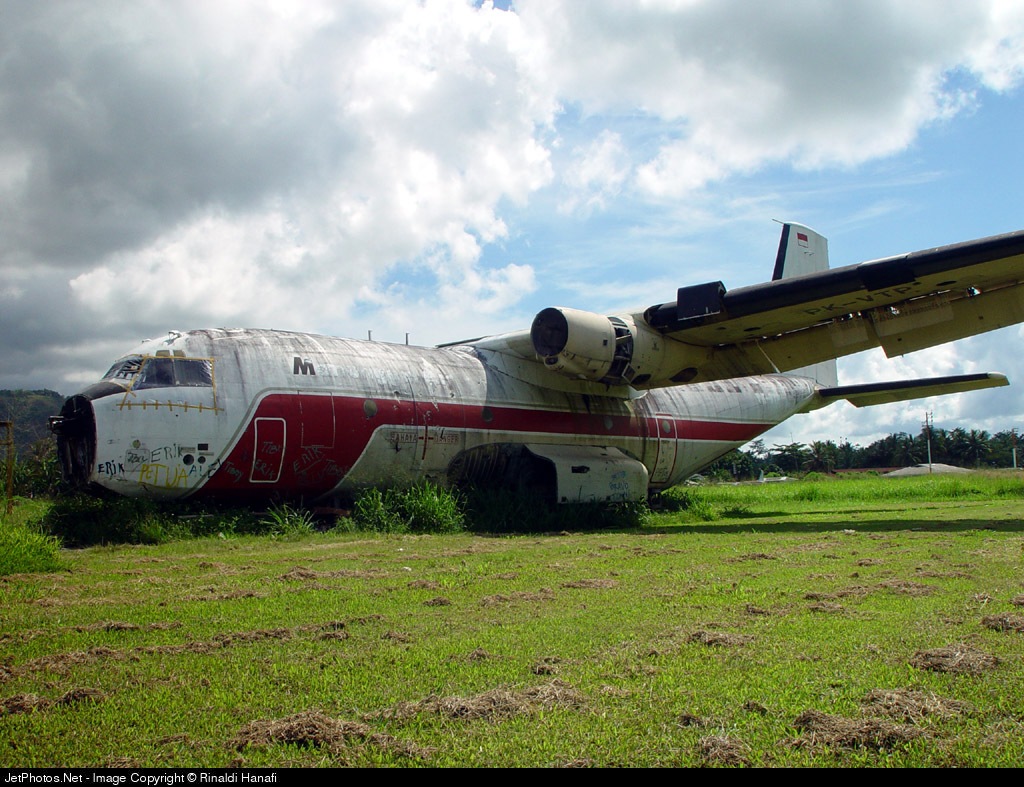
Crash of an Antonov AN-72 in Wamena
Date & Time:
Apr 21, 2002 at 0913 LT
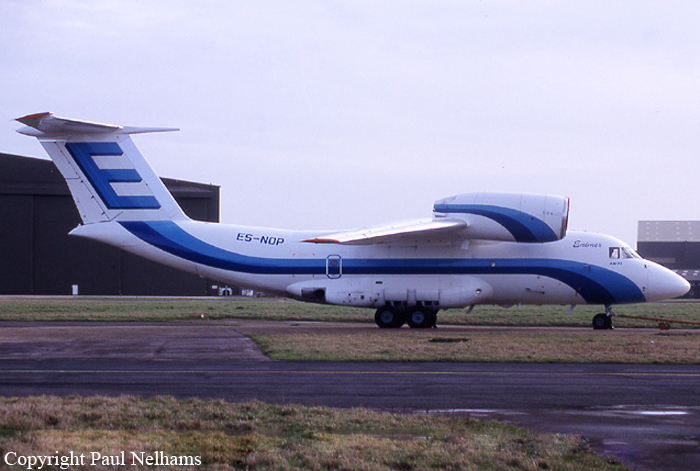
Registration:
ES-NOP
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Jayapura – Wamena
MSN:
36572010905
YOM:
1980
Crew on board:
4
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Captain / Total hours on type:
800.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
100
Aircraft flight hours:
1897
Aircraft flight cycles:
1376
Circumstances:
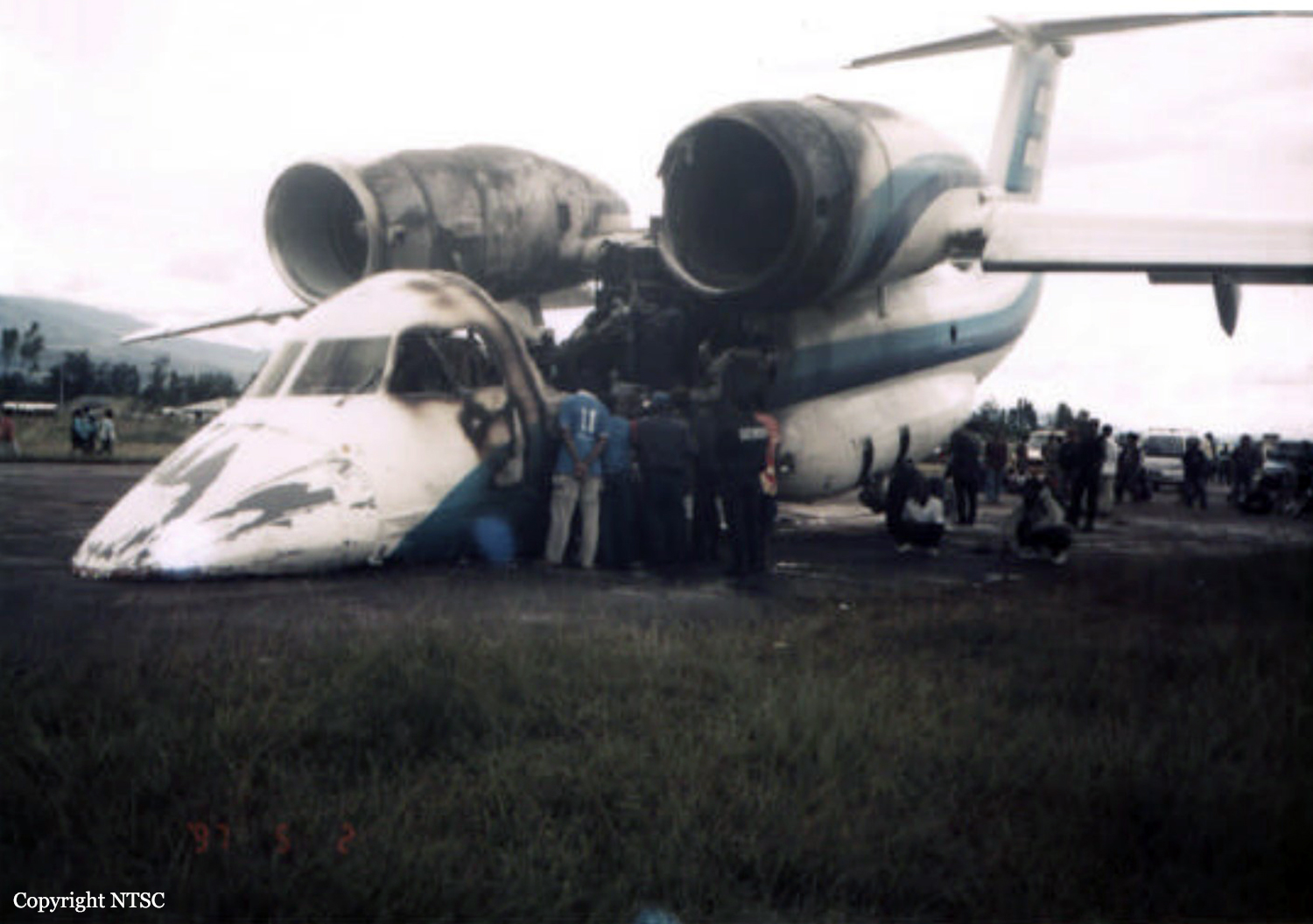
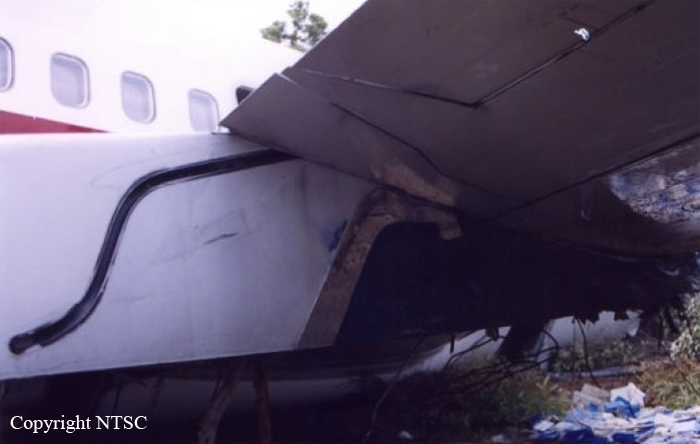
At 23:40 UTC / 08:40 LT (WIT) on Sunday April 21, 2002, the ES-NOP departed Sentani Airport, Jayapura, bound for Wamena. The aircraft, an Antonov AN-72, was being operated by PT Trigana Air Services as a cargo carrying charter transport flight. The flight crews of four included three cockpit crew personnel and a loadmaster. The flight was the third flight of eight flights planned for the day between Sentani Airport and Wamena airport. The first flight departed Sentani airport at 21:05 UTC / 06:05 LT. Arriving at Wamena at 21:40 UTC / 06:40 LT. The return flight from Wamena bound for Sentani, departing Wamena at 22:22 UTC/ 07:22 LT arrived at Sentani at 22:52 UTC/07:52 LT. The flights were reported normal, and the weather along the route was reported clear. The third return flight, from Sentani to Wamena departed Sentani at 23:40 UTC / 08:40 LT carrying a load of 7,481 kg. The weather at Jayapura and along the route was clear. The cruise altitude during the flight was 16,000 ft. After waypoint ‘Maleo’ the airplane over-flew the so called ‘north-gap’ and the descent was initiated while passing the ‘pass valley’. Three other airplanes were reported to be in the area, one Fokker F27 PK-YPQ which was enroute from Wamena airport to Jayapura, and two Antonov A26 aircraft, registration ER-AFQ and ER-AFE. Flying over ‘Yiwika’ 7 Nm from Wamena airport, and descending through 12,000 ft with speed of 330 km/hr, the ES-NOP overtook the ER-AFE. The flight crew had the runway in sight. The PIC acting as pilot flying, flew an ‘S’ approach pattern during the final flight path of Wamena airport. (arriving Wamena 24:15 UTC/09:15 LT). On final and at an altitude of 100 meters, the airplane was lined up to the runway 15-center line. The airplane touched down while still within the touchdown zone. The airplane bounced twice, the second and last bounce reported to be more severe than the first one. The airplane rolled down the runway, with the flight crew noticing an unusual nose down attitude. The PIC/Pilot Flying applied reverse power and brakes, controlling the aircraft by using rudder inputs. During the roll, the loadmaster, sitting behind the PIC’s seat saw black smoke coming from the floor of the forward side of the cargo compartment. The crew reported that the smoke hurt their eyes. The airplane decelerated with smoke emitted from the forward cargo compartment. After stopping, the loadmaster opened the airplane door taking the extinguisher to extinguish the fire. The PIC shut down the engines after the airplane came to a standstill then opened the left cockpit window. PIC then left the cockpit assisting the loadmaster extinguishing the fire, the F/O completed the shutdown procedure, as the smoke blocked out his vision. The Flight Engineer attempted unsuccessfully opened the overhead emergency exit. The F/O and Flight Engineer then evacuated through the left cockpit window, while the PIC and loadmaster exited through the door. Observing the occurrence, and as the crash bell was unserviceable, the ATC on duty called the Deputy Chief of the airport, and alerted the fire fighting brigade. The fire fighting personnel failed to start the fire truck, and after recharging the truck’s battery for about 10 minutes reattempt to start for a second time. This attempt again failed, and the battery was again recharged, while fire fighting personnel ran the airplanes final position carrying portable fire extinguisher. After another ten minutes of battery charging, the fire fighting truck was finally started, immediately proceeding to the accident site. After a refill of the fireextinguishing agent the fire was finally extinguished. Firefighting personnel extinguished the fire in about 30 minutes time. The airplane was seriously damaged, with the front side of the airplane completely burnt out, the fire cutting a hole from behind the cockpit roof until approximately the middle of the cabin in front of the roof. The cargo was totally consumed by fire. No one was injured during the accident. After the occurrence, Wamena airport was closed for Fokker 27 or bigger aircraft but opened for DHC-6 (Twin Otter) or smaller aircraft. The NTSC investigator team embarked to Wamena on that day (Sunday, April 21 2002). On Monday, April 22 2002, at 02.00 PM (LT), the investigator team give the clearance to remove the aircraft from the runway, at 05.00 PM (LT) the airport authority personnel started the efforts to removed the aircraft by big back hoe, at 08.30 PM (LT) ES-NOP has cleared from runway. On Tuesday April 23rd 2002, the Wamena airport activities back to normal as usual.
Probable cause:
The following findings were identified:
- The crew performed visual approach to Wamena airport at airspeed exceeded the provision on AN-72 manual.
- The crew failure to estimate distance to start the final turn properly made the unable to decrease speed and therefore unable to extend flap to landing configuration.
- The high rate of descent and flap configuration upon final activated GPWS warning.
- The landing (touchdown) speed was exceeded the prescribed value in the AN-72 manual and the aircraft has slight drift angle at first touchdown.
- After the first touch the aircraft bounced three times. This and the fact that the aircraft was at high loading lead to the failure of the nose gear.
- The fire was caused by the heat from the friction as the aircraft components skidding on the runway and the presence of hydraulic fluid leaking from the damaged system.
- There is no indication of any malfunction in the aircraft system that could contribute to the accident.
- There is no indication of misconduct in the maintenance of the aircraft that could contribute to the accident.
- The fire brigade at Wamena airport was not in ready condition at the time of the accident, which leads to failure to extinguish the fire in time. The failure resulted in heavy fire damage on the aircraft.
- The fire brigade was not able the handle the fire due to non-serviceable equipment and lack of training for the personnel.
- Government check pilot need to perform close supervision (onboard the flight or give exams) to AN72 crew according to CASR 121 and CASR 61. By the time the report is written, the investigation could not find the necessary document that stated whether PT. Trigana has the authority to represent the government on the matter.
Safety Threats:
It is to be noted that there is blank radio transmission area at the gap. The Aviation Safety of Department of Communication plan to install relay antenna to resolve the problem. In the meantime, the authority required all aircraft passing the gap to perform blind transmission. It is to be noted that the lack of type certificate made the investigation progress very slow. The difficulty was due to lack of knowledge in the Indonesian authority on the technical aspect of the aircraft. Indonesian DGAC stated that the special permit for non-TC aircraft to operate in Papua will only valid until 2004.
- The crew performed visual approach to Wamena airport at airspeed exceeded the provision on AN-72 manual.
- The crew failure to estimate distance to start the final turn properly made the unable to decrease speed and therefore unable to extend flap to landing configuration.
- The high rate of descent and flap configuration upon final activated GPWS warning.
- The landing (touchdown) speed was exceeded the prescribed value in the AN-72 manual and the aircraft has slight drift angle at first touchdown.
- After the first touch the aircraft bounced three times. This and the fact that the aircraft was at high loading lead to the failure of the nose gear.
- The fire was caused by the heat from the friction as the aircraft components skidding on the runway and the presence of hydraulic fluid leaking from the damaged system.
- There is no indication of any malfunction in the aircraft system that could contribute to the accident.
- There is no indication of misconduct in the maintenance of the aircraft that could contribute to the accident.
- The fire brigade at Wamena airport was not in ready condition at the time of the accident, which leads to failure to extinguish the fire in time. The failure resulted in heavy fire damage on the aircraft.
- The fire brigade was not able the handle the fire due to non-serviceable equipment and lack of training for the personnel.
- Government check pilot need to perform close supervision (onboard the flight or give exams) to AN72 crew according to CASR 121 and CASR 61. By the time the report is written, the investigation could not find the necessary document that stated whether PT. Trigana has the authority to represent the government on the matter.
Safety Threats:
It is to be noted that there is blank radio transmission area at the gap. The Aviation Safety of Department of Communication plan to install relay antenna to resolve the problem. In the meantime, the authority required all aircraft passing the gap to perform blind transmission. It is to be noted that the lack of type certificate made the investigation progress very slow. The difficulty was due to lack of knowledge in the Indonesian authority on the technical aspect of the aircraft. Indonesian DGAC stated that the special permit for non-TC aircraft to operate in Papua will only valid until 2004.
Final Report: