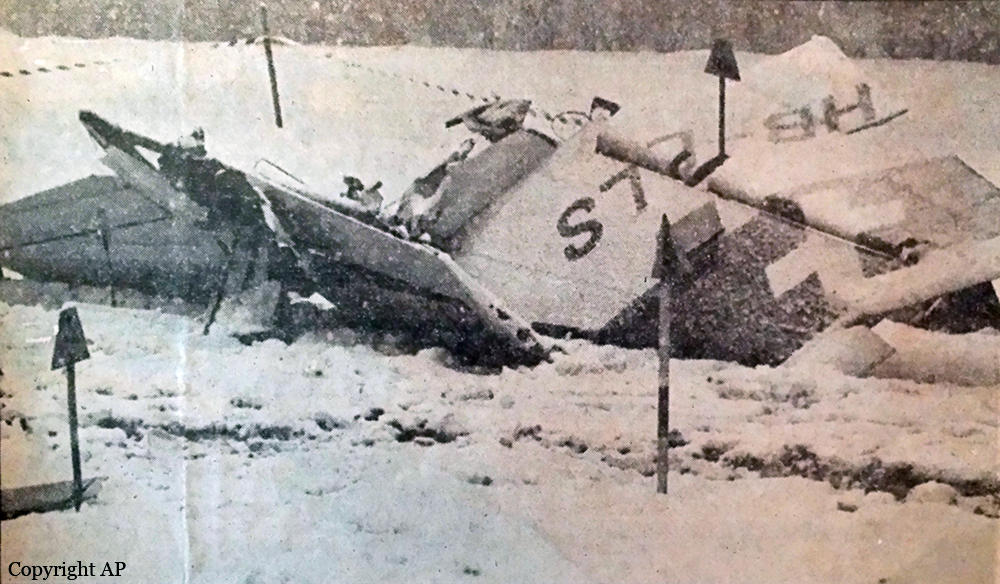
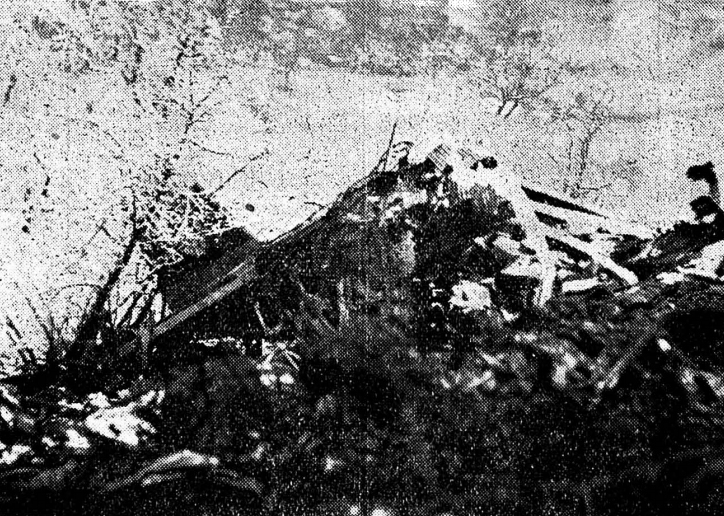
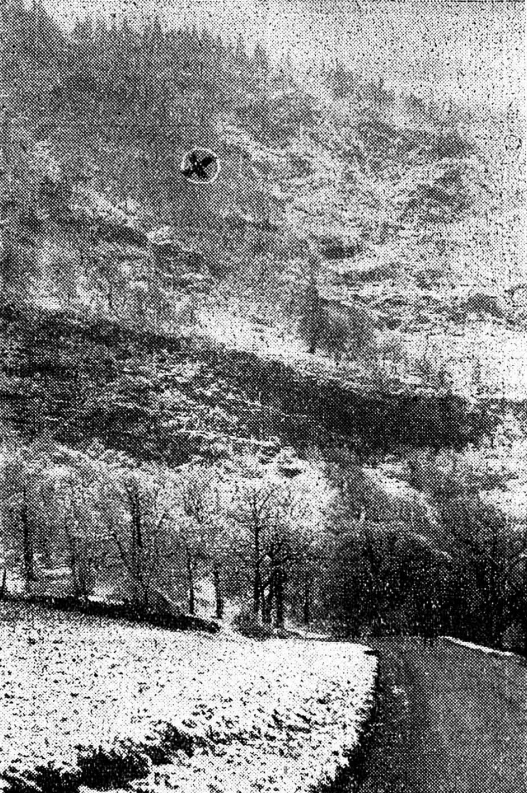
The twin engine aircraft was engaged in a charter flight from Bern to Düsseldorf, carrying one pilot and seven employees from the textile industry. Takeoff was completed from runway 32 partially covered with wet snow and after liftoff, the aircraft encountered difficulties to gain height and passed just over trees located from either side of the Aar River. Then the aircraft lost height, initiated a left turn then stalled and crashed in a snow covered field located near a wood, about 1,250 meters northwest of runway 14 threshold and 600 meters to the left of its extended centerline. The aircraft was destroyed and all eight occupants were killed.
Probable cause:
The accident was the consequence of a loss of control during initial climb in poor weather conditions. The following contributing factors were reported:
- The runway was contaminated with wet snow,
- Possible ice on wings and tail,
- High drag because the gear was still down,
- The total weight of the aircraft was 102 kilos above MTOW,
- The CofG was 0,56 inch (1,42 cm) beyond the aft limit,
- The pilot suffered high psychological tension,
- It is possible that the flaps were lowered at an angle of 15° prior to takeoff, during takeoff and during initial climb, which may reduce lift and increase drag.
- The runway was contaminated with wet snow,
- Possible ice on wings and tail,
- High drag because the gear was still down,
- The total weight of the aircraft was 102 kilos above MTOW,
- The CofG was 0,56 inch (1,42 cm) beyond the aft limit,
- The pilot suffered high psychological tension,
- It is possible that the flaps were lowered at an angle of 15° prior to takeoff, during takeoff and during initial climb, which may reduce lift and increase drag.
Final Report: