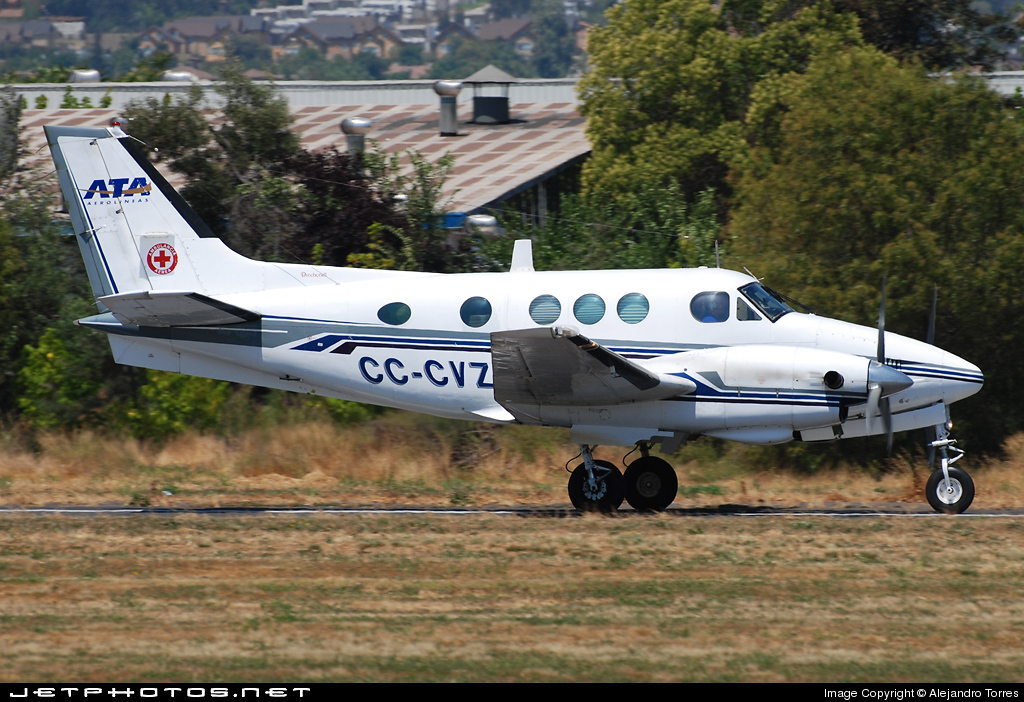
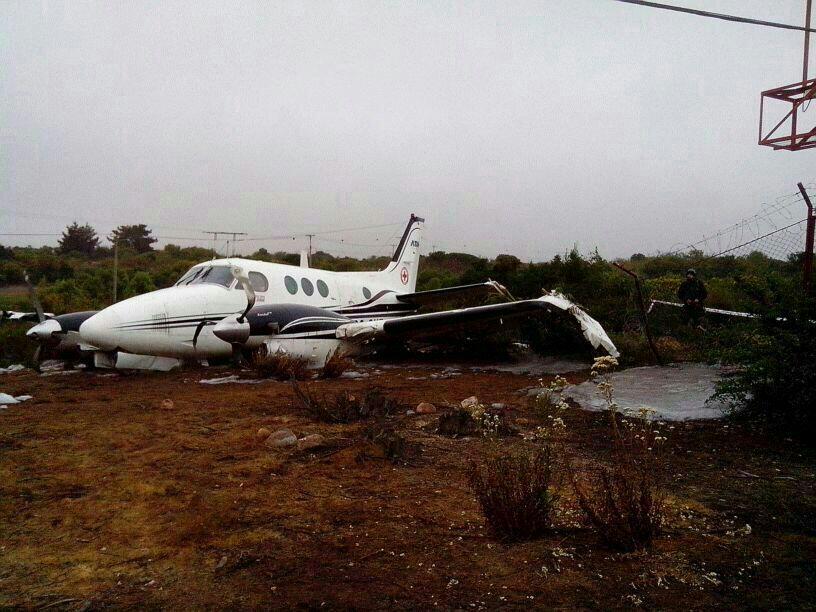
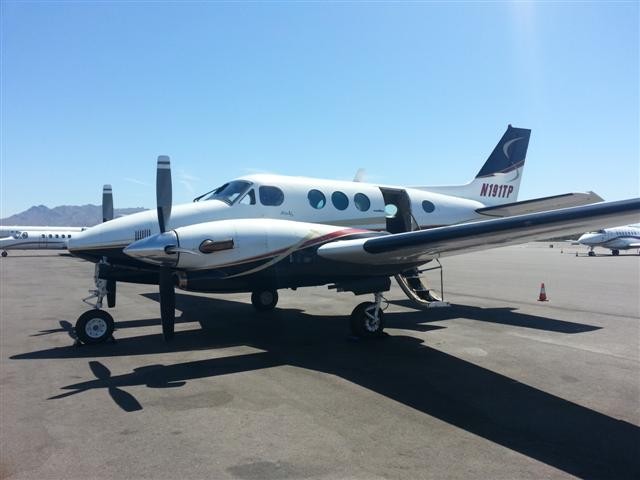
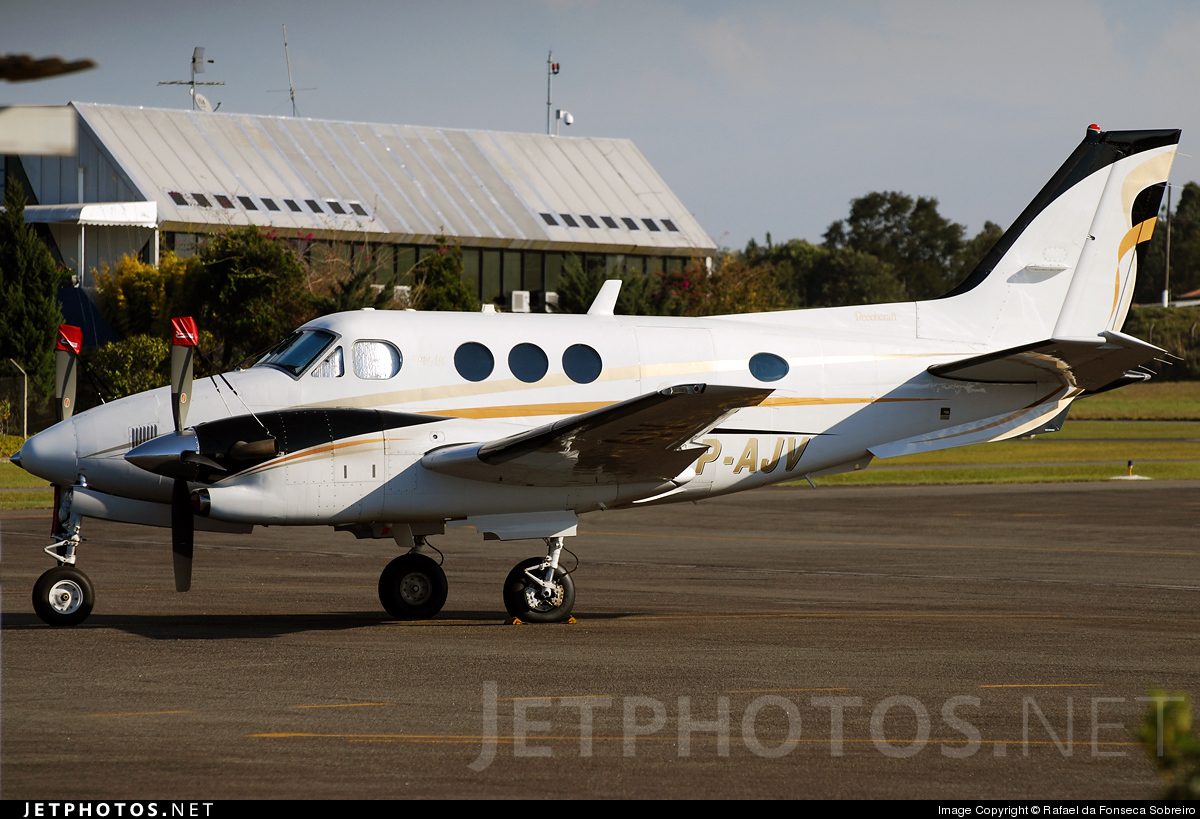
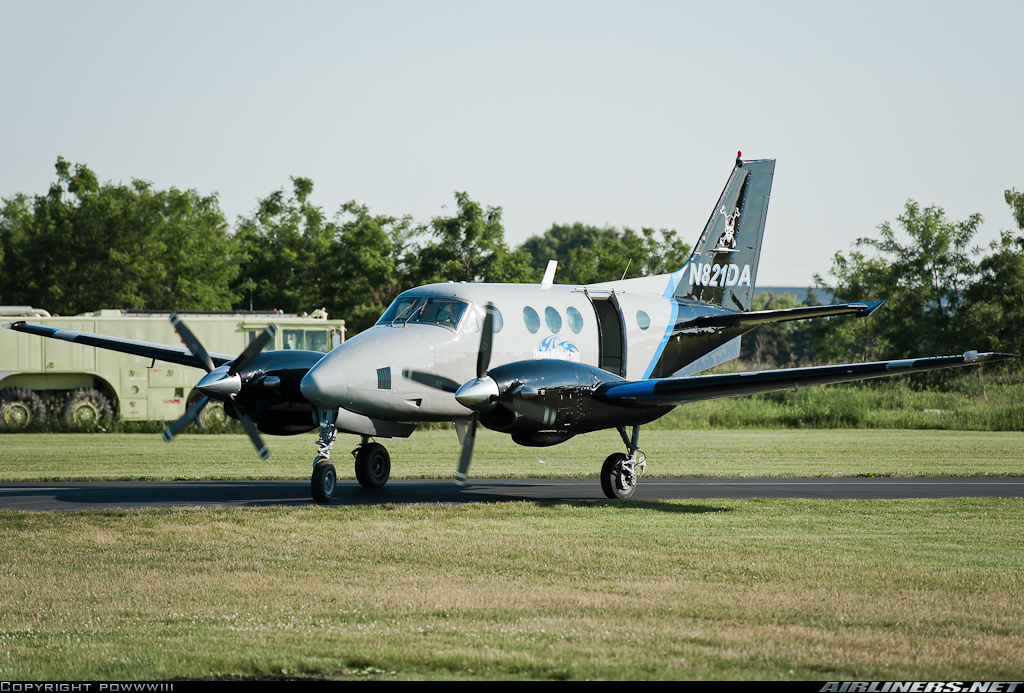
Crash of a Beechcraft B90 King Air in Viña del Mar
Date & Time:
Dec 19, 2013 at 2100 LT
Registration:
CC-CVZ
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Viña del Mar - Santiago de Chile
MSN:
LJ-441
YOM:
1969
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Captain / Total hours on type:
4000.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
17
Aircraft flight hours:
8870
Circumstances:
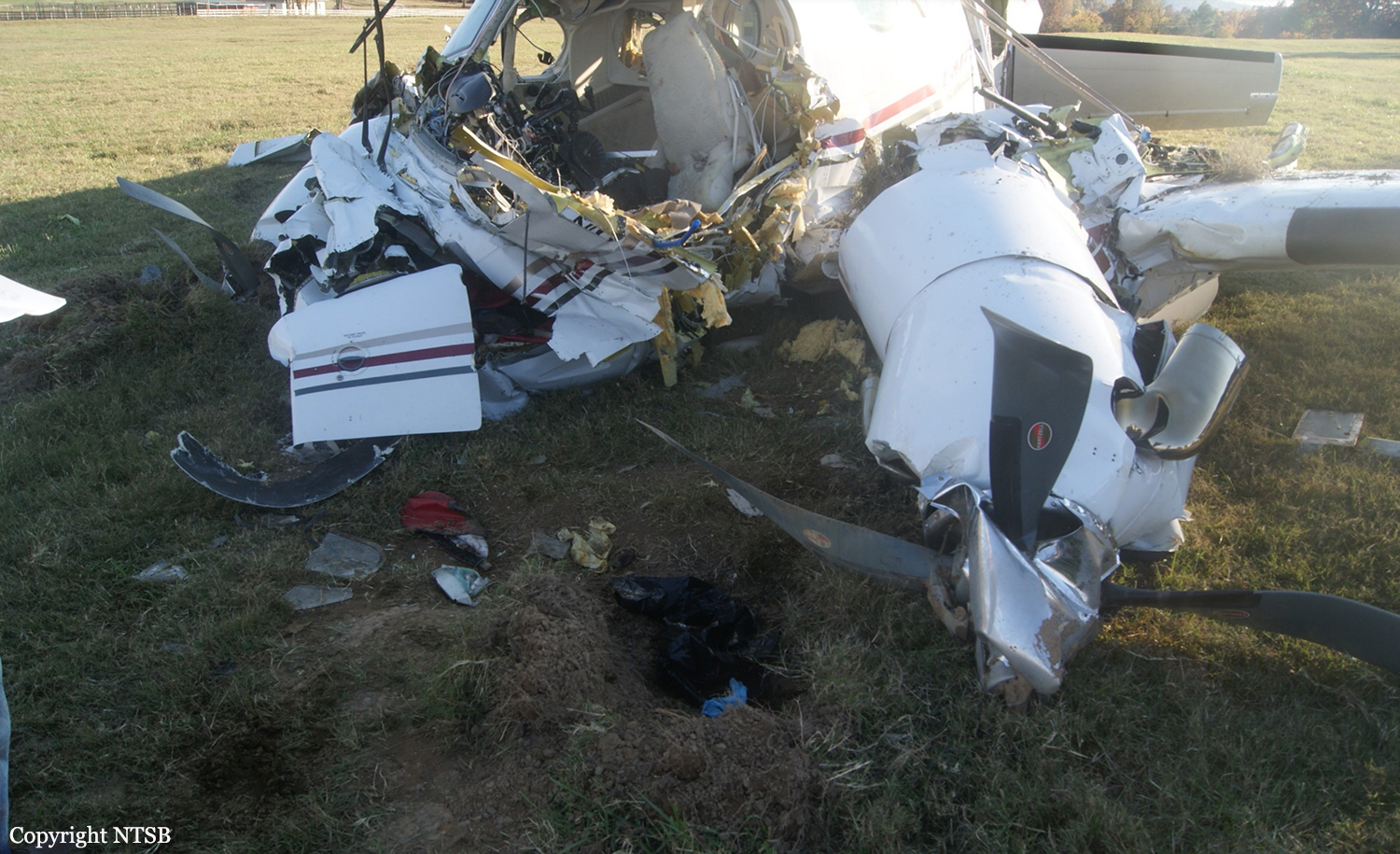
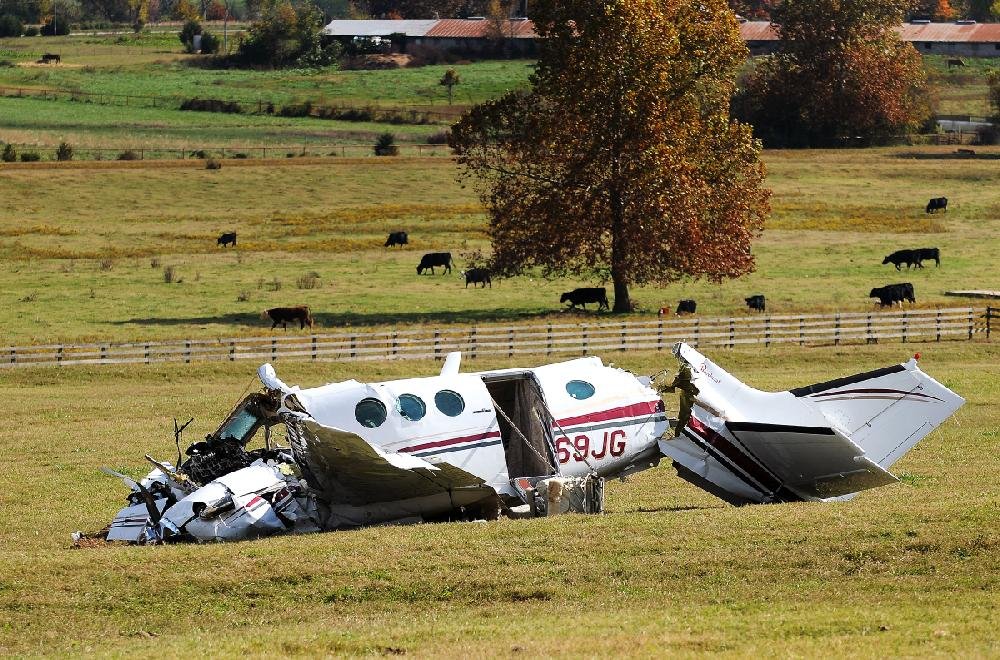
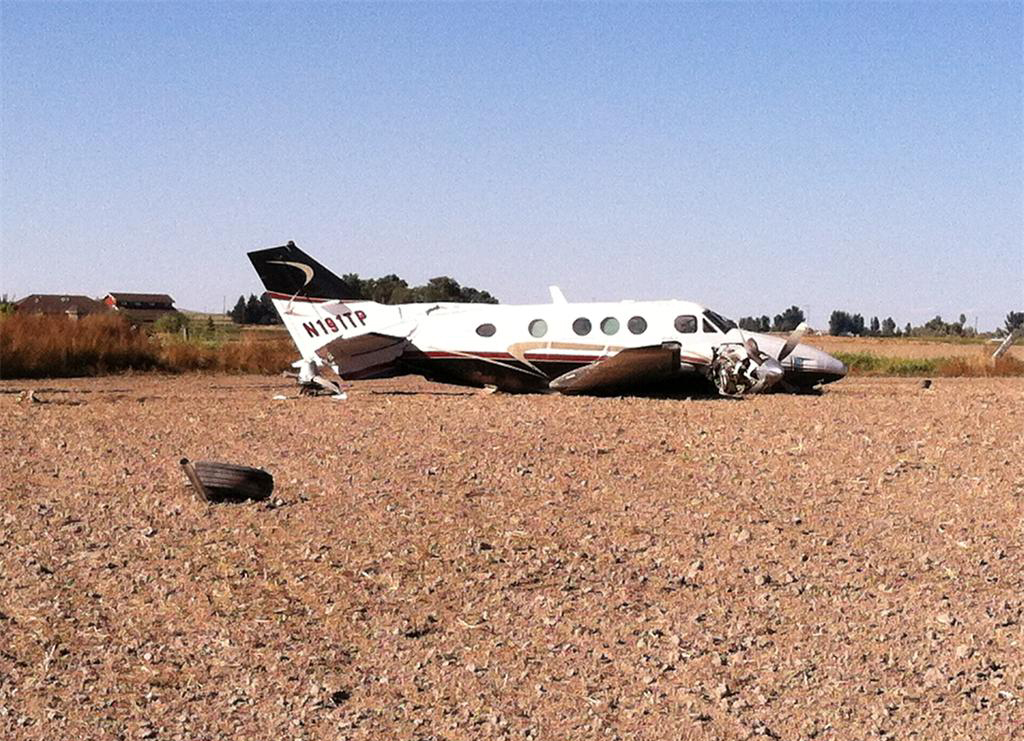
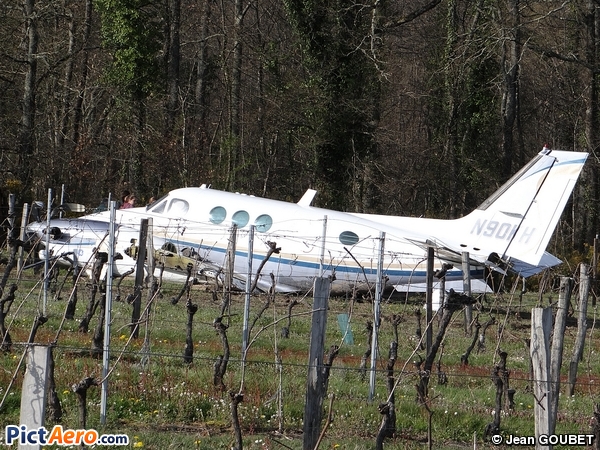
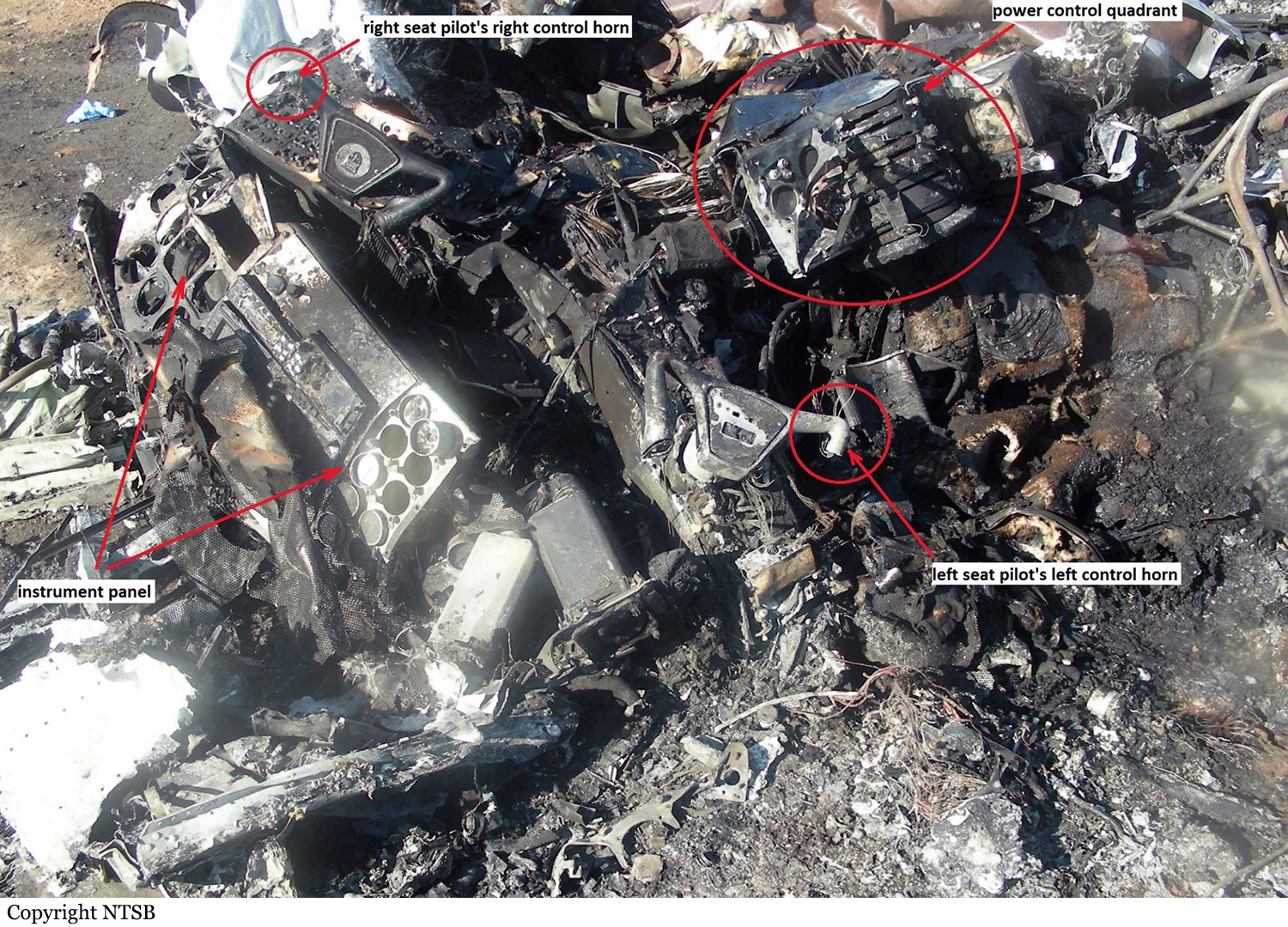
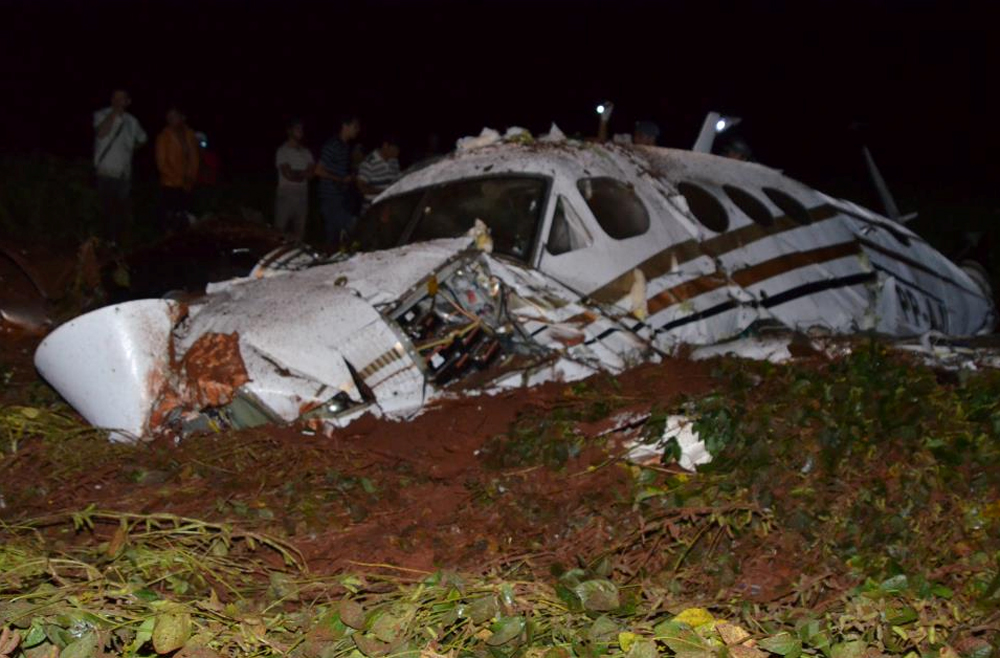
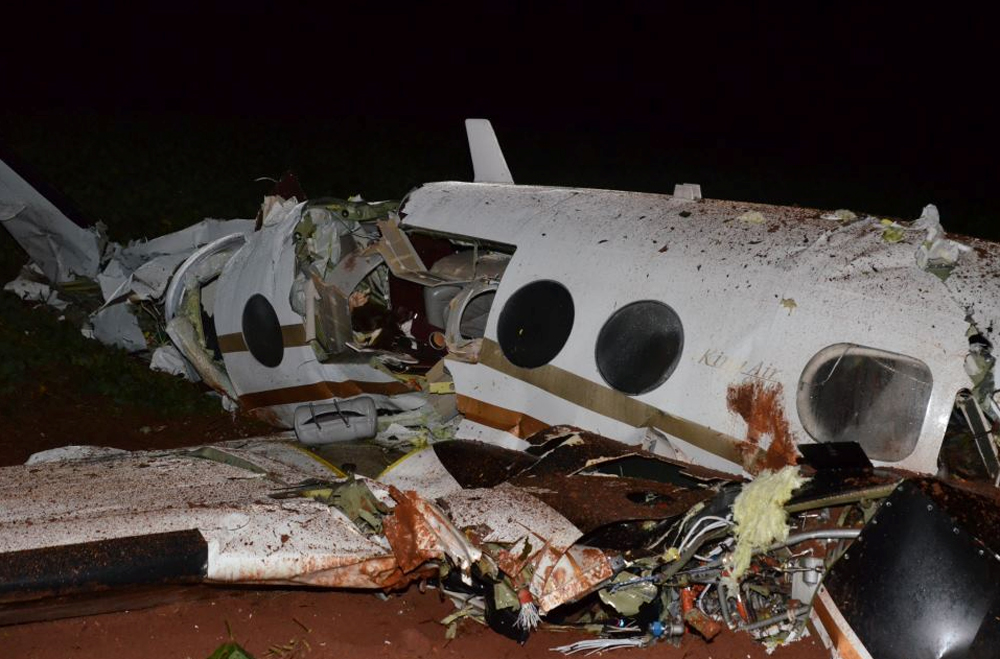
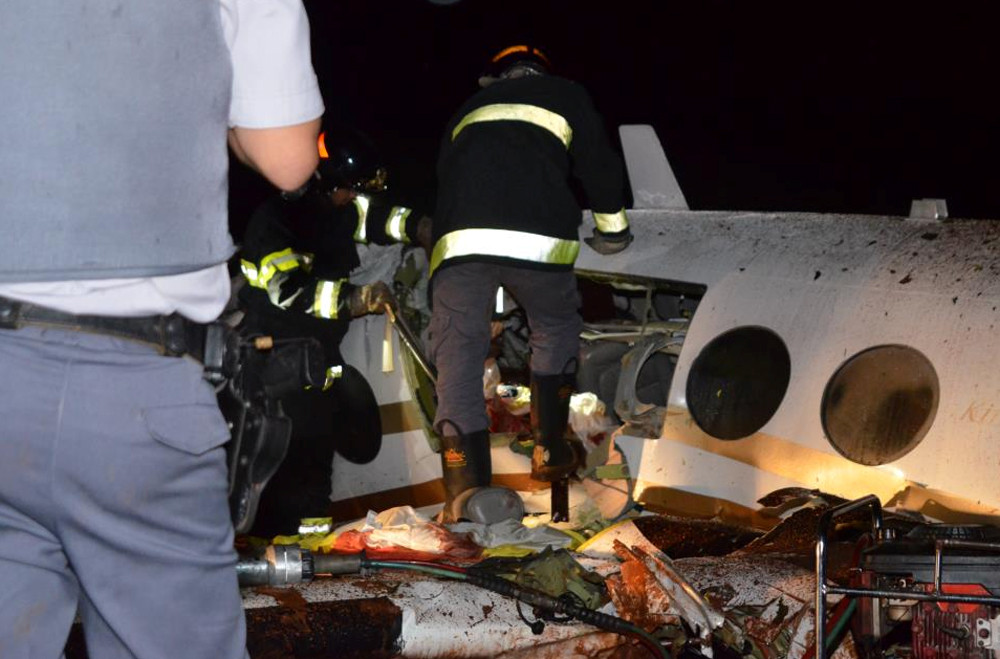
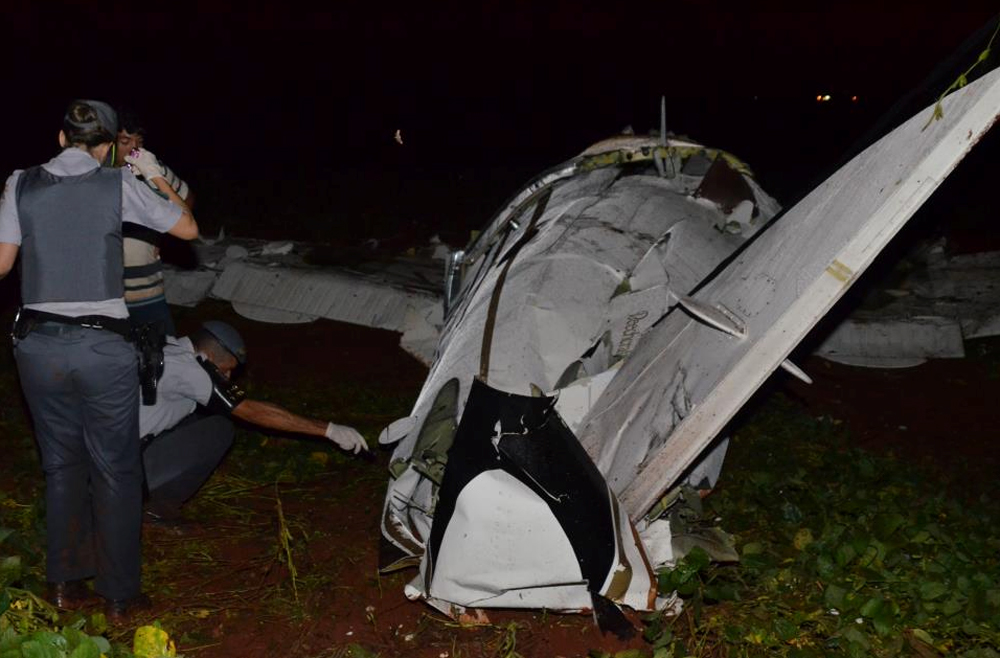
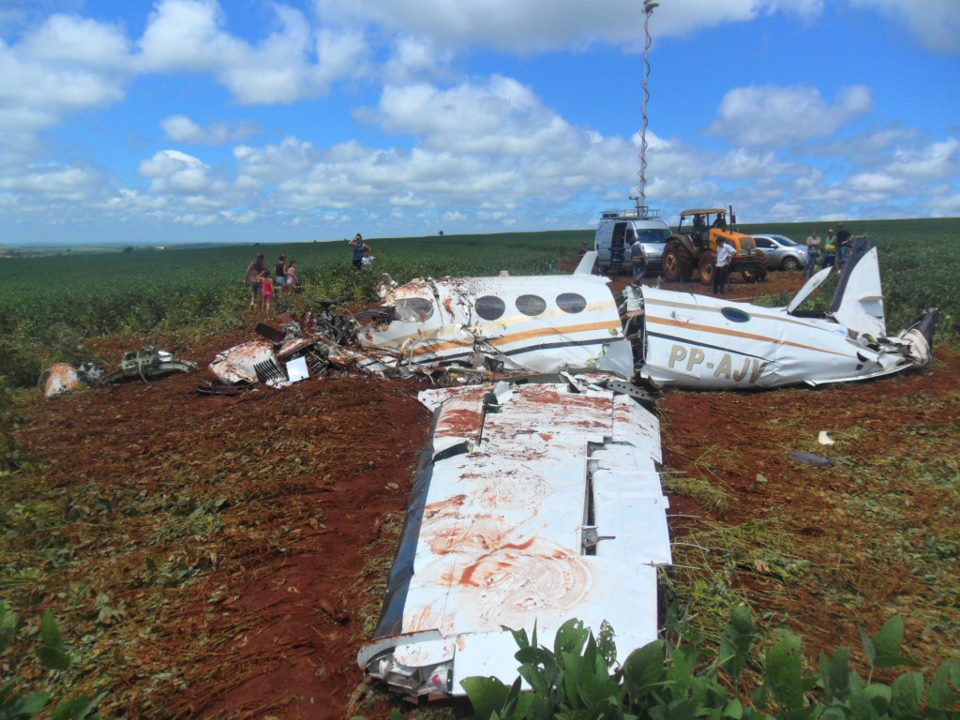
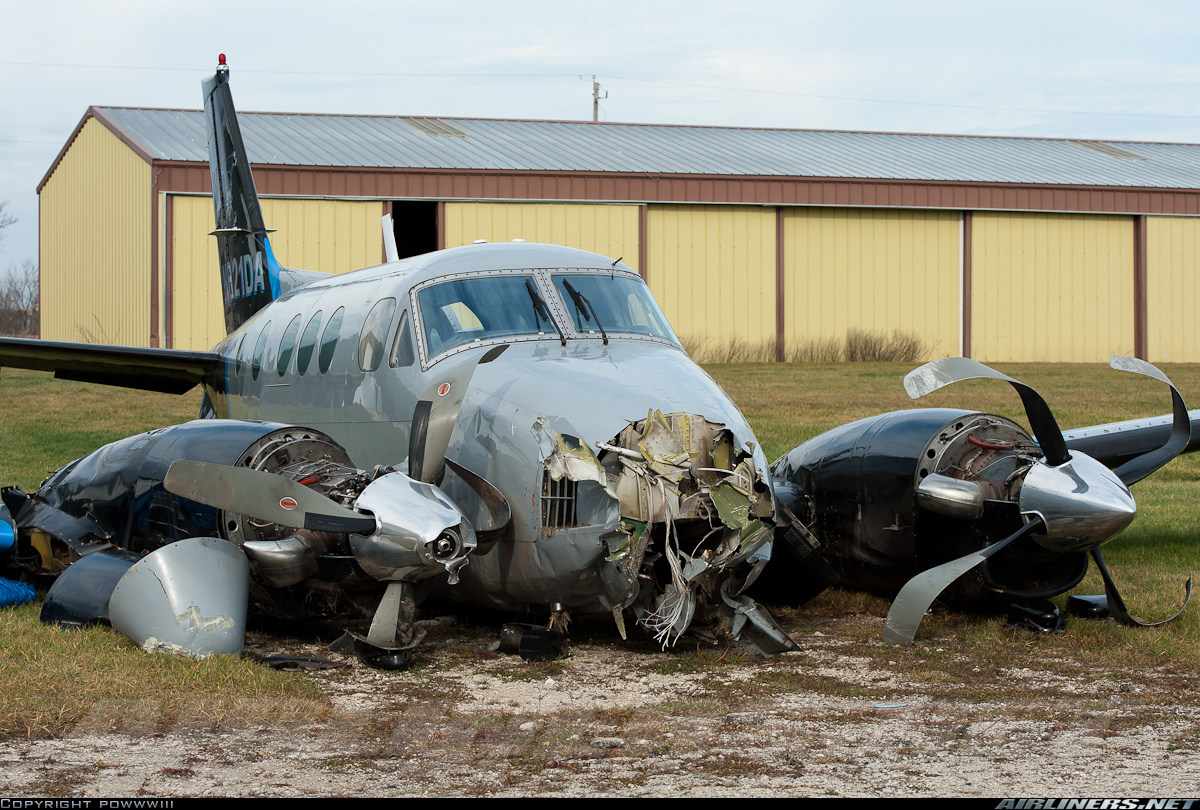
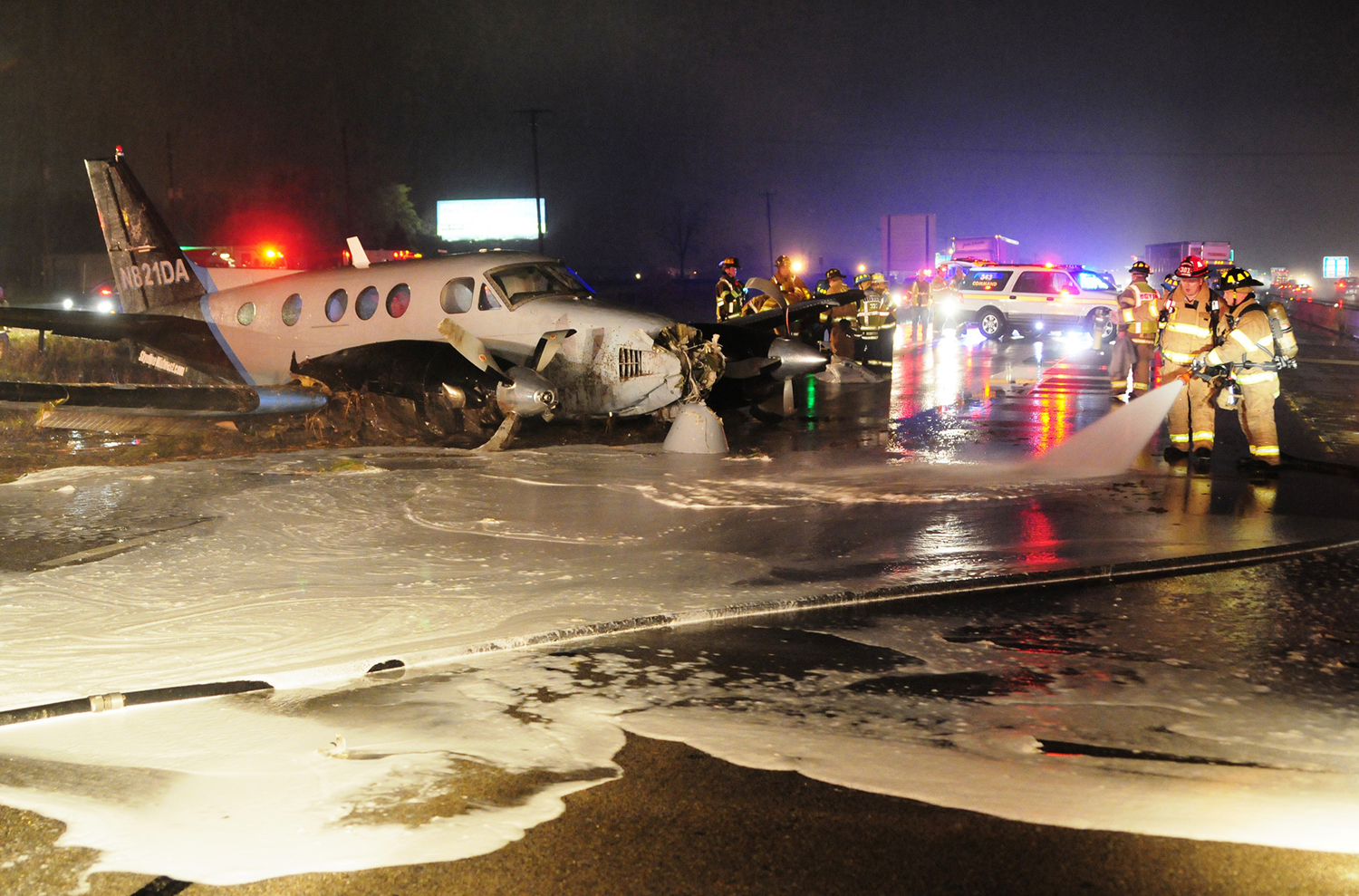
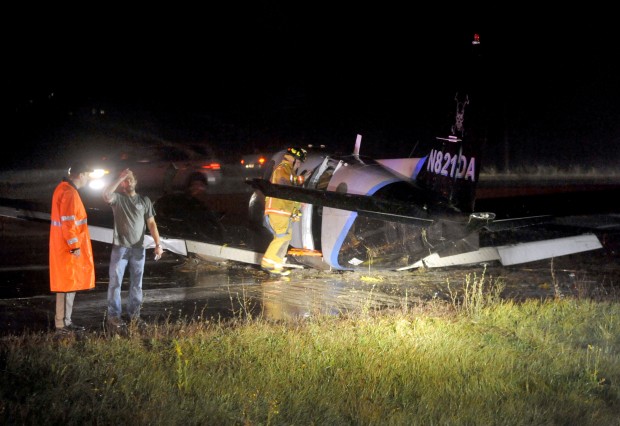
The crew departed Viña del Mar-Torquemada Airport on a positioning flight to Santiago de Chile. Shortly after takeoff, the crew encountered technical problems and elected to return. On approach, both engines failed and on short final by night, the aircraft stalled and crashed 450 metres short of runway 05. Both pilots escaped uninjured and the aircraft was damaged beyond repair.
Probable cause:
Both engines stopped during flight due to fuel exhaustion as the main fuel tanks were empty. It was not possible for the crew to transfer fuel from the auxiliary tanks (wing tips) due to the intermittent function of the fuel pump.
Final Report: