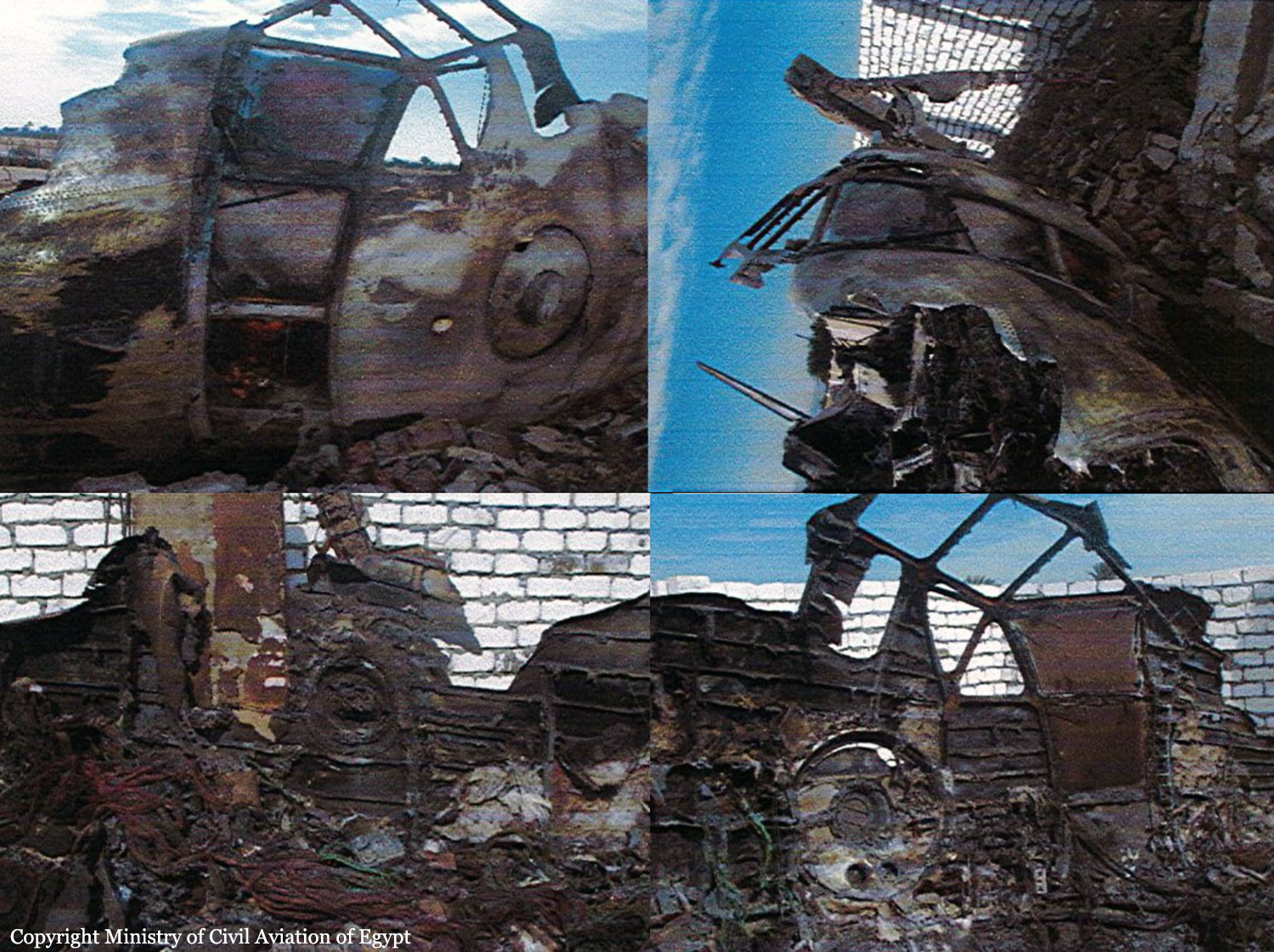Date & Time:
Feb 20, 2009 at 0418 LT
Type of aircraft:
Antonov AN-12
Registration:
S9-SVN
Flight Phase:
Takeoff (climb)
Flight Type:
Cargo
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Kisangani – Entebbe – Luxor – Mykolaiv
MSN:
6 3 443 10
YOM:
1966
Flight number:
LFT1015
Country:
Egypt
Region:
Africa
Crew on board:
5
Crew fatalities:
5
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
0
Other fatalities:
0
Total fatalities:
5
Aircraft flight hours:
11692
Aircraft flight cycles:
6451
Circumstances:
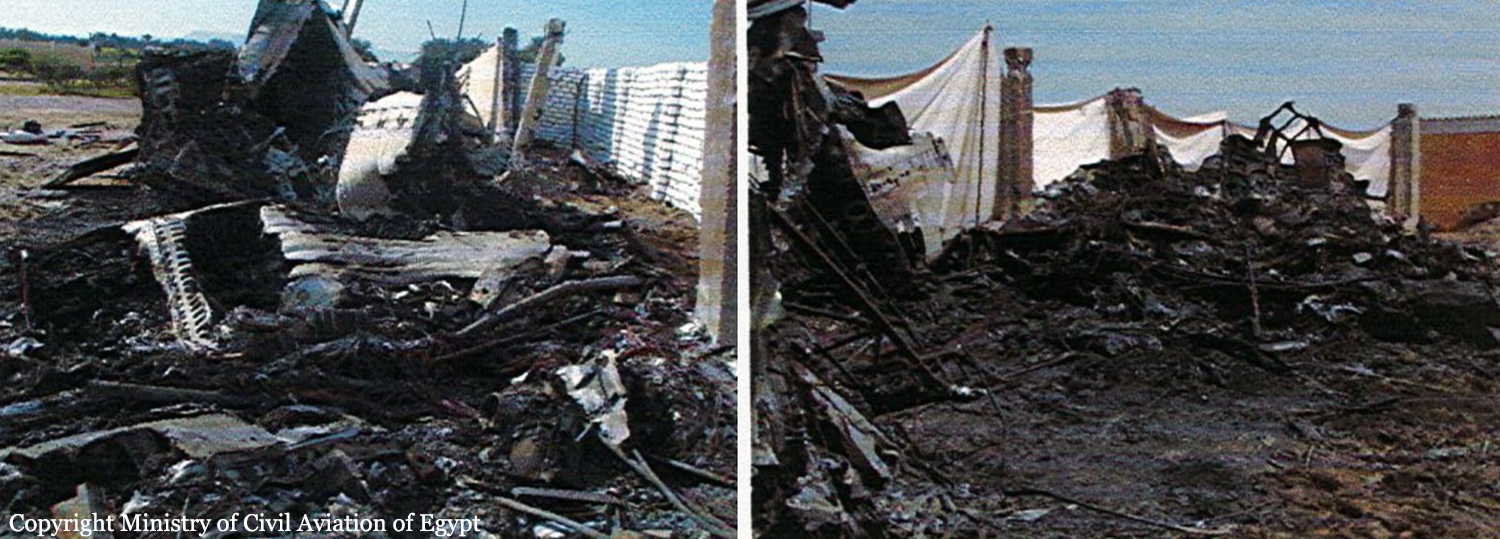
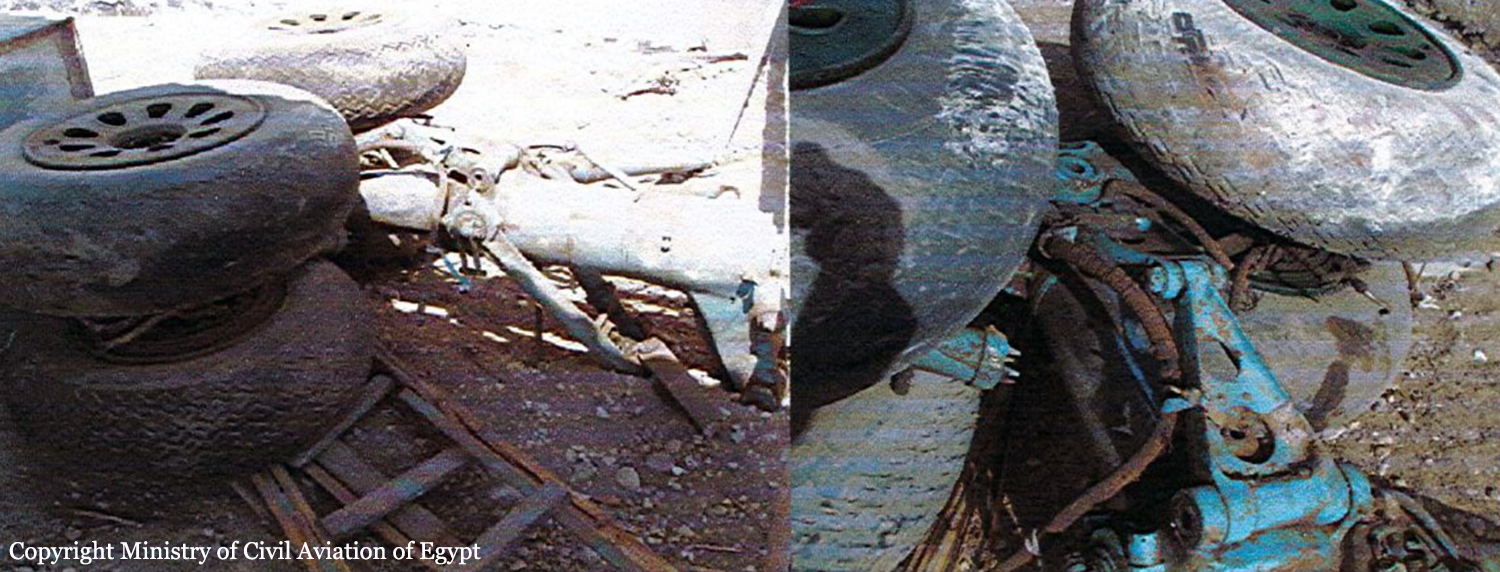
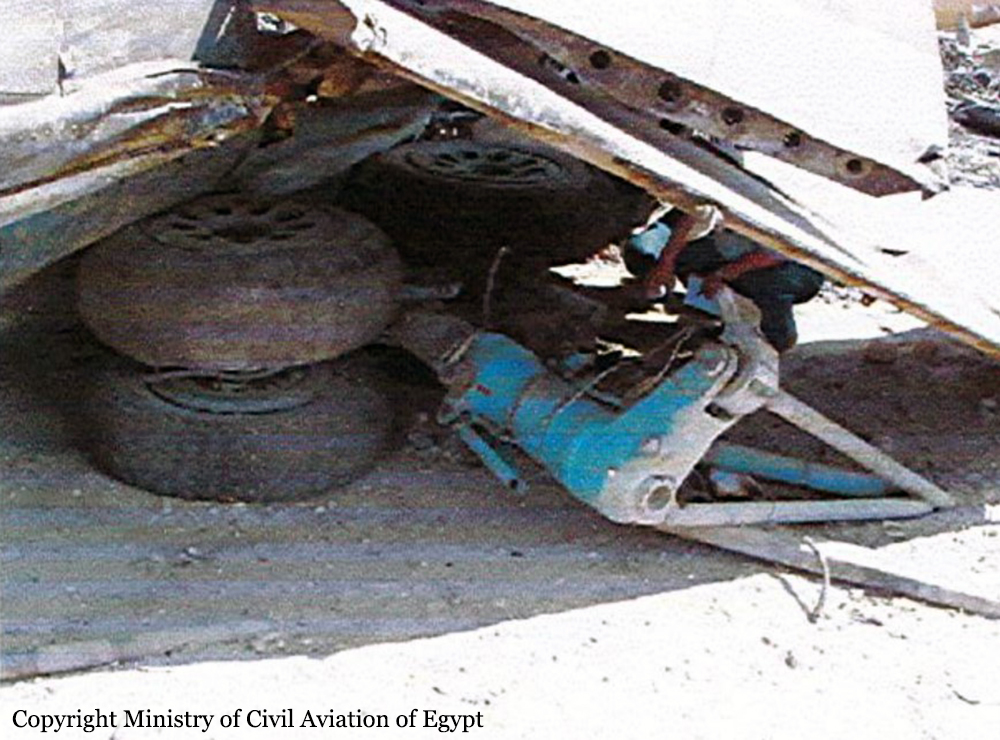
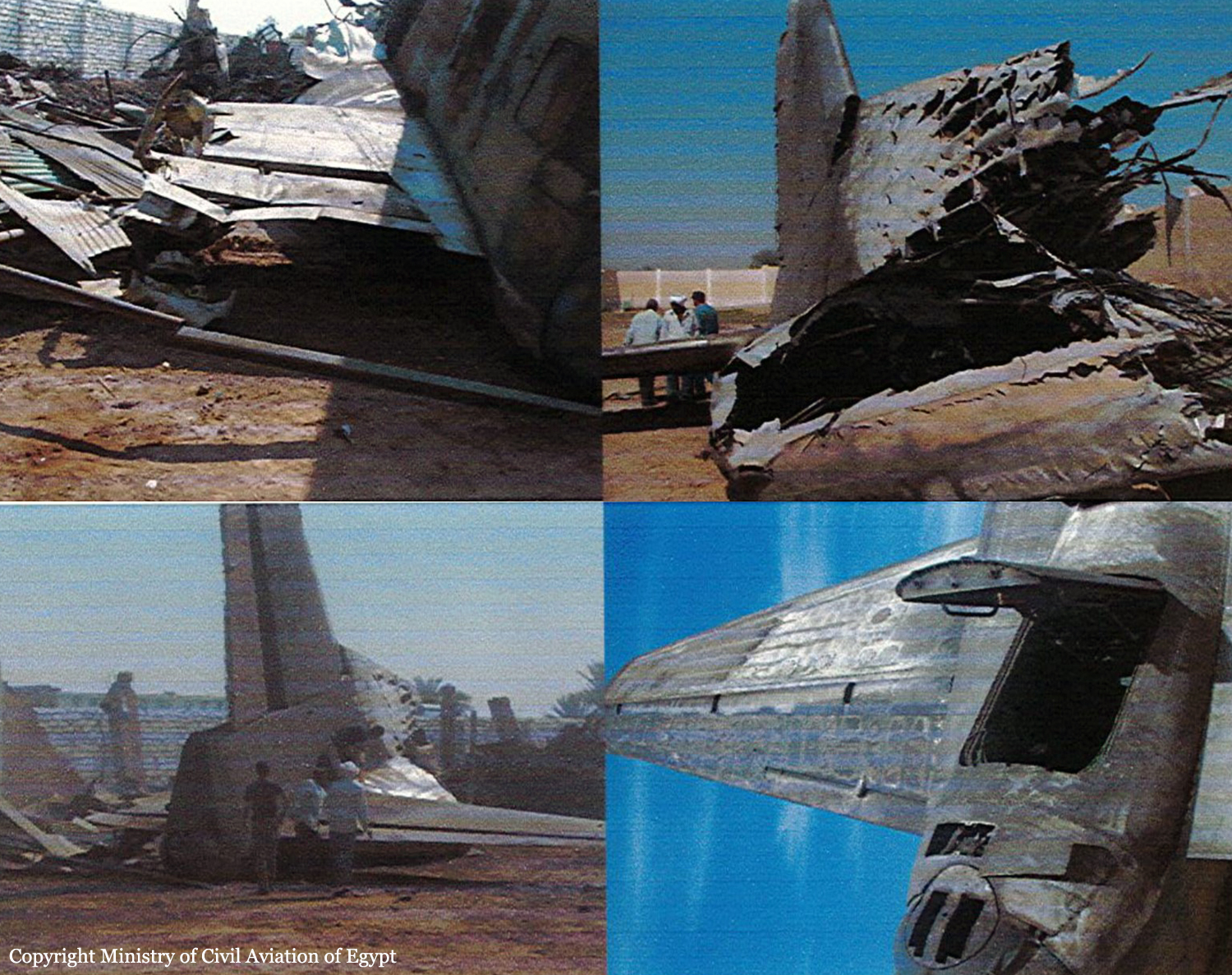
The four engine aircraft was transferred from Kisangani to Mykolaiv, Ukraine, for maintenance purposes. Two enroute stops were scheduled in Entebbe and Luxor. Ar 0417LT, the crew was cleared for takeoff. The aircraft started rolling on runway 02 for takeoff but it kept rolling on it till it reached its end. The aircraft continued rolling in the sand drifting from the runway centerline to the right, crossing a service road and eventually crashing into a military zone located 500 metres from the runway end. The aircraft crashed into one of the buildings inside the military unit causing complete destruction of the building. The right wing also crashed into another building putting the aircraft on fire and forcing the aircraft to turn right. The aircraft kept moving forward the military unit fence (next to Tiba-Luxor road) and stopped there, crashing in its way into oil barrel. The accident resulted in the total destruction and fire of the aircraft and the fatality of its crew but no further injuries.
Probable cause:
The following factors were identified:
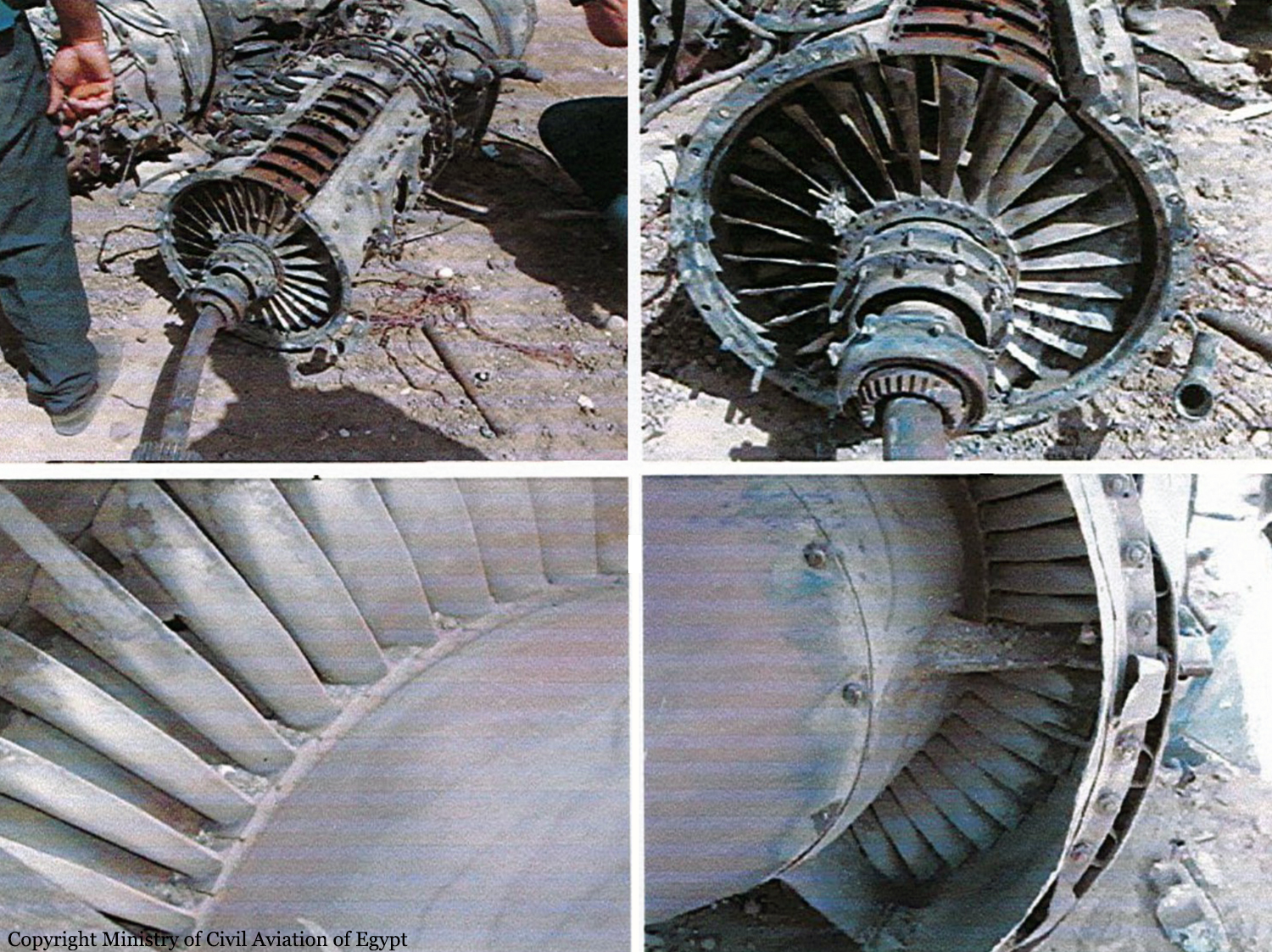
- Lack of available thrust which corresponded to the power of only two engines running during take off run,
- Lack of authorized maintenance of the aircraft,
- The uncoordinated crew actions in the critical situation (both pilots had previously flown as captains). The lack of coordination is confirmed by the braking trails left by the main landing gear at the end of RWY -02, based on FCOM instructions, and in case of rejected takeoff attempt, the crew had to set the throttles to idle, lower the nose gear to reach the runway and then use the propellers for braking (releasing them from the stops). Also, to reduce the roll and to maintain the direction they were to use the nose wheel steering and wheel brakes as well as emergency braking if needed. Actually the crew did neither of the above procedures, except using the main wheel brakes.
- Lack of available thrust which corresponded to the power of only two engines running during take off run,
- Lack of authorized maintenance of the aircraft,
- The uncoordinated crew actions in the critical situation (both pilots had previously flown as captains). The lack of coordination is confirmed by the braking trails left by the main landing gear at the end of RWY -02, based on FCOM instructions, and in case of rejected takeoff attempt, the crew had to set the throttles to idle, lower the nose gear to reach the runway and then use the propellers for braking (releasing them from the stops). Also, to reduce the roll and to maintain the direction they were to use the nose wheel steering and wheel brakes as well as emergency braking if needed. Actually the crew did neither of the above procedures, except using the main wheel brakes.
Final Report:
S9-SVN.pdf26.63 MB